Dr hossein akbari aghdam assistant professor orthopedy medical
advertisement

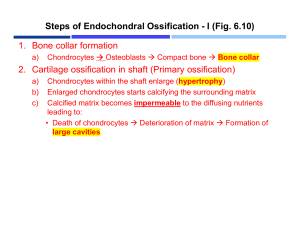
بنام خداوند بخشنده مهربان Epidemiology and biologic aspects in childeren s fractures Epidemiology of pediatric Trauma prerequisite optimal care strategies prevention strategies. trend toward surgical intervention Improvements in Technology Percutaneous methods Powered instruments Cannulated implants, Radiographic real time images, Rapid Healing minimally stabilized fracture Minimal Hospitalization The rising costs of hospitalization have created a trend to mobilize children to an outpatient setting as soon as possible. The Perfect Result Epidemilogy Of Fracture In Children Cultural differences Climatic differences Incidence of Fractures 0 t 16 years of age:boys 42%;girls27% Annual 2.6%boys;1.7%girls 1 to 2 ages high incidence of injuries(not fracture but injuries such laceration) Fractures show a linear increase with age gender Males predominate in late age groups Frist 2 years no significant gender diffrences Right versus Left Predominance of left upper extermity Season Houres of sunshine Younger age groups unaffected Time of day(2-3 pm) Age variation in fracture location Supracondylar fx first decade,peak at age 7 Femur fx 0 to 3 Fx of physis before skeletal maturity Single bone Radius)Most common) Humerus Tibia Specific area Distal radius Hand Elbow area Physal fx 21.7% Open fx 2.9% Etiology of fx Accidental trauma Nonacidental trauma (child abuse) Pathological conditions Accidental trauma fall from height Home environment Social factors School environments Fracture rate is low Peak time in the morning Play and Reccreational Activities Monkey bar Supracondylar FX risk Hardness of the playground surface Impact-absorbing surface such bark risk head injury But long bone FX risk Bicycle injury Skates Skate parks icrease the injury rate Suggest Supervision &training Motor Vehicle Accidents Children twice adult femoral fx struck automobile Recreational all-terrain vehicles (ATVs) Gunshot and Firearm injuries Complication 1.Growth arrest 2.infection Preventive Programs Study of incidence of FX Identify problem area Designe decrese the risk factors National compaigns Local community participation The biologic aspects of childern s FX Epiphysis At brith, each epiphysis (except the distal femur)completely cartilaginous Secondery center of ossification Only articular cartilage remain at maturity physis Metaphyseal ischemia Epiphyseal ischemia Metaphysis Torus fx occur in metaphysis Trabecular,fenestrated,compressible cortex Transverse lines of Park and Harris After trauma,general illness or local such osteomyelitis Temporary slowdown of normal longitudinal Growth Symmetrical in rapidly growing bone diaphysis periosteum-mediated membraneous appositional bone formation Endosteal remodeling No direct muscle attachment diaphysis and metaphisis except medial distal femoral attachment of adductor muscles periosteum Thicker Loosely attached to shaft but attach densely into the physeal periphery(zone of ranvier) Apophysis Tibial tuberosity Fibrocartilage instead of columnar cartilage Tensile responsive Ossification of secondary ossification center Tend to fail to tension Mechanisms of bone growth Endochondral ossification Physis Temporary cartilaginous tissue between primery and secondery ossification centers of long bone 7-9 w gestational age to skeletal maturity 15-17y Membranous ossification All axial and appendicular skeletal elements Via periosteum