Unit Organizer Imperialism and World War I 2015
advertisement

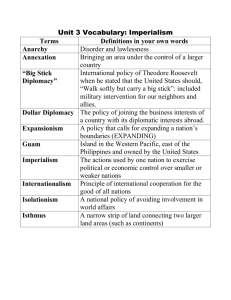
Class: United States History Last Unit: Reform: Populists & Progressives Name: Current Unit: Imperialism & WWI Next Unit: Roaring Twenties The Big Idea: At the turn of the century, the United States began to compete with Europe as an imperial power; but World War I caused the nation to return to isolationism. Date Learning Activities Essential Questions M/11/2 Overview of Unit L—Imperialism American Style Prep work for Soc. Circle Discussion. How and why did the United States take a more active role in world affairs? W/11/4 SC--Spanish American War Remember the Maine What were the causes and effects of the Spanish American War? F/11/6 Philippine Insurrection Cartoon Analysis PSA—For and Against U.S. Annexation of Philippines Was the United States justified in its annexation of the Philippines? PSA--U.S. Entry into WWI R--Wilson v. Zinn Should the United States have entered World War I? Meet in Library: Hearing & Vision Screening Terms Due I--Soldiers of WW Quiz on Terms L—WWI: The Homefront G—Civil Liberties During World War I T/11/10 F/11/13 T/11/17 TH/11/19 L – Wilson & the Treaty of Versailles M/11/23 Unit Review Test—Imperialism & WWI Interactive Notebooks Due! What was it like to be an American soldier during World War I? Did World War I strengthen democracy on the Home Front? Why did the United States senate reject the Treaty of Versailles? What caused the United States to become involved in Imperialism and World War I; and how was America changed by becoming a world power? Terms: Define in Notebook and Know for Quiz Read Chs. 9 - 10, pp. 248-315 People Places Events Ideas Alfred T. Mahan 251 Liliuokalani 254 William Randolph Hearst 257 Emilio Aguinaldo 259, 263-4 Theodore Roosevelt 260, 269-72 Pancho Villa 274 Woodrow Wilson 287-291, 306-9 Doughboys 302 John J. Pershing 302 Irreconcilables 308 Reservationists 308 Seward’s Icebox 252 Philippines 259 Panama Canal 270 Remember the Maine! 258 Open Door Policy 266 Platt Amendment 269 Lusitania 288-9 Zimmerman Note 291 Selective Service Act 292 Sedition Act 296 Great Migration 298 Schenck v. United States 300 Treaty of Versailles Commodities 251 Social Darwinism 252 Jingoism 257 Big Stick Diplomacy 269 Roosevelt Corollary 271 Dollar Diplomacy 273 Fourteen Points 305-6, 310 Over There Syndrome * Objectives: Students will… 1. Explain the ideals of American Imperialism including the influence of missionaries, politicians, naval expansionists, economic competition, and racism. 2. Identify the events which led to and the effects of the Spanish American War including the debate between imperialists and antiimperialists on the issues of Cuban independence, and annexation of the Philippines. 3. Identify the U.S. foreign policy in Latin America and the Far East including the Roosevelt Corollary, Open Door Policy, Big Stick Diplomacy (Panama Canal), Dollar Diplomacy, and Moral Diplomacy. Compare these earlier policies with U.S. relations with Latin America from 1932-2000. 4. Analyze the events which led to American involvement in World War I including American mobilization and support for the war. 5. Evaluate the impact of World War I at Home. 6. Compare the items in Wilson’s Fourteen Points with the provisions of the Treaty of Versailles and explain why the U.S. chose not to ratify the Treaty of Versailles. *Definition provided by Ms. Garvey; G=Glossary, L=Lecture, R=Reading, I=Internet, BB=Bring Book, SC=Socratic Circle, PSA= Primary Source Analysis