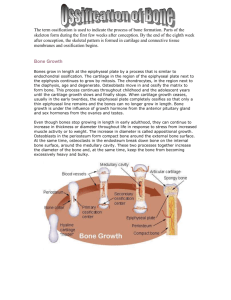
Name: Ch. 7 Review List the five different bone shapes and give an
advertisement
Name:_______________________________ Ch. 7 Review 1. List the five different bone shapes and give an example for each: a. __flat______ _______skull, sternum________ b. __long_____________ ____femur, radius, ulna________ c. __irregular_____________ ____vertebrae______ d. ___short__________ _______carpals________ e. ___sesamoid__________ __________patella______________ 2. Label the following diagram- terms: diaphysis, epiphysis, epiphyseal plate, periosteum, yellow marrow, articulating cartilage, endosteum, spongy bone, compact bone, red marrow USE DIAGRAM IN NOTES 3. List 2 differences and 2 similarities between intramembranous and endochondral ossification. Both start as chondrocytes and both form spongy bone first and then compact bone to the outside portion of bone. Intramembranous forms flat bones and start as undefined cartilage cells; endochondral form all bones besides flat and there is a primary and secondary ossification center. 4. Fill in the chart below: Factor Needed For Deficiciency’s Effect on Bones Vit D Ca absorption Rickets, osteomalacia Vit A Osteoblast/clast activity Effect bone growth and formation Vit C Collagen synthesis Fragile bones Pituitary growth hormone Stimulates epiphyseal growth Pituitary dwarfism, gigantism and acromegaly Thyroid hormone Stimulates cartilage replacement epiphyseal plates Stimulate growth plate/ossification Stimulates bone growth Premature ossification of growth plate Sex hormones Physical stress Stunted growth Hypertrophy/atrophy 5. Using the following diagram explain what is happening in each zone of the epiphyseal plate. Zone 1 Zone 1- Resting cells, anchor plate to bone Zone 2 Zone 3 Zone 2- chondorcytes go through rapid replication leading to growth Zone 4 Zone 3- cells enlarge and start to accumulate Ca+ Zone 4-chondrocytes die and osteoblasts begin to lay down bone 6. Explain the 4 steps of fracture repair and what is occurring at each step. a. Hematoma forms when blood vessels are ruptured by fracture b. Fibrocartilagenous callus forms when new blood vessels infiltrate the area c. Bony callus forms as chondrocytes die and are replaced by osteocytes d. Osteoclasts remodel bone to the original shape 7. Fill in the chart below: Vertebrae Number Unique Characteristics Cervical 7 Small body, bifid spinous process, transverse foramina Thoracic 12 Rib facet, larger body, spinous process projects inferiorly Lumbar 5 Largest body, spinous process projects posteriorly Atlas 1 Facets for articulation of occipital condyle on skull Axis 1 Has dense which articulate with the atlas to allow for rotation of the skull Sacrum 1 Five fused vertebrae, sacral foramen, sacral canal, sacral haitus 8. List the two primary and two secondary curves of the spine: a. __thoracic and pelvic_________ b. __cervical and lumbar_______________ 9. Define the following terms: Foramen- opening in bone Meatus- tubelike opening Sinus- empty air filled space Condyle-rounded process for articulation with a bone Head- enlargement at the end of bone Facet- flat surface where bones articulate Tuberosity-knoblike process Spine-thorn like ridge or projection Trochanter-large projection or process Crest-ridge like projection Process-prominent projection Suture-interlocking lines where bones meet 10. Distinguish between lordosis, kyphosis and scoliosis. Lordosis- exaggerated lumbar curvature Scoliosis- exaggerated lateral curvature of the spine Kyphosis- exaggerated thoracic curvature (hunchback) 11. Explain the homeostatic process bones go through when there is an increased Ca+ content in blood and when there is a decreased Ca+ content in blood. Be sure to explain the relationship between osteoblasts and osteoclasts in this process. Increase Ca in blood Decrease Ca in blood