Individual Project I
advertisement

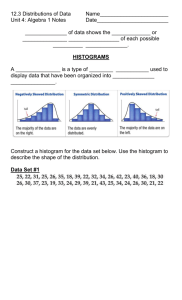
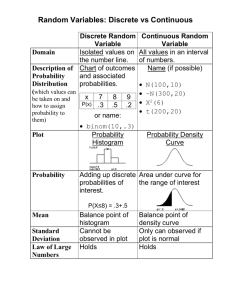
IET 603 Quality Assurance in Science & Technology Travis Fisher Chapter Outline 3.1 - DESCRIBING VARIATION 3.2 - IMPORTANT DEISCRETE DISTRIBUTIONS 3.3 - IMPORTANT CONTINUOUS DISTRIBUTIONS 3.4 - PROBABILITY PLOTS 3.5 - SOME USEFUL APPROXIMATIONS Chapter Overview To show how simple tools of descriptive statistics can be used to express variation quantitatively in a quality characteristic when a sample of data on this characteristic is available. To introduce probability distributions and show how they provide a tool for modeling or describing the quality characteristics of a process. Describing Variation No two units of product produced by a process are identical. Some variation is inevitable. Statistics is the science of analyzing data and drawing conclusions, taking variations in the data into account. …Variation Stem & Leaf Display A Stem & Leaf display is one of the most useful graphical techniques for summarizing and presenting data. …Stem & Leaf Display The Histogram Histograms are a more compact summary of data than a stem-and-leaf plot. Constructing a Histogram Is a chart that displays distribution, center location, and variation of data by categorizing data. Unlike bar graph (commonly used in Excel), it can show distribution of data. Using Minitab a Histogram from the data below using the following steps. …Constructing a Histogram …Constructing a Histogram …Constructing a Histogram Shows distribution in comparison to normal curve of same mean and standard deviation. …Histogram Box Plot Boxplot is used to obtain information about the shape, dispersion, and mid-value of given data. Spot outliers. Used to assess the symmetry of the data. Constructing a Box Plot Go to Minitab > Graph > Boxplot Choose the option “Simple” Select the data column …Constructing a Box Plot Box Plot Analysis The line drawn through the box represents the median of the data. The edge above the median represents the first quartile (Q1), while the edge below represents the third quartile (Q3). Thus the box portion of the plot represents the interquartile range (IQR = Q3-Q1), or the middle 50% of the observations. The lines extending from the box are called whiskers. The whiskers extend outward to indicate the lowest and highest values in the data set (they exclude outliers). Extreme values, or outliers, are represented by dots. A value is considered an outlier if it is outside the box (greater than Q3 or less than Q) by more than 1.5 times the IQR. Brush may be used on the graph to find the values of outliers. Probability Distributions A probability distribution is a mathematical model that relates the value of the variable with the probability of occurrence of that value in the population. Normality Test There are various methods to check for Normality. We will discuss one of the most commonly used methods: Probability Plot Follow the path in Minitab: Minitab > Graph > Probability Plot Consider the following data of the number of accidents in a yearly highway accident report. Normality Test: Probability Plot Normality Test: Probability Plot Normality Test: Probability Plot P – value = 0.436. Since p – value is greater than 0.05, the given data is normal. 0.05 is the alpha value (alpha risk / type – I error the significance level). Generally, the value assigned is 5% unless stated otherwise or demanded by the process. Normality Test: Probability Plot The discrete probability distribution of the number of successes in a sequence of n independent yes/no experiments, each of which yields success with probability p. …Binomial Distributions References AuthorStream. (2013). Retrieved from http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:MUUMYyOrpp8J:www.aut horstream.com/Presentation/aSGuest34389-294160-introduction-minitab-education-pptpowerpoint/+minitab+ppt&cd=1&hl=en&ct=clnk&gl=us Montgomery, D. C. (2009). Introduction to Statistical Quality Control Sixth Edition. Questions?