Lesson 9 – Project Human Resource Management
advertisement

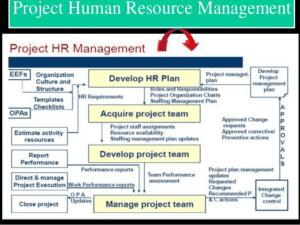
MGT 30725 PROJECT MANAGEMENT LESSON 9: PROJECT HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Conducted By: Dr. Madhu Fernando, PMP, DBA, MEng. 1 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Human Resource Management in Project involved planning for human resources in project, acquiring project team, develop and manage them. First process here, Develop Human Resource Plan, describes the human resource planning process. It describes how people should be allocated the project and release them. This process also involve preparing resource calendar, and maintaining resource pool. Most of these activities can be done through the PMO. WHAT GOES IN THE HUMAN RESOURCE PLAN Roles and Responsibilities : describing, Role, Responsibility, Authority and expected Competency Project Organisational charts and reporting relationships Staffing Management Plan : this is a part of the HRM Plan. It usually includes the following details: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Staff acquisition: instruction on how to acquire project team members, cost distributions among projects and cost centers, where they will be located, etc. Resource Calendars Staff release plans Training needs Recognition and rewards Compliance Safety policies and procedures HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT – EXECUTION PROCESSES Project Human Resource Management involve getting the most use of the people in the project. Following three execution processes are followed to achieve this. • Acquire project team • Develop project team • Manage project team ACQUIRE PROJECT TEAM – PROCESS SUMMARY Tools and Techniques: Pre-assignment Negotiation Acquisition Virtual teams DEVELOP PROJECT TEAM – PROCESS SUMMARY Tools and Techniques: Interpersonal skills Training Team-building activities Ground rules Co-location Recognition and rewards MANAGE PROJECT TEAM – PROCESS SUMMARY Tools and Techniques: Observation and conversation Project performance appraisals Conflict management Issue log Interpersonal skills FOUR STAGES OF TEAM DEVELOPMENT Forming - at the beginning of the project where team meets and learn about the project and each other. Work independently, not as a team Storming – while they work on the project, they will have different ideas, ways of working, creating a destructive environment Norming – Project team begin to work together and adjust work habits and behaviors that support the team. This is where the team begins to trust each other Performing – Team work together as a well-organized unit and work through issues effectively. Moving from independence to interdependence. Adjourning – Team completes the work and moves on from the project. MOTIVATING THE TEAM - THEORIES Part of the project manager’s role is knowing how to motivate the project team. Some of the motivational theories: Theory X (punishment) and Y (trust) Achievement Theory – needs for achievement motivate people Maslow’s hierarchy of needs MASLOW’S HIERARCHY OF NEEDS Self Actualization Doing what one can do best, full realiz potential, self development, creativity Self-esteem, reputation, respect from Esteem recognition and self confidence Love, belonging, togetherness, appr Social group membership Economic security, protection fro Safety harm, disease and violence Food, water, clothing, Physiological shelter, etc. CONFLICT MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES Withdrawal: retreating or withdrawing from a potential disagreement. It’s a win-lose situation. Smoothing: de-emphasizing or avoiding areas of differences and emphasizing areas of agreement. Neither party wins and the problem will not be solved. Compromising: bargaining and searching for solutions that bring some degree of satisfaction to the parties in a dispute. Characterized by a “give and take” attitude. Forcing: exerting one’s viewpoint at the potential expense of another. Often characterized by competitiveness and a win-lose situation. Collaborating / problem solving: Incorporating multiple view points and insights from differing perspectives; leads to consensus and commitment.