Lower-Dev. Reading
advertisement

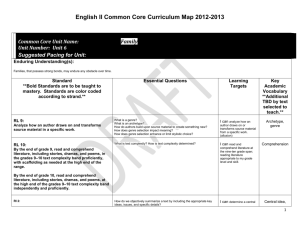
READ 0860 List “A” Appeal Part I: Reading Curriculum: The most important point to stress is that teaching reading is a spiral—the same concepts are taught with increasing complexity using more and more sophisticated texts. For example: From the Minnesota Academic Standards-- English Language Arts K-12—note the following 6th grade benchmark: 6.4.1.1 “Cite textual evidence to support analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as inferences drawn from the text.” Notice how little of the language changes for the 9th grade benchmark: 9.4.1.1 “Cite strong and thorough textual evidence to support analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as inferences drawn from the text.” Part II: Proof of Text Level: For the “Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity” on p. 51 of the Benchmarks, it reads that for 6th, 7th, and 8th grade students that they should “read and comprehend literature and other texts…in the grade 6-8 text complexity band proficiently.” The same exact language is used for the 9-12th grade benchmark on p. 53---but the text complexity band increases with the corresponding grade-level. Normandale’s READ 0860 was placed on “List A” due to the appearance of below high school-level concepts being taught in this course. This is not the case; however, since the course materials used are at or above a 9th grade text complexity band. The textbook used for our course is at a reading level of 913 (See Document A). The pre and post tests used for this course, published by Townsend, use reading selections varying from 9.9 to 12.1 (See Document B). And lastly, The Curious Incident of the Dog in the Nighttime, the book used in our course, measures at a Lexile level of 1180—which has the grade equivalency of 10th grade. Part III: Normandale’s READ 0860 Common Course Outline vs. Minnesota Academic Standards— English Language Arts K-12—Reading Standards: Normandale’s Common Course Outline was in the process of being revised as a part of our department’s program review this spring. However, after completing the full revision, it was put on hold to await the findings of the MnSCU Shared Outcomes Committee in order to ensure that any new Common Course Outline would be in compliance with the MnSCU committee’s findings. Therefore, when this course was reviewed to determine if the level of READ 0860 was in compliance with the Financial Aid statute, its new content was not available. As a result of this assessment of our program, we will be posting the revised Common Course Outline to our website immediately, even though the MnSCU Shared Outcomes Committee has not yet finalized a list of common outcomes to use across the MnSCU system (See Document C). The following Learning Outcomes on Normandale’s updated READ 0860 Common Course Outline correspond with the following Reading Benchmarks for Grade 9-10 students (page 52 and pages 56-57 of the Minnesota Academic Standards—English Language Arts K-12): http://education.state.mn.us/MDE/EdExc/StanCurri/K-12AcademicStandards/ Benchmark Number 9.4.1.1 Reading Benchmarks: Literature— Grade 9-10 students Key Ideas and Details READ 0860 CCO Content Area “Cite strong and thorough textual evidence to support analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as inferences drawn from the text” 2. Reading Comprehension Strategies b. Metacognitive Strategies iv. inference c. Text Structure Analysis i. Identifying Central Ideas—stated and implied READ 0860 CCO Learning Outcomes 1. Read and comprehend collegelevel materials independently for a variety of purposes. 2. Interpret text using a critical thinking, problem-solving approach. 9.4.2.2 “Determine a theme or central idea of a text and analyze in detail its development over the course of the text, including how it emerges and is shaped and refined by specific details; provide an objective summary of the text.” 2. Reading Comprehension Strategies b. Metacognitive Strategies vi. Determining Importance d. Text Structure Analysis i. Identifying Central Ideas—stated and implied ii. Identifying supporting details 3. Post-reading Strategies b. Summarizing and Paraphrasing 1. Read and comprehend collegelevel materials independently for a variety of purposes. 2. Interpret text using a critical thinking, problem-solving approach. 5. Summarize passages from a variety of texts. 7. Utilize reading strategies to comprehend a variety of texts. 9.4.4.4 “Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in the text, including figurative language and connotative meanings; analyze the cumulative impact of specific word choices on meaning and tone.” 2. Reading Comprehension Strategies b. Metacognitive Strategies iv. Inference 1. Figurative language 2. Connotation d. Vocabulary Acquisition 4. Critical Thinking c. Identifying Tone 9.5.1.1— Reading Benchmarks: Informational Text—Grade 9-10 students “Cite strong and thorough textual evidence to support analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as inferences drawn from the text.” 2. Reading Comprehension Strategies b. Metacognitive Strategies iv. Inference c. Text Structure Analysis i. Identifying Central Ideas—stated and implied 9.5.2.2 “Determine a central idea of a text and analyze its development over the course of the text, including how it emerges and is shaped and refined by specific details; provide an objective summary of the text." 2. Reading Comprehension Strategies c. Metacognitive Strategies vi. Determining Importance d. Text Structure Analysis i. Identifying Central Ideas—stated and implied ii. Identifying supporting details 3. Post-reading Strategies b. Summarizing and Paraphrasing 1. Read and comprehend collegelevel materials independently for a variety of purposes. 2. Interpret text using a critical thinking, problem-solving approach. 7. Utilize reading strategies to comprehend a variety of texts. 8. Demonstrate new strategies for vocabulary development 1. Read and comprehend collegelevel materials independently for a variety of purposes. 2. Interpret text using a critical thinking, problem-solving approach. 1. Read and comprehend collegelevel materials independently for a variety of purposes. 2. Interpret text using a critical thinking, problem-solving approach. 5. Summarize passages from a variety of texts. 7. Utilize reading strategies to comprehend a variety of texts. 9.5.3.3 “Analyze how the author unfolds an analysis or series of ideas or events, including the order in which the points are made, how they are introduced and developed, and the connections that are drawn between them.” 2. Reading Comprehension Strategies a. Annotation b. Metacognitive Strategies iv. Inference 2. Connotation v. Determining Importance c. Text Structure Analysis 4. Critical Thinking a. Fact vs. Opinion b. Identifying Bias c. Identifying Tone d. Evaluating the author e. Defining an argument 1. Read and comprehend collegelevel materials independently for a variety of purposes. 2. Interpret text using a critical thinking, problem-solving approach. 7. Utilize reading strategies to comprehend a variety of texts. 9.5.4.4 “Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a text, including figurative, connotative, and technical meanings, analyze the cumulative impact of specific words choices on meaning and tone.” 2. Reading Comprehension Strategies b. Metacognitive Strategies iv. Inference 1. Figurative language 2. Connotation d. Vocabulary Acquisition 4. Critical Thinking c. Identifying Tone 9.5.5.5 “Analyze in detail how an author’s ideas or claims are developed and refined by particular sentences, paragraphs, or larger portions of a text.” 2. Reading Comprehension Strategies b. Metacognitive Strategies v. Determining Importance c. Text Structure Analysis i. Identifying central ideas—stated and implied ii. Identifying supporting details iii. Identifying the author’s purpose iv. Patterns of organization v. Transitions 4. Critical Thinking a. Fact vs. Opinion b. Identifying Bias 1. Read and comprehend collegelevel materials independently for a variety of purposes. 2. Interpret text using a critical thinking, problem-solving approach. 7. Utilize reading strategies to comprehend a variety of texts. 8. Demonstrate new strategies for vocabulary development 1. Read and comprehend collegelevel materials independently for a variety of purposes. 2. Interpret text using a critical thinking, problem-solving approach. 7. Utilize reading strategies to comprehend a variety of texts. 9.5.6.6 “Determine an author’s point of view or purpose in a text and analyze how an author uses rhetoric to advance that point of view or purpose." 9.5.10.10 “By the end of grade 9, read and comprehend literary nonfiction in the grades 910 text complexity band proficiently, with scaffolding as needed at the high end of the range.” “By the end of grade 10, read and comprehend literary nonfiction at the high end of the grades 9-10 text complexity band independently and proficiently.” c. Identifying Tone d. Evaluating the author e. Defining an argument 2. Reading Comprehension Strategies b. Metacognitive Strategies v. Determining Importance c. Text Structure Analysis i. Identifying central ideas—stated and implied 4. Critical Thinking a. Fact vs. Opinion b. Identifying Bias c. Identifying Tone d. Evaluating the author e. Defining an argument 1. Pre-reading a. Metacognition b. Establishing a Purpose c. Previewing and Prediction 2. Reading Comprehension Strategies a. Annotation b. Metacognitive Strategies i. Connections ii. Questions iii. Visualizing iv. Inference 1. Figurative Language a. Similes b. Metaphors c. Personification d. Hyperbole e. Idioms 2. Connotation v. Determining Importance vi. Monitoring Comprehension 1. Recognizing comprehension problems 2. Employing appropriate fix-up strategies to repair comprehension c. Text Structural Analysis i. Identifying central ideas—stated and implied ii. Identifying supporting details 1. Read and comprehend collegelevel materials independently for a variety of purposes. 2. Interpret text using a critical thinking, problem-solving approach. 7. Utilize reading strategies to comprehend a variety of texts. 1. Read and comprehend college-level materials independently for a variety of purposes. 2. Interpret text using a critical thinking, problemsolving approach. 3. Read as a means for lifelong learning. 4. Read as a way to understand themselves and others. 5. Summarize passages from a variety of texts. 6. Connect readings to personal experience and prior knowledge. 7. Utilize reading strategies to comprehend a variety of texts. 8. Demonstrate new strategies for vocabulary iii. Identifying the author’s purpose iv. Patterns of Organization v. Transitions d. Vocabulary Acquisition i. Context Clues and Structural Analysis ii. Word Parts iii. Develop strategies to learn new words 3. Post-Reading Strategies a. Reflection and Reaction b. Summarizing and Paraphrasing c. Note-taking Strategies i. Outlining ii. Mapping 4. Critical Thinking a. Fact vs. Opinion b. Identifying Bias c. Identifying Tone d. Evaluating the author e. Defining the argument development. Document A Author: John Langan ISBN/SKU: 1-59194-200-4 Year: 2010 Page Count: 708 Reading Level: 9-13 Related to: TP READING SERIES Weight: 2.200 Ten Steps to Advancing College Reading Skills, Fifth Edition, is one of the most popular books in the Ten Steps college reading skills series. It can be used as either a core or an advanced developmental reading text. http://www.townsendpress.com/store/product/ten-steps-to-advancing-college-reading-skills-5e/ Document B Read 0860 Test Form B Readability Reading 1 Readability Formula Grade Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level 10.4 Gunning-Fog Score 13 Coleman-Liau Index 12.7 SMOG Index 9.5 Automated Readability Index 10.5 Average Grade Level 11.2 Reading 2 Readability Formula Grade Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level 11 Gunning-Fog Score 14.6 Coleman-Liau Index 12.1 SMOG Index 10.5 Automated Readability Index 11 Average Grade Level 11.8 Reading 3 Readability Formula Grade Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level 9 Gunning-Fog Score 11.7 Coleman-Liau Index 11.3 SMOG Index 8.4 Automated Readability Index 9 Average Grade Level 9.9 Reading 4 Readability Formula Grade Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level 11.9 Gunning-Fog Score 13.4 Coleman-Liau Index 13.3 SMOG Index 10.9 Automated Readability Index 11.1 Average Grade Level 12.1 Read 0860 Form A Readability Reading 1 Readability Formula Grade Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level 9.7 Gunning-Fog Score 12.7 Coleman-Liau Index 11.7 SMOG Index 9.7 Automated Readability Index 9.6 Average Grade Level 10.7 Reading 2 Readability Formula Grade Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level 10 Gunning-Fog Score 12.5 Coleman-Liau Index 13.4 SMOG Index 9 Automated Readability Index 10.7 Average Grade Level 11.1 Reading 3 Readability Formula Grade Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level 9.7 Gunning-Fog Score 12.6 Coleman-Liau Index 10.5 SMOG Index 8.8 Automated Readability Index 9.8 Average Grade Level 10.3 Reading 4 Readability Formula Grade Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level 10.8 Gunning-Fog Score 14.1 Coleman-Liau Index 12.6 SMOG Index 10.3 Automated Readability Index 10.9 Average Grade Level 11.7 Document C NORMANDALE COMMUNITY COLLEGE COMMON COURSE OUTLINE READ 0860, READING SKILLS A. COURSE DESCRIPTION 1. 4 credits 2. 4 hours per week lecture, no lab hours 3. Prerequisites—EAP 0855 (C/P) or higher or eligible for READ 0860 4. Co-requisites—None 5. MnTC Goals—None This course offers preparation for reading college-level material. Topics include pre-reading, reading, and post-reading strategies as well as critical thinking to improve comprehension, increase vocabulary, and develop thoughtful responses to reading. The close relationship of reading, writing, and thinking will be emphasized. B. DATE LAST REVISED May 2014 C. OUTLINE OF MAJOR CONTENT AREAS 1. Pre-reading a) Metacognition b) Establishing a Purpose c) Previewing and Prediction 2. Reading Comprehension Strategies a) Annotation b) Metacognitive Strategies i. Connections ii. Questions iii. Visualizing iv. Inference 1. Figurative Language a. Similes b. Metaphors c. Personification d. Hyperbole e. Idioms 2. Connotation v. Determining Importance vi. Monitoring Comprehension 1. Recognizing comprehension problems 2. Employing appropriate fix-up strategies to repair comprehension c) Text Structure Analysis i. Identifying central ideas—stated and implied ii. Identifying supporting details iii. Identifying the author’s purpose iv. Patterns of Organization v. Transitions d) Vocabulary Acquisition i. Context Clues and Structural Analysis ii. Word Parts iii. Develop strategies to learn new words 3. Post-Reading Strategies a) Reflection and Reaction b) Summarizing and Paraphrasing c) Note-taking Strategies i. Outlining ii. Mapping 4. Critical Thinking a) Fact vs. Opinion b) Identifying Bias c) Identifying Tone d) Evaluating the author e) Defining an argument D. LEARNING OUTCOMES 9. Read and comprehend college-level materials independently for a variety of purposes. 10. Interpret text using a critical thinking, problem-solving approach. 11. Read as a means for lifelong learning. 12. Read as a way to understand themselves and others. 13. Summarize passages from a variety of texts. 14. Connect readings to personal experience and prior knowledge. 15. Utilize reading strategies to comprehend a variety of texts. 16. Demonstrate new strategies for vocabulary development. E. LEARNING OUTCOMES (Mn Transfer Curriculum) None F. METHODS USED FOR EVALUATION OF STUDENT LEARNING Course assessment may include the following: 1. quizzes and tests 2. classroom assignments, small group activities and graded assignments 3. journal writing 4. Pre and post tests G. SPECIAL INFORMATION None