Is this a target? - West Virginia Department of Education
advertisement

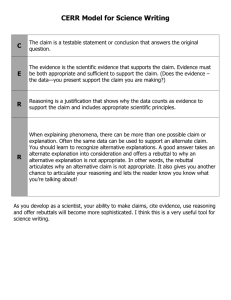
October 24-26, 2010 Vision Mission Goals All West Virginia educators continually grow in their professional expertise and improve their professional practice by working together interdependently in collaborative teams supported by collaborative cultures. To create district and school-based collaborative teams whose goals are to promote higher levels of learning for all students through formative classroom assessment practices and collaborative team processes. Create a core of CTN schools that include teacher collaborative teams supported by school leadership teams Engage in professional development designed to enhance effective collaboration and school-based decision-making Focus improvement efforts on building collective capacity to impact student outcomes Provide a structured support system to assist schools as they move along the continuum of implementation A Touch of Greatness Freedom Writers Stand and Deliver West Virginia Department of Education Individual growth does not ensure organizational growth. Organizations need more than well-developed individuals. Effective leaders focus on developing the culture and the collective capacity of the organization. Center for Creative Leadership (2003) Michael Fullan (2007) Richard Elmore (2006) Student achievement gains and other benefits are influenced by organizational characteristics beyond the skills of individual staff. We saw schools with competent teachers that lacked the organizational capacity to be effective with many students. The task for schools is to organize human resources into an effective collective effort. Newmann and Wehlage,(1995) Teacher Collaborative Teams School Leadership Team District Leadership Team Regional Support Teams Teacher Collaborative Teams Organized into teams on the basis of shared responsibility for addressing the critical questions of teaching and learning with a particular group of students –by content, course or grade level School Leadership Team School administrators and collaborative team leaders (representing each teacher collaborative team) form a School Leadership Team that supports the work of teacher teams using a distributed model of leadership. Math teachers discuss how to phrase test questions during a team meeting before morning classes at the Adlai E. Stevenson High School staff cafeteria in Lincolnshire, Illinois. —John Zich for Education Week West Virginia Department of Education MAJOR POINTS LEARNED THESE IDEAS SQUARED WITH MY OWN THINGS STILL GOING ON IN MY HEAD BEST Describe a positive assessment experience you have had. Explain why it was positive. WORST Describe a negative assessment experience you have had. Explain why it was negative. Best when I scored high enough on my ACT to go to college the science fair when you knew what you were going to be assessed on, when the teacher made it very clear and all anxiety was eliminated Our teacher allowed us take assessments when we were ready - a self-paced schedule. I always performed better when I knew I was ready. When I was in second grade the teacher had us to explain the water cycle any way we wanted. I was allowed to express my knowledge through drawings and I loved it! Worst taking all standardized tests. I had real test anxiety! when I ran out of time and felt pressure and disapproval from the teacher a 'game' that my high school studies teacher liked to play when we were a little out of control. The assessment was impossible to complete in one class period and EVERYONE failed. It was added to our grade and lowered everyone's GPA. We need to provide the language and the tools to administrators, teachers and students so they can communicate accurately about assessment. Continuous (Formative) Classroom Assessment For Learning Classroom Level Users Common Formative Assessments Content Level Users (Students, Teachers and Parents) Job-Alike Collaborative Teacher Teams Periodic Benchmark Assessments Program Level Users (Teacher Teams and School Leaders) Annual Accountability Testing (State Summative Test) Institutional/Policy Users (School, District and State Leadership) What is the primary aim of assessment? • Who will use the information gathered? • What decisions will they make? • The primary purpose of assessment is not to rate, rank and sort students, but to provide meaningful feedback that informs decisions. Assessment of Learning Summative Assessment An event after learning Benchmark Assessment An event after learning Assessment for Learning Formative Assessment A process during learning Classroom Assessment For Learning A process during learning Determine ultimate (overall) type of target the objective represents: knowledge target reasoning target performance skill target product target Identify its underpinning learning targets Objective/Benchmark: Overall Target Type: Knowledge Reasoning Performance Skill Product Learning Targets What are the knowledge, reasoning, performance skill or product targets underpinning the standard/objective? Knowledge Targets Reasoning Targets Performance Skill Targets Product Targets Objective/Benchmark: First Grade Reading /English Language Arts Produce writing to communicate with different audiences for a variety of purposes. Overall Target Type: Knowledge Reasoning Performance Skill Product Learning Targets What are the knowledge, reasoning, performance skill or product targets underpinning the standard/objective? Knowledge Targets Know what a sentence is Understand concept of word choice Reasoning Targets Distinguish the uses or meanings of a variety of words (word choice) Performance Skill Targets Holds a pencil correctly Print letters correctly Space words Use lines & margins Stretch out sounds in words to create a temporary spelling of a word Product Targets Write sentences with varied beginnings A learning target is an achievement expectation we hold for students. It’s a statement of what we want the student to learn. Is this a target? Math Decimals Page 152 in the book Going on a decimal hunt Read decimals and put them in order Students who could identify their learning scored 27 percentile points higher than those who could not. (Marzano, 2005) Objective/Benchmark: First Grade Reading /English Language Arts Produce writing to communicate with different audiences for a variety of purposes. Overall Target Type: Knowledge Reasoning Performance Skill Product Learning Targets What are the knowledge, reasoning, performance skill or product targets underpinning the standard/objective? Knowledge Targets Know what a sentence is Understand concept of word choice Reasoning Targets Distinguish the uses or meanings of a variety of words (word choice) Performance Skill Targets Holds a pencil correctly Print letters correctly Space words Use lines & margins Stretch out sounds in words to create a temporary spelling of a word Product Targets Write sentences with varied beginnings Standard/Objective: Drive with skill. Type: Knowledge Reasoning Product Performance Skill Learning Targets What are the knowledge, reasoning, skill or product targets underpinning the standard/objective? Knowledge Targets Reasoning Targets Performance Skill Targets •Know the law •Understand informal rules of the road •Analyze road conditions, vehicle performance, and other driver’s actions •Understand what different parts of the car do •Read signs and understand what they mean •Understand what “creating a danger” means •Understand what “creating a hazard” means •Other? •Compare/contrast this information with knowledge and past experience •Driving actions such as: steering, shifting, parallel parking, looking, signaling, backing up, braking, accelerating, etc. •Synthesize information and evaluate options to make decisions on what to do next •Evaluate “Am I safe?” and synthesize information to take action if needed. •Other? •Fluidity/automaticity in performance driving actions. •Other? Product Targets None Since the ultimate type of target is a performance skill, there are no embedded product targets An Analogy A pilot guides a plane or boat toward its destination by taking constant readings and making careful adjustments in response to wind, currents, weather, etc. A teacher using formative classroom assessment practices does the same: - Plans a carefully chosen route ahead of time - Takes numerous readings along the way - Changes course as conditions dictate Take a few minutes to reflect on what you have heard and use your graphic organizer to write down your thinking. British researchers Paul Black and Dylan Wiliam completed a comprehensive review of 250 international studies exploring the connection between formative assessment practices and student achievement (1998) Does improved formative assessment cause better learning? Do formative assessment practices need improving? Is there evidence about how to improve formative assessment? Increased commitment to high-quality classroom assessments Increased descriptive feedback; reduced evaluative feedback Increased student involvement in the assessment process Black and Wiliam, 1989 …achievement gains from using such assessment-for-learning strategies were “among the largest ever reported for educational interventions.” -Black and Wiliam (1998) • • More frequent testing does not necessarily mean greater gains. The strategies Black and Wiliam refer to involve students in the entire process. .7 Standard Deviation Score Gain = 25 Percentile Points on ITBS 70 SAT Score Points 4 ACT Score Points Largest Gain for Low Achievers Successful schools are places where teams of teachers meet regularly to focus on student work through assessment and change their instructional practice accordingly to get better results. Michael Fullan, 2000 Assessment Issues of Quality Select a proper assessment method Select or create quality items, tasks, and rubrics Sample—gather enough evidence Control for bias Design assessments so students can selfassess and set goals Selected Response Multiple Choice based on observation of a performance or a product and True/False Matching Fill in the blank Label a diagram Extended Written Response: Writing in response to a question or prompt Performance Assessment: Assessment judgment of its quality Personal Communication Questions Conferences Interviews Oral Examinations Selected Extended Performance Personal Response Written Assessment Communication Response Knowledge Reasoning Performance Skills Product Imagine you are going to go skydiving. Presumably, you will want to have a parachute that has a very good chance of opening properly. The skydiving company has provided you with the assessment scores of three students from a recent parachute-packing course. These three are the only people they employ to pack parachutes, so you have to have a parachute packed by one of them-unless you want to jump without a parachute! Please note the competency/mastery level for each assessment, as shown on the chart in the next slide and carefully consider which student you want to pack your parachute. FINAL PACKING DEMONSTRATION RESEARCH WRITTEN PAPER EXPLANATION ON OF WRITTEN FINAL EXAM PARACHUTE VOCABULARY HISTORY STEPS OF PARACHUTING QUIZ 90 ASSESSMENT ASSESSMENT ASSESSMENT ASSESSMENT 1 ASSESSMENT ASSESSMENT 2 ASSESSMENT ASSESSMENT 3 ASSESSMENT 4 5 6 78 9 80 70 60 COMPETENCY/MASTERY LEVEL 50 STUDENT 1 STUDENT 2 40 STUDENT 3 30 20 10 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 READ MANUAL AND PARACHUTE ANSWER SKETCH OF THE QUESTIONS DEMONSTRATION SEQUENCING QUIZ 7 8 9 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) What was the learning objective? Which assessments match the learning objective? Which student will you choose to pack your parachute? Why? If these scores were used to assign a report card grade, could you determine which student(s) had mastered the objective? How many of the assessments were at the knowledge level? #1-Research paper #2-Read and answer questions #3-Written explanation #4-Sequence Steps quiz #5-Vocabulary quiz #6-Label parts of a parachute drawing #7-Written final exam #8-Packing demo #9-Final packing demo Standard/Objective: Packing a Parachute Type: Knowledge Reasoning Product Performance Skill Learning Targets What are the knowledge, reasoning, performance or product targets underpinning the standard/objective? Knowledge Targets Reasoning Targets Performance Skill Targets Product Targets None Since the ultimate type of target is a performance skill, there are no embedded product targets Page 4