University of South Florida - Hillsborough Community College
advertisement

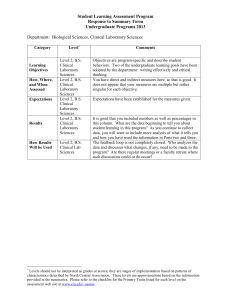
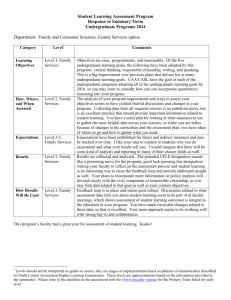
Quality Enhancement Challenge S. David Stamps, Provost and Vice President for Academic Affairs University of South Florida 1 SACS Reaffirmation • Compliance Certification Report Due August 2004 • Quality Enhancement Plan Due January 2005 2 Quality Enhancement Plan • An opportunity to improve the quality of programs and services 3 QEP Institutional Improvement with Special Attention on Student Learning 4 A Plan For The Next Ten Years 5 We would have improved General Education. • Reasons – These have changed since originally conceived. – Exit courses were never funded or adequately supported. – It is just time for a re-examination. 6 Broader Approach • Look at how we deliver undergraduate curriculum • Raise questions and introduce ideas for consideration 7 Reinvention Center Stony Brook Reinventing Undergraduate Education – Bruce Cochrane – Georg Kleine – Stu Silverman – David Stamps http://naples.cc.sunysb.edu/pres/boyer.nsf 8 Boyer Commission Report 1998 • Research-Based Learning • Inquiry-Based • Freshman Foundation • Interdisciplinary • Communication Skills • Information Technology • Capstone Experience • Apprentice Teachers • Faculty Reward Systems • Community 9 Why is this important to USF? • Research 1 status • Evidence-based decision making • Undergraduate students for graduate school • Research-based community engagement • High technology and information-based society 10 Why do we hear? • Graduates are not independent thinkers • They don’t make rational choices • They don’t pursue their aspirations 11 What have we learned about past history that can enlighten us about the future? 12 The Challenge of Liberal Education • Go beyond the traditional conception • Lagemann: “the practical liberal arts” http://www.gse.harvard.edu/news/features/lag emann02012003.html 13 Carnegie • Higher education is far more oriented to professional and technical degrees than in 1970s. • 1970s – over 50% in liberal arts • 2000 – over 60% in pre-professional & technical fields 14 Many Students • I need to get a job! • I just want a degree! • Students: – Seek relationship between course of study and job – Graduate without a clear sense of direction 15 Question • Are colleges and universities developing narrowly designed professional and technical fields of study with liberal arts components that are without direction? 16 USF – Research 1 University • Prepare students for graduate study? • Provide insights and skills necessary for career entry and change? • Provide learning experiences for better appreciation/understanding of world? 17 Practical Liberal Arts (Lagemann) • • • • • • • • Having a calling . . . Knowing who one is Beliefs, values, where one stands Choices Social interconnectedness Civic responsibility Respect for tolerance Evidence-based decision-making Respect for values of due process 18 This is not about one individual’s calling but about one’s calling in society and across societies. 19 Research-based Undergraduate Curriculum • Begin by asking … 20 What Conditions • What conditions currently exist that would enhance an undergraduate research program? 21 What Changes • What policies, structures, expectations, etc. need to be changed to establish an undergraduate research program? 22 Research 1 quality • How does the quality of instruction differ in a Research 1 university from that of a comprehensive university? 23 Assumptions • For consideration .. 24 Assumption • Undergraduate students will go to graduate school. 25 Assumption • Undergraduate students will have a research and inquiry experience. 26 Assumption • The undergraduate research program will be comprehensive in approach and conceptual in nature. 27 Assumption • Undergraduates will receive a value-added education if they have a research experience even if they do not continue to graduate school. 28 Assumption • The undergraduate research experience will provide an emphasis on evidence-based decisionmaking. 29 Assumption • The undergraduate research experience will provide opportunities for research that is community-based. 30 A liberal arts curriculum can support a researchbased undergraduate experience. 31 Possible Gen Ed Core Levels Approach 1. Writing, argumentation, and library skills 2. Oral presentation skills 3. Writing in the major 32 Undergraduate Research is Developmental • Beginning – ideas & interests • Intermediate – experience & skills • Advanced – independent research 33 - Our Challenge How to overcome faculty and students’ lack of concern or appreciation of the value of undergraduate research. 34 A possibility – Introductory Seminar • Lay groundwork • Mentoring relationships 35 Research 1 University Challenges Balancing roles • Curriculum • Pedagogy • Experiential learning 36 Curriculum Aspects • Intellectual Skills – Critical thinking – Critical reading – Problem-solving – Analyzing, integrating, etc. – Writing effectively – Ability to formulate questions 37 Curriculum Aspects • Broad Definitions/Understanding – Epistemological sophistication – Cross cultural understanding – Scientific/qualitative literacy – Collaboration – Civic and social responsibility – Life-long learning self-regulated 38 Pedagogy Change • • • • Process of inquiry Make observations Pose questions Learners engaged in questions posed by faculty • Directed to collect certain data • Learners select among questions and pose new questions 39 Pedagogy Change • Directed to collect data • Guided in process of evaluating data collected • Identify sources of information • Analyze • Identify assumptions • Propose explanations • Guiding learning should be role of faculty 40 Pedagogy of Engagement • Problem-based learning • Experiential learning • Service learning 41 A Challenge for Quality Enhancement Undergraduate Research University of South Florida 42