Industrialism: Changes in Way of Life Worksheet
advertisement

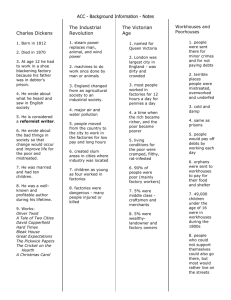
Industrialism Changes the Way of Life What did the factory system do? The factory system changed the way people lived, worked, and introduced a variety of problems for society. Quality of life improves Coal provided __________ for homes Wore better clothing Ate more ___________ Cities grew Urbanization __________________ – city building and the _______________ of people into cities. Between 1800-1850 more than _________ cities had populations of 100,000+ Glasgow and Berlin quadrupled in size. London Replaced _____________ as the largest city in Europe Population of 1 million Leader in _________________ Major Cities Birmingham and Sheffield became ________-smelting centers. Leeds and Manchester dominated textile manufacturing. Liverpool and Manchester were the center of the cotton industry. Living conditions No plans, ________________ codes, or building codes controlled the growth of English cities. They lacked adequate _______________, education, and ____________ protection. Unpaved streets had no ______________ and collected ___________ of garbage. Workers lived in dark, __________shelters, whole families crowded into _______ bedroom. Sickness Widespread _______________ epidemics regularly swept through the slums of Great Britain. In 1842, British government study showed an average life span to be ________ years for working-class people in a large city, while it was _________years for the countryside. Cholera Cholera is an infection of the small _____________ that causes a large amount of watery diarrhea. Symptoms: Abdominal cramps; Dry mucus membranes or mouth; Dry skin; Excessive thirst; Glassy or sunken eyes; Lack of tears; _______________ Mary Barton Fiction novel written by Elizabeth Gaskell in 1848. It is about a family living during Britain’s industrial time. While it’s fiction, it gives an ________________portrayal of life during that time period. Working Conditions The average worker spent ___________ hours a day at the job, _________ days a week. Factories were poorly ______ Factories were ______________ Machines injured workers in countless ways. There was no ___________________ program to provide aid in case of injury. Coal Miners The most ______________ conditions of all were found in the coal mines. Frequent ________________ Damp conditions Constant breathing of coal ____________made the average coal miner’s life span ______ years shorter than other workers. A Middle Class Emerges The Industrial Revolution brought enormous _________ to Great Britain. Most of this wealth went to ___________ owners, shippers, and merchants. These wealthy people created the ___________class. It was a social class of skilled workers, professionals, businesspeople, and wealthy farmers. Poor Workers Poor workers saw _________ improvement in their own living and working conditions. Many machines ________________ workers and put people out of a job. In response, workers smashed the machines they thought were putting them out of work. The Luddites A group of poor workers named after Ned Ludd. The Luddites __________ whole factories in northern England beginning in 1811. They destroyed ______________________ Outside the factories, mobs _____________ over poor working and living conditions. Children Children went to work as ____________ as they were able to help the support the family. They typically began factory work at the age of ________. They worked ___________________ hour days with only a lunch break. They were often ___________________ to stay awake. Effects of Industrialization 1. Size of Cities Growth of factories, bringing job seekers to cities. Urban areas doubling, tripling, or quadrupling in size Factories develop near sources of energy Many new industrial cities specializing in certain industries 2. Living Conditions No sanitary codes or building controls Lack of adequate housing, education, and police protection Lack of running water and indoor plumbing Frequent epidemics sweeping through slums Eventually better housing, healthier diets, and cheaper clothing 3. Working conditions Industrialization creating new jobs for workers Workers trying to keep pace with machines Factories dirty and unsanitary Workers running dangerous machines for long hours in unsafe conditions Harsh and severe factory discipline Eventually, higher wages, shorter hours, and better working conditions 4. Emerging Social Classes Growing middle class of factory owners, shippers, and merchants Upper class of landowners and aristocrats resentful of rich, middle class Lower middle class of factory overseers and skilled workers Workers overworked and underpaid In general, a rising standard of living, with some groups excluded