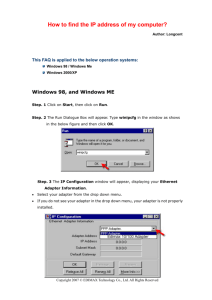
Type of Submission
advertisement

Type of Submission : Article
Title
: Configuring SI B2B JMS 1.1 Async Receive Adapter with WSMQ queue.
Keywords
: Sterling Integrator, JMS 1.1 Async Receive Adapter, WSMQ queue,
Connection Factories, Destinations
Author
: Swathi BN
Job Title
: Software Developer, IBM B2B Sterling Integrator Group
Email
: swathi_kumar@in.ibm.com
Company
: IBM
Abstract
: This article aims at providing detailed steps along with screen shots in
Configuring SI B2B JMS 1.1 Async Receive Adapter to listen to a queue
configured on WSMQ server.
This article also outlines the probable issues that can occur in starting
up the adapter and resolution to overcome them.
Reviewer
: Vincent Tkac, Sterling B2Bi Software Architect
vtkac@us.ibm.com
NOTE: - In writing this article, all the configurations and tests were carried out on 5020402 version of
SI and 7.5 version of WSMQ server.
Configurations at the WSMQ server side:1. In the MQ Explorer, right click on the ‘JMS Administered Objects’ menu and select the menu option
‘Add Initial Context’.
2. Upon opening of the ‘Add Initial Context’ wizard, select the desired JNDI namespace location.
In this example, File System is chosen as the JNDI namespace location.
Note down the JNDI Service Provider’s Factory class which is
‘com.sun.jndi.fscontext.RefFSContextFactory’.
3. Provide the desired Bindings directory location.
4. Navigate to the next screen.
5. Provide the Context nickname of your choice or use the default one that appears on the screen.
6. Click on ‘Finish’ button to finish adding the initial context.
7. Now expand the newly created initial context object.
8. Right click on ‘Connection Factories’ menu item and this will open the wizard for creating new
connection factory.
9. Specify a name for the connection factory and note down the name.
10. Navigate to next screen and select the type of connection factory and go to the next screen.
In this example connection factory type is set to ‘Connection Factory’.
11. Select ‘MQ Client’ as the transport type and navigate to the next screen.
12. Leave the defaults as is in the next screen and navigate further to the properties screen.
13. In the properties screen, select ‘Connection’ properties and set the ‘Base queue manager’ to the
queue manager to which the adapter needs to connect to.
Change the ‘Connection list’ value to the hostname/IP of the machine where WSMQ server is
installed and provide the port on which the queue manager is running.
14. Then in the Channel properties screen, select one of the channels available with the queue
manager that was mentioned in the previous step.
15. Click on ‘Finish’ button to finish creating the Connection Factory.
16. Now right click on the Destinations menu to create a new JMS destination object.
17. Provide a JMS destination object name and select the desired destination type and navigate to the
next screen. Leave the defaults as in on the next page and navigate further to properties screen.
In this example, destination type is set to ‘Queue’.
18. In the general properties section, select the same queue manager that was used in creating the
connection factory and one of the queues that’s available with the queue manage , to which the
JMS 1.1 Async Receive Adapter should listen to and click on ‘Finish’ button to complete the process
of creating the JMS destination object.
19. Once this is done, just disconnect the created JMS Administered Objects and reconnect so that all
the properties are set and take effect.
20. Note that the bindings file will be present at the Bindings Directory location that was mentioned
while creating the JMS Administered Object.
Configuring the JMS 1.1 Async Receive Adapter on B2B Sterling Integrator:1. Install the required wsmq jars corresponding to the WSMQ server version using the install3rdparty
command.
By default on SI versions 5020300 and higher, the 7.0.1.6 version of MQ libraries are shipped
along with the product.
Since for all the tests in the this document MQ 7.5 version is used, a sample command for
installing the MQ 7.5 version libraries is shown below:Linux
: ./install3rdParty.sh wsmq 7.5 –j <path_to_mq_jars_folder>/*.*
Windows : install3rdParty.cmd wsmq 7.5 –j <path_to_mq_jars_folder>\*.*
Care should be taken to ensure that there are no multiple entries of com.ibm.mq.jar file
corresponding to different MQ versions in the dynamicclasspath.cfg file.
If not, even though the adapter is enabled, it does not pick any message that is present on the
queue.
Simplest way to get rid of this issue is to comment out the entries of com.ibm.mq.jar file in the
dynamicclasspath.cfg.in file that doesn’t correspond to the MQ version which is being used, and
execute setupfiles and restart SI.
This issue is explained in detail at the end of this document.
2. Copy the bindings file from the server machine to any accessible location on to the machine where
the SI server is installed. Note down this location.
3. Login to SI dashboard. Navigate to Deployment->Services->Configuration.
4. Create a new service of type JMS 1.1 Async Receive Adapter.
5. Provide the desired name for this adapter and a description.
6. Select the JNDI connection type in the next screen.
7. In the JMS Connection Params screen, provide the
a. Context Factory value as com.sun.jndi.fscontext.RefFSContextFactory
b. URL value as file:///<bindings_file_loction> on SI installed machine.
c. ConnectionFactory value as the name of the Connection Factories created on WSMQ
server.
d. Receive Destination value to the name of the Destination created on WSMQ server.
e. Connection UserName and Password fields to be filled accordingly to the user/password
value used to create the JMS Administered objects on the WSMQ server.
8. In the Pooling Params screen, select the desired Success Business Process and complete the
adapter configuration by going with default values for other fields or filing the values as required.
This business process gets bootstrapped when a message is received by SI. Essentially it is this
business process that controls what happens with the message after it is received by SI.
NOTE: - Transactions can be enabled in JMS 1.1 Aync Receive Adapter by setting the ‘Is Session
Transacted’ parameter to ‘Yes’ in the Pooling Params screen.
There are two scenarios where these transactions can be useful:
i.
When the bootstrap mode of the BP is async or default: - Before kicking off the BP the
payload is stored in the DB. The transaction will be committed as soon as the persistence
of the message to the DB is successful. If the DB is down, then the session is rolled back
and the message is returned. Failure of bootstrapped BP does not ensure that the
message is returned to the destination.
ii.
When the bootstrap mode of the BP is sync: - The session is committed only if the
bootstrapped BP has successfully finished. Failure in the BP results in returning the
message back to the destination.
The success business process can be configured to execute in three different modes:i.
Default (default) :- Async mode. On receiving a message a Business Process is kicked off in
a separate thread. This ensures that the adapter is free to receive another message
without waiting for the business process to finish. Using transactions here ensures that if
system fails to persist the message then it is returned back to the provider. If the business
process fails, then the message is NOT returned back.
ii.
FIFO - First In First Out (FIFO) mode ensures that the bootstrapped business process runs
in FIFO mode. It can be considered as an async mode that guarantees the ordering of
bootstrapped business processes. FIFO mode can be used where order of the
bootstrapped business process should be same as received message. FIFO provides the
ability to kick off a business process in a separate thread, but ensures that the kicked off
business processes follows the correct order. As a result, you should be careful when
selecting your transaction strategy with FIFO.
iii.
Non Queued - Sync mode. On receiving a message a Business Process is kicked off in the
same thread. This ensures that the adapter is blocked; new messages are not received
until the business process has completed. Using transactions here ensures that if the
business process fails, then the message is returned back.
Testing:1. Place a message on the WSMQ server queue to which the adapter is listening to.
2. Verify the success BP getting executed on SI upon receipt of the message by the adapter.
Known issues in starting up the adapter or receiving messages from the queue:1. Even though the SI UI shows that the adapter is enabled, the adapter does not pick any message
that is present on the queue.
In the noapp.log.xxx file, the following error will be logged:Exception in thread "Thread-564"
[2014-05-20 10:34:19.837] ALL 000000000000 GLOBAL_SCOPE java.lang.VerifyError: JVMVRFY012
stack shape inconsistent; class=com/ibm/mq/ese/jmqi/ESEJMQI,
method=spiConnect(Ljava/lang/String;Lcom/ibm/mq/jmqi/system/SpiConnectOptions;Lcom/ibm/m
q/jmqi/MQCNO;Lcom/ibm/mq/jmqi/handles/Phconn;Lcom/ibm/mq/jmqi/handles/Pint;Lcom/ibm/
mq/jmqi/handles/Pint;)V, pc=17
Root cause:This error occurs because of multiple entries for com.ibm.mq.jar for different WSMQ versions in the
dynamicclasspath.cfg file.
Resolution:Remove the jar file entries from the dynamciclasspath.cfg file for the version that does not
correspond to the WSMQ server version.
2. Exception while starting adapter asynchronously.
The following error will be logged in the jms.log.xxx file :ERRORDTL [1400598441006]org.springframework.jms.JmsSecurityException: JMSWMQ2013: The
security authentication was not valid that was supplied for QueueManager 'TEST' with connection
mode 'Client' and host name localhost(1414)'.; nested exception is
com.ibm.msg.client.jms.DetailedJMSSecurityException: JMSWMQ2013: The security authentication
was not valid that was supplied for QueueManager 'TEST' with connection mode 'Client' and host
name localhost(1414)'.
Please check if the supplied username and password are correct on the QueueManager to which
you are connecting.; nested exception is com.ibm.mq.MQException: JMSCMQ0001: WebSphere MQ
call failed with compcode '2' ('MQCC_FAILED') reason '2035' ('MQRC_NOT_AUTHORIZED').
Root Cause:Channel Authentication Records(CHLAUTH) is enabled on the WSMQ queue to which the JMS
adapter is trying to connect to.
Resolution:Disable CHLAUTH for the queue.
Example:C:\Program Files (x86)\IBM\WebSphere MQ\bin > runmqsc <queue_manager_name>
ALTER QMGR CHLAUTH(DISABLED)