Health Systems Characteristics Survey
advertisement

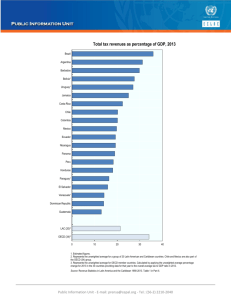
OECD experience on fiscal sustainability Joint OECD/WHO Meeting on Financial Sustainability of Health Systems Edwin Lau Deputy Head, Budgeting & Public Expenditures Division, OECD 28 June 2012 Health is 2nd largest public expenditure area in OECD 36 Structure of general government expenditures, 2007 & 2010 (% of total expenditures) 32 28 2007 24 2010 20 16 12 8 4 0 Social protection Health Education Economic affairs General public services (excluding interest) Interest* Source: OECD Fiscal Consolidation Survey 2012. Public order and safety Defence Recreation; Housing and Environment culture and community protection religion amenities And health expenditures are rising Annual average growth in real 7.2.3. Annual average growth inper realcapita per capita expenditure on health and GDP, 2000-2009 (or (or expenditure on health and GDP, 2000-2009 nearest nearestyear) year) New challenges: Annual average growth rate in real health expenditure per capita (%) 11 • Ageing populations : ex. Korean population aged over 65 years will represent 37% of total Korean population in 2050 • Uptake of new technology : more costly and requires more skills and training • Increase in multi-morbidity : continuing care, complications & acute care have considerable bearing on health spending SVK 9 KOR POL 7 EST GRC IRE CZE TUR CHL GBR 5 BEL ESP FIN NZL NLD SVN OECD 3 ITA CAN DNK SWE AUS USA MEX NOR JPN FRA AUT ISL DEU CHE HUN Source: OECD PRT HealthISR Data 2011. 1 LUX -1 1 3 -1 Annual average growth rate in real GDP per capita (%) Source: OECD Health Data 2011. 5 Is health crowding out other expenditure areas? 18 Change in structure of spending between 2007 & 2010 (% of GDP) 16 14 2007 2010 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Social protection Health Education Economic affairs General public services (excluding interest) Interest Source: OECD Fiscal Consolidation Survey 2012. Public order and safety Defence Recreation; Housing and Environment culture and community protection religion amenities Health measures frequently proposed in fiscal consolidation plans % 75 Out of 30 responding countries 60 45 30 15 0 Source: OECD Fiscal Consolidation Survey 2012. And proposed reductions are significant % of GDP 1.2 1.0 Impact of programme measures on the health sector, 2009-16 Plan 2012 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 Source: OECD Fiscal Consolidation Survey 2012. Plan 2011 Short-term cuts ≠ effectiveness or fiscal sustainability Achieving all of these goals: OBJECTIVES Delivering healthcare efficiently Maximizing health outcomes Increasing the distribution of health (equity) Maintaining fiscal stability Requires these challenges to be tackled: CHALLENGES Both technical & allocative efficiency Maximizing outcomes for a given level of inputs (programme effectiveness ) A financing system that reflects society’s consensus on risk pooling & cross subsidies A revenue stream that is both stable (broadbased) and predictable (counter-cyclical, stability for planning & pricing) Fiscal sustainability (willingness to pay for a7 level of demand) Purpose of SBO Health Sustainability Network • Financial situation calls on for new forms of co-operation to achieve fiscal sustainability, but also value for money, and access and equality of health care. • Main objectives: • • • • Establish institutional dialogue, clarity of roles, and common objectives and vocabulary Find and disseminate appropriate good practice Better share existing work (analysis and data) • Assist countries moving towards universal access to health insurance OECD organised a first meeting in Nov 2011: o o Successfully brought together Health Budget officials from Ministries of Health and Ministries of Finance, as well as Social Security Institutions/Health Insurance Funds Strong interest by both countries and other international organisations (WHO, World Bank andADB) Balancing demand for care with ability to pay Sessions 3&4 Design of health financing system Session 6 Co-ordination function Setting healthcare expenditure levels Estimating future & current health Session 6 spending needs Expenditure management Revenue Generation Sessions 5 Sessions 3&4 9