Distribution of Water (surface and underground)
advertisement

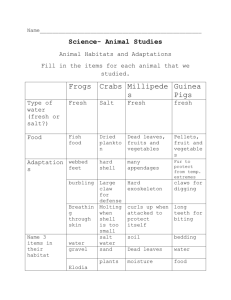
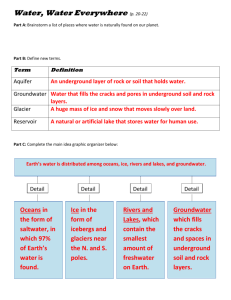
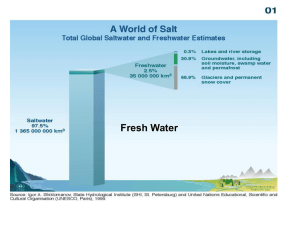
Distribution of Earth’s Water The Oceans Water covers about 75% of the Earth’s surface 97% is salt water 3% is fresh water only 1% of fresh water can be used There are 4 major bodies of water: Atlantic Ocean Pacific Ocean Indian Ocean Arctic Ocean Ice - 76% of fresh water - Most of Earth’s fresh water is locked in thick sheets of ice near the North and South Poles. - Icebergs – huge chunks of floating ice made of fresh water. Rivers and Lakes – .34% of fresh water – Very little fresh water but important to people who live near them. Groundwater - 23% of fresh water (shallow and deep combined) - Water fills the cracks and spaces in underground soil and rock layers. Surface Water River Systems a. Tributary – streams and smaller rivers that feed into a main river b. Watershed – land area that supplies water to a river system. c. Divide – separates one watershed from another by a ridge of land Pond a. Body of fresh, standing water b. Smaller than lakes – sunlight reaches the bottom c. Formed when water collects in hollows or low-lying areas of land d. Home too many animals including frogs, crayfish, sunfish, water lilies, algae, etc. Lakes - Body of fresh water that no sunlight reaches the bottom - Deep and big - Formed two ways Same as a pond Powerful forces that shape Earth’s surface such as ice depressions, crust movement or volcanoes Wetlands – a land area that is covered with water during part or all of the year. – 3 types • Marshes – grass covered by shallow water • Swamps – flooded forests with trees – usually in warm, humid climates • Bogs – depression from ice sheets – usually in cold climates Water Underground Movement – Permeable – water runs through the ground • Gravel – Impermeable – water cannot pass through easily • Clay • Granite Zones Saturated – soil is totally filled with water Unsaturated – soil can still accept water Ground water – Springs – ground water bubbles or flows out of cracks in rock to Earth’s surface – Aquifer – underground rock or sediment that holds water – Well – channel dug into an aquifer to provide a supply of water – Geyser – hot spring from which water periodically erupts out Using Freshwater Resources How People Use Fresh Water – Household purposes – Industry – Transportation – Agriculture • Irrigation – supplying water to areas of land to make them suitable for growing crops – Recreation Conserving Water Reduce Recycle Reuse Pollution – addition of any substance that has a negative effect on water or the living things that depend on the water