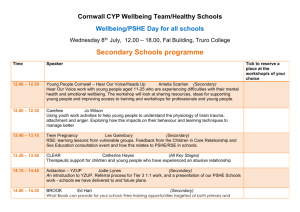
PSHE presentation - Portsmouth Teaching School Alliance
advertisement

PSHE Health and Education in School Karen Monteith Health Development Officer and PSHE Project Developer Health Improvement & Development Service House Keeping Be responsible for your own learning Respond to the comment not the person Health Improvement & Development Service Learning Outcomes To have the confidence, strategies and resources to deliver PSHE To have an awareness of what support is available in Portsmouth To have a better understanding of the health profiles of Portsmouth To be able to apply the key principles of effective PSHE teaching and learning in our own practice Health Improvement & Development Service Welcome Introductions Health Improvement & Development Service Why is health important to education? What do we mean by health? What role does education play? What are your responsibilities? PSHE is a bridge between education and public health. Chief Medical Officer, 2013 Health Improvement & Development Service What is health? WHO definition of Health: Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity. Health Improvement & Development Service Determinants of Health Health Improvement & Development Service Health Improvement & Development Service How pupils benefit from PSHE support the development of physically, emotionally and socially healthy young people support the development of essential employability skills for the 21st Century, reduce or remove barriers to learning, such as bullying, low self-esteem, unhealthy/risky behaviours. Health Improvement & Development Service How schools benefit from PSHE maximising academic achievement ‘Healthy School’ validation ; local health outcomes fulfilling statutory duty to promote wellbeing; promote the spiritual, moral, cultural, mental and physical development of pupils; prepare pupils for the opportunities, responsibilities and experiences of later life. fulfilling the expectations of the National Curriculum providing evidence for Ofsted judgements Health Improvement & Development Service “It is difficult to see how safety and safeguarding can be good if PSHE education provision is poor. If pupils are kept ignorant of their human, physical and sexual rights; or how to protect themselves and others, or know where to go to for help, they are not being adequately safeguarded.” [Janet Palmer HMI, 2014] Health Improvement & Development Service Our role Young people’s needs change and we need to respond effectively Focus on reducing risks and increasing resilience Skills and attributes rather than just knowledge Identify risk factors and protective factors Health Improvement & Development Service • • • • • • • People? Teaching? Profile? Commitment? Leadership & management? Experience? Pupils? Time? Resources? • Internal or external opportunities available for developing PSHE at your school? Health Improvement & Development Service • • • • • • • People? Teaching? Profile? Commitment? Leadership & management? Experience? Pupils? Time? Resources? • Internal or external conditions/ competing priorities/ changes etc that might adversely affect PSHE development at your school? Risk factors Abuse Neglect Truanting Early sexual behaviour Antisocial behaviour Exposed to parental substance misuse Health Improvement & Development Service Protective factors Positive parenting Sense of belonging in school and community Positive peer relationships and adult relationships Positive activities and hobbies Support There should be a universal requirement for schools to teach age appropriate PSHE ... The evidence, along with the views of pupils, teachers and parents, supports this position Public Health England, July 2014 Health Improvement & Development Service Crunch moment Knowledge skills and attributes Health Improvement & Development Service Least effective teaching methods scare tactics and images knowledge-only approaches ex-users and the police as drug educators where their input is not part of a wider prevention programme peer mentoring schemes that are not evidence-based Health Improvement & Development Service Most effective teaching methods Relevant to pupils Clear learning objectives and outcomes Treated no differently to other subjects Clear boundaries and ground rules Questioning techniques to probe and deepen understanding Consistent teaching Delivered confidently Open questions Time to reflect Health Improvement & Development Service OFSTED All schools have a statutory duty to provide a broad, balanced curriculum which promotes: wellbeing; the spiritual, moral, cultural, mental and physical development of pupils; and prepare pupils for the opportunities, responsibilities and experiences of later life. Health Improvement & Development Service OFSTED’s key changes Emphasis on impact across all key judgements Impact of the culture of the school Importance of safeguarding as a golden thread throughout all judgements, including the testing of leaders’ work to meet the new Prevent Duty The importance of a broad and balanced curriculum A brand new judgement – personal development, behaviour and welfare Alignment of the judgements on early years and 16-19 study programmes Health Improvement & Development Service Inspectors will evaluate to which the school successfully promotes ad supports pupils’: Inspectors will evaluate the extent to which the school successfully promotes and supports pupils’: •..employability skills so that they are well prepared for the next stage of their education, employment, self-employment or training •understanding of how to keep themselves safe from relevant risks such as abuse, sexual exploitation and extremism, including when using the internet and social media •knowledge of how to keep themselves healthy, both emotionally and physically, including through exercising and healthy eating •personal development, so that they are well prepared to respect others and contribute to wider society and life in Britain. Health Improvement & Development Service Safeguarding We know we have a safeguarding culture when Children and learners feel safe Children and learners are aware of a range of safeguarding matters, including domestic abuse or sexual exploitation Children and learners are kept safe from the dangers of radicalisation and extremism (implementation of PREVENT duty) e-safety, relationships (including sexual relationships) knives, water, fire, electricity, roads, railways Health Improvement & Development Service We know we have a safeguarding culture when: Effective action taken to prevent and tackle discriminatory and derogatory language - disabilist, homophobic, racist •Children and learners able to understand, respond to and calculate risk effectively… (child sexual exploitation, domestic violence, FGM, forced marriage, substance misuse, gang activity, radicalisation and extremism*) and are aware of support available to them Health Improvement & Development Service What this looks like in Primary Germs, personal hygiene and hand washing Harmful household products and medicines Road, water, fire and electrical safety Basic emergency aid/accessing help Legal and illegal drugs, their effects and risks Judging what kind of physical contact is acceptable or unacceptable Internet and social media safety How to resist peer-pressure and how to ask for help Managing the ‘pressure’ or expectations I place on myself Giving and receiving consent Health Improvement & Development Service Activity Use local and national stats around the room for a quiz Health Improvement & Development Service Milestones in a young persons life Go out for the first time Cross my first busy road without someone to watch over me Travel to school on my own for the first time Have my first sleepover Be offered my first taste of alcohol Have my first kiss Make a choice for my career path Sign my first legally binding contract Attend my first interview Health Improvement & Development Service Preparation for a safe environment Openness but without personal stories Keeping the conversation in the room (but be clear on limits of confidentiality) A non-judgmental approach The right to pass (& not putting people ‘on the spot’) Making no assumptions Listening to others (& commenting on what’s said, not the person who said it) Use of appropriate language Health Improvement & Development Service Distance the learning Stories/scenarios Film/DVD/TV clip Photo Puppets “Imagine a boy or girl of about your age who lives and goes to school round here…” Health Improvement & Development Service Active options Instead of: • Being given information. • Writing down what they know • Being told a number of facts, or reasons for something. • Watching an entire video then discussing ‘the message’. • Whole class discussion. • Being given answers. • Reading about how to do something. Health Improvement & Development Service Try: • Researching information. • Preparing a presentation. • Doing a card sort activity. • Discussing timeline questions at key moments. • ‘Think, pair, share’ discussion. • Problem solving in groups. • Rehearsing skills through role play. Assessment and Evaluation Assessment Evaluation • Looks in at the learning • Is the use of activities to gauge what has been learnt and what needs to be learnt. • Looks out at the experience • Considers how effective activities, approaches and materials have been in achieving the learning objectives. Health Improvement & Development Service Why Assess 1. To monitor our provision. 2. To give us and pupils (and parents) feedback about their progress and how their learning might be improved. 3. To provide tracking data for the school. 4. To improve learning and increase pupils’ motivation. 5. To classify pupils or give them a ‘level’. 6. To help pupils to reflect on and identify what they have learnt. 7. To allow others to see the impact PSHE education is having for learners and for whole-school outcomes. Health Improvement & Development Service Tools for Assessment Questioning Draw & Write Brain storm / graffiti wall / mind map ‘The story so far’ Role play and scenarios Mock TV or radio interviews Blogs and podcasts Presentations Discussions Quizzes Written work including leaflets, projects, displays etc. Health Improvement & Development Service Public Health What is it? Who works there? What do they do? Why do they do it? Health Improvement & Development Service Signposting and further reading The link between pupil health and wellbeing and attainment. Public Health England Nov 2014 PSHE education: a review of impact and effective practice. Department for Education March 2015 Promoting children and young people’s emotional health and wellbeing. Public Health England March 2015 The relationship between outstanding schools and outstanding PSHE education. PSHE Association Nov 2014 PSHE Association website Not yet good enough. PSHE in schools OFSTED May 2013 www.areyousorted.co.uk Health Improvement & Development Service