Final Review Powerpoint
advertisement

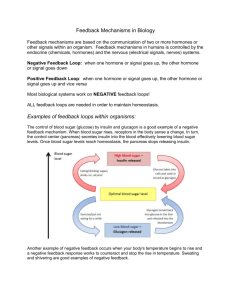
B cells give rise to plasma cells, which produce ------------------ Antibodies Name the structure which is often referred to as the pacemaker of the heart Sino-atrial node / SA node APC Name this cell T-cell Name this cell B-lymphocyte Name this cell Name this cell Name this cell Plasma cells T helper cell Name this cell Cytotoxic T cell Name this cell Memory B-cells Name this cell Virus infected host cell Name 1 characteristic of non-specific immunity (aside from it’s non-specificity) No memory Identify whether these are part of innate immune response or the acquired immune response Natural killer cells Innate Lymphocytes Innate Macrophages Innate and acquired Humoral immunity is mediated by which type of lymphocytes? B-lymphocytes What surface marker is present on helper T-cells? CD 4 Which type of immunity involves antigen-presenting cells? (A) Humoral immunity (B) Cell-mediated immunity Cell-mediated immunity Name 2 components of saliva 1. Salivary amylase 2. Mucin 3. Lysozyme What are villi? Where are they found? What is it’s function What kind of cells line the villus Villi are finger like projections On the walls of the small intestine Where absorption of digested food occurs It is lined by columnar epithelium What are gastric pits? Depressions in the stomach lining that lead to gastric glands What three things are produced by the gastric glands? 1. Pepsinogen 2. HCl 3. Mucin How is pepsinogen activated? The longer inactive pepsinogen is cleaved to form pepsin by the HCl. The resultant pepsin activates formation of more of itself ( + feedback) What is chyme? The partially digested food that is present in the stomach. Is usually acidic and Can be described as a soupy liquid Where does chyme go? What controls it’s flow? Chyme leaves the stomach to enter the duodenum The pyloric sphincter controls it’s flow into the duodenum Name one protein-digesting enzyme produced by the pancreas Trypsin / Chymotrypsin While chyme is acidic, the food in the duodenum is neutral in pH What secretion is responsible for this pH change? The bicarbonate base in the pancreatic juice Which enzyme breaks down fats? Which organ produces this enzyme? Where does fat digestion occur? Is fat absorbed through the blood or lymph? Lipase Pancreas Small intestione Lymph (lacteal vessel) Which bacterium causes ulcers? Helicobacter pylori Type-1 diabetes Also called as? Time of onset? Pathology – what is the trouble? Treatment? Juvenile diabetes Young age Insulin supplementation Destruction of pancreatic cells that produce insulin. An auto-immune disorder Type-2 diabetes Also called as? Time of onset? Pathology – what is the trouble? Adult-onset diabetes Middle/old age Insulin receptor deficiency or malfunction Which two hormones control blood glucose levels? Insulin and glucagon Which organ is responsible for the release of these hormones? Pancreas Which hormone is released when blood glucose levels are high? Insulin Which cells are the targets of insulin? Muscle and liver cells What exactly does insulin do? Induces muscle and liver cells to take up glucose from blood stream and store it as glycogen Which hormone is released when blood glucose levels are low? Glucagon Glucagon is produced by ----------------Pancreas What are the targets of glucagon? Muscle and liver cells What exactly does glucagon do? Promotes muscle and liver cells to break-down glycogen and release glucose What hormone is produced by the stomach? Gastrin What is gastrin’s function? Promotes release of gastric juices by the stomach When is gastrin secreted? Only when chyme is present Name the hormone produced by adipose tissue Leptin Does leptin stimulate or suppress appetite? suppresses appetite What hormones are produced by the duodenum? CCK and secretin What are the functions of CCK and secretin? CCK suppresses appetite CCK and secretin promote release of bile by the gall bladder And pancreatic juice by the pancreas When are these hormones produced? Only when chyme is present in the duodenum What protects the stomach from it’s own acids? The layer of mucus that lines the stomach Name the chamber that receives deoxygenated blood from all parts of the body Right atrium Which 2 blood vessels bring all this deoxygenated blood? Superior and inferior vena cava Where does the blood go from here? To the right ventricle Which valve controls the flow of blood in this direction? Tricuspid valve Yes Is this valve supported by chordae tendanae? What are chordae tendanae, exactly? Chords of tendon that anchor valves the walls of the ventricle Which chamber of the heart pumps blood to the lungs? Right ventricle Which blood vessel carries blood to the lungs? Pulmonary artery Does it carry oxygenated or deoxygenated blood? Deoxygenated What are the 2 phases of the cardiac cycle? Systole and diastole What cardiac events characterize systole? Ventricles contract Blood is pushed up the arteries (pulmonary artery and aorta) SL valves are open; AV valves close Lubb Exerts pressure on the arteries – measured as 120 mm of Hg Name 1 factor that affects systole Exercise Name 1 factor that affects diastole Hardening of the arteries – leading to poor arterial recoil