Flyer
advertisement

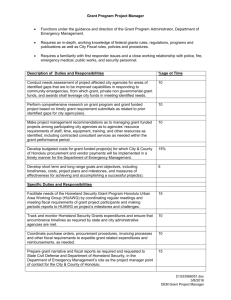
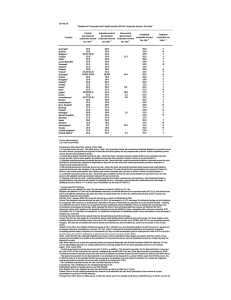
Network on Fiscal Relations across Levels of Government Purpose Fiscal relations between levels of government are a high priority on the political agenda of most OECD and non OECD countries. Sub-central governments represent on average, 22% of public revenues, 31% of public spending and 66% of public investment in OECD countries, and their spending amounts to 15% of GDP. The Fiscal Network: • Provides member countries with the analytical and statistical underpinnings of intergovernmental fiscal relations and sub-national public finance; • Is a high level, multidisciplinary policy dialogue platform, between policy makers from different ministries (Finance, Interior, Budget, etc.); • Contributes to overcoming the often compartmentalised and sometimes even contradictory policy perspectives in national capitals. Participants Source: OECD Network on Fiscal Relations across Levels of Government 16 contributing countries 3 OECD Directorates 30 countries provide statistical and policy information (Centre for Tax Policy and Administration, Economics Department and Public Governance and Territorial Development Directorate) Fiscal Network Other International Organisations participate actively (IMF, EU, Council of Europe, etc.) Visit our website for more information: http://www.oecd.org/ctp/federalism Accession and Partner countries are strongly invited to join • Property taxation; • Debt management at the sub-national level Current Activities • Consolidation at the sub-national level Future Challenges • Decentralisation and regional disparities Experts Meetings Taxonomy of grants Statistical Databases OECD Fiscal Decentralisation Database. Paris, March 2011 Balances, consolidated expenditure, consolidated revenue, tax revenue, user fees, transfers. Sub-Central Tax Competition Berne, 31 May-1 June 2010 Taxing power of sub-central governments in Economic Crisis and Sub-Central Fiscal Policy Paris, 12 June 2009 OECD countries Revenue structure of sub central government: autonomous tax revenue, shared taxes, earmarked and non-earmarked grants. Borrowing and fees Taxes versus Grants Vienna, May 29-30 2008 Fiscal Equalisation in OECD Countries Zaragoza, June 2006 The Efficiency of Sub-Central Spending Intergovernmental grants. grants by donor and recipient sub-sector; grant revenue by type of grant and grants by government function http://www.oecd.org/ctp/federalism/oecdfiscaldecentralisati ondatabase.htm Paris, 19-May-2006 Working Papers WP 13, Apr-11: WP 12, Jan-10: WP 11, Jan-10: WP 10, Jun-09: WP 9, Jun-09: WP 8, May-09: WP 7, May-09: WP 6, May-08: WP 5, Jun-08: WP 4, Sep-07: WP 3, Sep-06: WP 2, Sep-06: WP 1, Sep-06: Tax competition between sub-central governments Fiscal Policy across Levels of Government in Times of Crisis Explaining the Tax-Grants Balance Finding the Dividing Line between Tax Sharing and Grants: A Statistical Investigation The Fiscal Autonomy of Sub-Central Governments: An Update The Spending Power of Sub-Central Governments: A Pilot Study Taxes and Grants: On the Revenue Mix of Sub-Central Governments Market Mechanisms in Sub-Central Public Service Provision Promoting Performance: Using Indicators to Enhance the Effectiveness of Sub-Central Spending Fiscal Equalization in OECD Countries Intergovernmental Transfers and Decentralized Public Spending Fiscal Autonomy of Sub-Central Governments Fiscal Rules for Sub-Central Governments: Design and Impact http://www.oecd.org/ctp/federalism/fiscalfederalismnetworkworkingpapers.htm Visit our website for more information: http://www.oecd.org/ctp/federalism