The First Generation of Computers

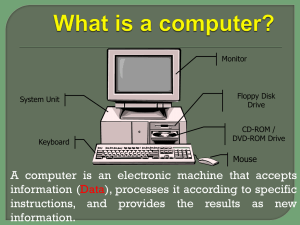
What is a computer?
Monitor
System Unit
Floppy Disk
Drive
Keyboard
CD-ROM /
DVD-ROM Drive
Mouse
A computer is an electronic machine that accepts information ( Data ), processes it according to specific instructions, and provides the results as new information.
Chapter:o1
Computer overview
=> Computer: A computer is an electronic device that can perform a different types of operations in accordance with set of instructions is called program.
=> Data: Data are raw facts.
=>Information: Information is meaningful data.
=> Input-Process-Output(IPO Cycle) : Certain input is needed to accomplished a task , a process is carried out on the input to obtain the output.
Functional Components of a computer:
INPUT
UNIT
CENTRAL
PROCESSING UNIT
OUTPUT
MAIN MEMORY
In IPO Cycle, First stage is performed in computer by input unit, Second stage is performed by its central processing unit and the Third stage is performed by output unit.
The main memory holds the input and intermediate output during the processing.
=>
INPUT UNIT:
The input unit is performed by the input devices attached to the computer. Input unit is responsible for taking input and converting it into computer understandable form(the binary code).
EXAMPLES:KEYBOARD,MOUSE MICR,
OMR, OCR, JOYSTICK.
=> Central Processing Unit:
The CPU is the control Centre for a computer .it
guides , directs, governs, its performance. It is brain of computer.
=> The CPU divided into two parts:
(a).Arithmetic Logic UNIT(ALU): The ALU performs all four arithmetical (+, -,*,/) and some logical operations(<, >,<=,>=,<>).
(B) CONTROL UNIT(CU): The CU control and guides the interpretation , flow and manipulation of all data and information. The CU sends control signals until the required operation are done properly by ALU and memory. It also responsible for execute the program. The CU gets program instruction from memory and executes the one after the other. After getting the instructions from memory in CU, the instruction is decoded and interpreted.
=> OUTPUT UNIT: The output unit is performed by the output devices attached to the computer. the output coming from CPU is in the form of electrical binary signals which needs conversion in some form which can be easily understood by human beings i.e. characters, graphical or audio visual.
Examples: Monitor, printer , plotter, speaker.
=> MEMORY: The memory is a device which can store the data and information.
=> MEMORY CELL: It is a device which can store a symbol selected from set of symbols.
bit
0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 cell 0 cell 1
=> BYTE OR NIBBLE: A group of 8 bits is called byte and a group of 4 bits is know as nibble.
Unit
1 Bit
8 Bits
2 10 i.e. 1024 bytes
2 10 i.e. 1024 KB
2 10 i.e. 1024 MB
2 10 i.e. 1024 GB
2 10 i.e. 1024 TB
2 10 i.e. 1024 PB
2 10 i.e. 1024 EB
2 10 i.e. 1024 ZB
2 10 i.e. 1024 YB
2 10 i.e. 1024 Bronto
Bytes
Short Name
Bit
1 Byte
1 KB
1 MB
1GB
1TB
1PB
1EB
1ZB
1YB
1 BRONTO BYTE
1 GEOP BYTE
Full Name
Binary Digit
Byte
Kilo Byte
Mega Byte
Giga Byte
Terra Byte
Peta Byte
Exa Byte
Zetta Byte
Yotta Byte
Bronto Byte
Geop Byte
=> There are two types of memory
(a). Primary (Main ) Memory: It is also know as temporary Memory. Ram and Rom
(b).
Secondary Memory: To store the data and information permanently. CD, Hard disk.
=> Hardware : The physical and tangible parts of the computer. i.e. The components that can seen and touched. Monitor ,mouse etc.
=> peripherals: The peripherals are devices that surround the system unit. Examples: keyboard, mouse, speaker, printer, monitor.
=> Software : The set of program that govern the operation of a computer system.
Types of Software
There are two types of software
1.System software
2. Application Software
System software: The software that controls internal computer operations is called system software
system software Divided into two parts
Operating system
Language system.
Operating system(os): An operating system is a program which acts as an interface between a user and the hardware(i.e. all computer resources)
Functions of operating system:
(i).It provide the instructions to prepare user interface.i.e, way to interact with user whether through typed commands or through graphical symbols.
(ii). Loads necessary programs (into the computer memory) which are required for proper compute functioning.
(iii). Coordinates how programs work with the CPU , keyboard, Mouse, Printer, and other Hardware as well as with other software
(iv). Manages way information is stored on and retrieved from disks
A set of software instructions that tells the computer what to do is called a computer program .
Major Component of Computer System are:
1.Single Program OS.
As the name suggests , this OS is single user operating system , so only one user program can be supported and executed by it at any point.
2.MultiProgram OS .
It supports multiprogramming.i.e., more than one user can be supported by it, therefore ,more than one user programs are loaded and active in the main store at he same time.
3.Time Sharing OS.
This OS uses the time sharing technique.
Each active user program is given a fair share of CPU time( δ),if the time elapses or an I/O operation is requested, CPU shifts over to the next jobs waiting and the previous program.
4.Real Time os: The jobs have fixed deadlines and the jobs have to be completed within their deadlines. the system performance is measured by its ability to complete its jobs within specified deadlines. If a job cannot be complete within its deadline, its situation is called deadline overrun.
5. Multiprocessing os: The Multiprocessing os is capable of handling more than one processors as the have to be executed on more than one processor(CPU)
Examples of operating systems are: Unix, Windows
NT, Windows XP, MS-DOS, Linux, Solaris, VMS, OS/2 and System
=>Language processors: It is a collection of program that convert high level language program into machine level language program.
High-level language: A high-level language consists of instructions, or statements, that are closer to English and common mathematical notation.
When programming in a high-level language, you do language of the CPU.
Assembler: It translates(converts) the assembly language program into an equivalent machine language program.
Interpreter: IT Converts a High level Language program into machine language by converting and executing it line by line. if there is any error in any line, it reports it at the same time and program execution cannot resume until the error is rectified.
Once a given instruction has been executed, then it translates and executes the next, and so on.
Compiler: It Translate(convert) the Entire HLL program into machine language program in one go, and reports all errors of the program along with the line numbers.
All instructions are compiled before any are executed by the CPU.
Application Software: It is a set of programs necessary to carry out operations for a specified application.
=> Application software Categories into two types:
(a). Customized Application software : This type of software is tailor –made software according to a user’s requirements. The software is developed to meet all the requirements specified by the user.
(b). General Application software : This type of software is developed keeping in mind the general requirements for carrying out specific task
Strength and Weakness of a computer:
=> Computer Strengths:
(i). Speed: Computer are much faster as compared to human beings. A computer can perform a task in a minute that may take day if performed manually.
(ii). High storage Capacity: Computers can store a large amount of information in very small space.
(iii). Accuracy: Computer s can perform all tha calculations and comparisons accurately provided the hardware does not malfunction.
(iv). Reliability: Computers can immune(protect) to tiredness and boredom or fatigue(mental exhaustion) .
(v ). Versatility: Computers can perform repetitive jobs efficiently. They even can work in the area where human brain can err.
Computer Weakness:
(i).
Lack of Decision Making Power:
Computer cannot decide on their own.
(ii). IQ Zero: Computers are dumb machines with zero IQ
=> FIRMWARE: It is prewritten program that is permanently stored in read only memory
(ROM). It configures the computer and not easily modifiable by the user. Example:
BIOS(BASIC INPUT OUTPUT SERVICE)
=> Liveware: The people associated with and benefited from the computer system.
The History of Computers
The origin of computers can be traced back to inventors who were interested in processing information and developing devices to simply tedious arithmetic calculations.
Calculation in Early Times
Abacus(3000BC)
allowed the user to manipulate data
Babylon, 3000 BC
Still in use today beads on rods to count and calculate
I- Ancient Counting Machines
2- The Roman Numerals
I II III IV V VI VII VIII IX X
3- The Arabic Numerals
(base 10)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Napier’s Log’s and Bones(1550-1617)
► Slide Rule 1962
► based on Napier’s rules for logarithms
► used until 1970s
► It simplified and used logs to transform multiplication problem to addition problem and division to subtraction
Pascal’s Adding Machine
1642
The Pascaline is a mechanical calculating(adding) device invented by the French philosopher and mathematician
Blaise Pascal in 1642. It capable of addition and subtraction
.it worked on clock work mechanism principle.
Leibnitz’s calculator
1671
The Leibniz Wheel was invented by the famous mathematician Leibniz in 1671.It perform ( + , - , * , / ) . this machine performed multiplication through repeated addition of number.
JACQUARD’S LOOM
1801
=>Punched Cards were used by the French weaver Joseph
Jacquard in 1801. The cards carried weaving instructions for the looms, later this idea offered a great use for storing info.
CHARLES BABBAGE’S DIFFERENCE ENGINE
=>In 1822 Charles Babbage
(English mathematician, philosopher), sometimes called the “father of computing” built the
Difference Engine.
=>Machine designed to automate the computation
(tabulation) of polynomial functions (which are known to be good approximations of many useful functions)
=>Based on the “method of finite difference”
=>Implements some storage
1822
1852
As designed, it would have been programmed using punch-cards and would have included features such as sequential control, loops, conditionals and branching. If constructed, it would have been the first “computer” as we think of them today.
Difference Engine c.1822
huge calculator, never finished
Analytical Engine 1833
could store numbers calculating “mill” used punched metal cards for instructions powered by steam!
accurate to six decimal places
The Tabulating Machine
Herman Hollerith , American inventor, worked at the
Census Bureau & later taught at MIT
A machine which used punch cards and did the mechanical work of tabulating the population
Won the Census Bureau contest and contract; selling
56 of his Tabulating Machines
Organized his own company and continued to produce the machines for the census
Merged with other companies eventually becoming known as International Business Machines – IBM
1943 – Howard Aiken & Grace Hopper –
Harvard Mark I Computer
The IBM Automatic Sequence Controlled Calculator
(ASCC) Computer was created by IBM for Harvard
University, which called it the Mark I. First universal calculator.
Mark-I
It used electro magnetic signals
It was slow machine took 3-5 seconds to perform a calculation
It was inflexible
It could perform basic arithmetic as well as complex calculations
(GENERATION OF COMPUTER)
Modern age of computers is divided into five generations of computers
First Generation (1949-1955)
Second Generation (1956-1965)
Third Generation (1966-1975)
Fourth Generation (1976-Present)
Fifth Generation (Present and Beyond)
The First Generation of Computers
The first computers used vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for memory, and were often enormous, taking up entire rooms. They were expensive to operate and in addition to using a great deal of electricity, generated a lot of heat, which was often the cause of malfunctions. First generation computers relied on machine language, the lowestlevel programming language understood by computers, to perform operations, and they could only solve one problem at a time. Input was based on punched cards and paper tape, and output was displayed on printouts. The UNIVAC and ENIAC computers are examples of first-generation computing devices. The UNIVAC was the first commercial computer delivered to a business client, the U.S. Census Bureau in 1951.
CHARACTERISTICS
First generation computers were based on vacuum tubes.
The operating systems of the first generation computers were very slow.
They were very large in size.
Production of the heat was in large amount in first generation computers.
Air conditioning required
Machine language was used for programming.
First generation computers were unreliable.
They were difficult to program and use.
Frequent hardware failure
Applications:
These computers were used for record keeping and payroll processing
ENIAC
ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator
And Calculator)
Developed by John Presper Eckert (1919-
1995) and John W. Mauchley (1907-1980)
Developed in 1946
Space requirement 30 X 50 sq. ft.
30 ton weight and 18000 vacuum tubes
70000 registers, 10000 capacitors
6000 switches and 150,000 watts electicity
cosr $ 400000
ENIAC
When ENIAC completed calculations it inform the users by turning on a sequence of lights
It was used until 1955
Only one system of ENIAC was developed
When operated the lights of near by area were dimmed
EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable
Automatic Calculator)
Developed by John Von Neuman (1903-
1957)
It contain a memory to store data and programs as well
EDSAC (Electronic Delay Storage
Automatic Calculator)
Developed in 1949 by Britishes
Prop.M.V.Wilkes .
IT uses mercury delay lines for storage.
UNIVAC
UNIVAC (UNIVersal Automatic Computer)
Developed by John Presper Eckert, Jr., and John
Mauchly
Developed in 1951
First commercial computer
Could manipulate numeric as well as textual data
UNIVAC
SECOND GENERATION
TIME PERIOD : 1956s- 1965s
TECHNOLOGY USED : Transistors
SIZE AND SPEED : Lesser size and increased speed
LANGUAGE USED : Assembly language and languages like
TRANSISITORS
COST : Cost decreased
COBOL and FORTRAN
UNIVAC
1108
OTHER FEATURES : More efficient and reliable.
Though the transistors still generated a great deal of heat that subjected the computer to damage, it was a vast improvement over the vacuum tube.
Second-generation computers still relied on punched cards for input and printouts for output.
EXAMPLE : UNIVAC 1108, IBM 1401, CDC 1604
IBM 1401
THIRD GENERATION
TIME PERIOD : late 1966s-1975's
TECHNOLOGY USED : Integrated Circuit
IBM
360/50
SIZE AND SPEED : Size Lesser and speed further increased
LANGUAGE USED : Operating System was developed.
COST : Cost decreased further
OTHER FEATURES : Instead of punched cards and printouts, users interacted with third generation computers through keyboards and monitors and interfaced with an operating system, which allowed the device to run many different applications at one time with a central program that monitored the memory.
Computers for the first time became accessible to a mass audience because they were smaller and cheaper than their predecessors.
EXAMPLE : IBM-360 series, Honeywell Model 316,
Honeywell – 6000 series, CDC – 1700.
FOURTH GENERATION
TIME PERIOD : 1976s-today
TECHNOLOGY USED : Microprocessor
SIZE AND SPEED : Reduced size and
• tremendous speed
LANGUAGE USED like PASCAL,
COST
: High Level Languages
COBOL, C, C++, JAVA
: Reduced Cost
OTHER FEATURES : Microprocessors also moved out of the realm of desktop computers and into many areas of life as more and more everyday products began to use microprocessors.
• As these small computers became more powerful, they could be linked together to form networks, which eventually led to the development of the Internet.
• Fourth generation computers also saw the development of
GUIs, the mouse and handheld devices.
The Macintosh 128K , the first Macintosh, was the first commercially successful personal computer to use images, rather than text, to communicate
.
EXAMPLE : Intel 4004, Apple Macintosh
Intel 4004D microprocessor
FIFTH GENERATION
TIME PERIOD : today--beyond
TECHNOLOGY USED : Microprocessor
SIZE AND SPEED : Reduced size and tremendous speed
LANGUAGE USED : Based on Artificial intelligence
COST : Reduced Cost
OTHER FEATURES : Fifth generation computing devices, based on artificial intelligence, are still in development, though there are some applications, such as voice recognition, that are being used today.
The goal of fifth-generation computing is to develop devices that respond to natural language input and are capable of learning and selforganization.
The use of parallel processing and superconductors is helping to make artificial intelligence a reality.
The goal of fifth-generation computing is to develop devices that respond to natural language input and are capable of learning and self-organization .
EXAMPLE : Parallel Inference Machine
Note: Artificial Intelligence is the branch of computer science concerned with making computers behave like humans.
• Voice Recognition is the field of computer science that deals with designing computer systems that can recognize spoken words.
Classification of Computers of On the basis of
How It Functions
The current classifications of computers place them into
Three categories:
Analog Computer
Digital Computer
Hybrid Computers
Classification of Computers of On the basis of
Analog
Computers
• Operate on continuous data, like measuring temp. changes
• Faster
• Accuracy of an analog computer is restricted to the accuracy with which physical quantities can be sensed and displayed.
• Specific Purpose computers
Digital
Computers
• Digital computers work on discrete data.
• digital computer can process data with greater accuracy
• We generally use digital computers for business and scientific data processing.
Hybrid Computers
• Hybrid computers are computers that comprise features of analog computers and digital computers .
• The digital component normally serves as the controller and provides logical operations , while the analog component normally serves as a solver of differential equations .
Digital Computer classified into two types
(i). Purpose –wise
(ii). Size and Performance wise
(i ). Purpose –wise digital computer are classified into two types.
(a). Special-purpose computer : It is designed to performed a specific task. the instructions to carry out the task are permanently stored in the machine.
(b). General-purpose computer: it can work on different types of programs input to it and be used in countless applications.
The program are not permanently stored .
Size and Speed Based Classification of digital
Computer Systems
The current classifications of computers place them into five categories:
Embedded computer,
,Microcomputers (Personal Computers)
Minicomputers,
Mainframes,
Super Computers,
=> Embedded computers: These computers are typically preprogrammed for a specific task, such as tuning to a particular television frequency. Examples: television, washing machine.etc.
PERSONAL COMPUTER
The term microcomputer, also known as personal computer (PC), or a computer that depends on a microprocessor.
A microcomputer contains a central processing unit (CPU) on a microchip (the microprocessor), a memory system (read-only memory and random access memory), placed on a motherboard.
Example: desktop, notebook, laptop, handheld devices.
Charcteristics: developed in 1980 designed for single user not very powerful or expensive found in homes
Micro computer also divided into three types
PDA(Personal digital assistants)
Laptops and desktop personal computer.
Workstations:
• Between minicomputer and microcomputer- in terms of processing power.
• Looks like PC and used by one person.
MINICOMPUTER
Another term rarely used anymore, minicomputers fall in between microcomputers (PCs) and mainframes
(enterprise servers).
Minicomputers are normally referred to as mid-range servers now.
Characteristics:
Smaller than mainframe
Can do several jobs at once
Can be used by many people at one time
Used by small companies
MAINFRAME
In the early days of computing, mainframes were huge computers that could fill an entire room or even a whole floor.
As the size of computers has decreased while the power has increased, the term mainframe has fallen out of use in favor of enterprise server. You'll still hear the term used, particularly in large companies to describe the huge machines processing millions of transactions every day.
Characteristics:
Expensive
Powerful and fast
Is not limited to one job
Used by business and small government organizations
The main difference between a supercomputer and a mainframe is that a supercomputer channels all its power into executing a few programs as fast as possible, whereas a mainframe uses its power to execute many programs simultaneously.
SUPER COMPUTER
The fastest type of computer.
Supercomputers are very expensive and are employed for specialized applications that require immense amounts of mathematical calculations.
For example, weather forecasting requires a supercomputer.
Other uses of supercomputers include animated graphics, , nuclear energy research, and petroleum exploration.
Characteristics
Powerful
Expensive
Dedicated to one purpose - weather, satellites, military
Used by large governments or very large companies
Can be used by thousands of people at the same time
Very large - fill rooms
Sixteen racks of IBM's Blue Gene/L supercomputer can perform 70.7 trillion calculations per second, making it the fastest machine known so far.
Generations of Electronic Computers
Technology
Size
First
Generation
Vacuum
Tubes
Filled Whole
Buildings
Second
Gen.
Third
Gen.
Transistors Integrated
Circuits
(multiple transistors)
Filled half a room
Smaller
Fourth Gen.
Microchips
(millions of transistors)
Tiny - Palm
Pilot is as powerful as old building sized computer