Monitoring and Evaluation

Monitoring and Evaluation
Charles Katende PhD.
Director of Monitoring, Evaluation and Research
JHPIEGO
(An affiliate of John Hopkins University)
Session Objective
• To increase participants understanding of the concepts used in designing M&E
Frameworks and Plans
• To build participants competence in designing Program M&E Plans
Expected Results
• At the end of the sessions participants will know about Program frameworks, M&E frameworks and the difference between the two frameworks
• Participants will be able to identify and select appropriate indicators for a program.
• Participants will be able to produce a program monitoring and evaluation framework.
Introduction…
• Write the health problem addressed by a major public health program in your country
• Write at up to three specific objectives of a public health program that addresses the above mentioned health problem.
• Write down two indicators the program mentioned above uses to monitor it progress or performance towards its objectives.
What is Program Monitoring, Evaluation?
Monitoring is the routine process of data collection and measurement of progress toward program objectives.
Evaluation is the use of social research methods to systematically investigate a achievement of a program’s results
Key Questions
• What is the purpose of carrying out M&E
• Who needs, uses M&E Information
• Who carries out M&E?
• How is M&E carried out?
• When should M&E be carried out?
What is the purpose….?
• Improve program implementation
– Data on program progress and implementation
– Improve program management and decision making
• Inform future programming
• Inform stakeholders
– Accountability (donors, beneficiaries)
– Advocacy
Who needs, uses M&E Information?
• Managers
To Improve program implementation…
To Inform and improve future programs
• Donors
• Governments
• Technocrats
Inform stakeholders
• Donors
• Governments
• Communities
• Beneficiaries
Who conducts M&E….?
Program implementer
Stakeholders
Beneficiary
Remember ..
M&E Technical skills
Participatory process
How to carry out M&E…?
Key Features
1.
Program Framework : Analyze and systematically lay out program elements
2.
Identify key elements to monitor and evaluate.
3.
Determine and describe the measures to be used for monitoring and evaluation
4.
Develop M&E Framework and action plans , including data collection and analysis, reporting and dissemination of findings.
Program Framework
What do you know about your program….?
Program Framework
• Systematic lay out of the program elements and path showing what the program plans to:
do ……………..achieve!
Program Framework
• Based on a theoretical, empirical model, or general understanding
Public health Problem
Population, system level factors that cause the public health problem
Action/interventions that can change the factors and ultimately alleviate/eliminate the problem
Results Framework
Improved Health Status
Impact:
Strategic Objective:
Intermediate Result:
Improved (Sustained) Use of Key Health Services and Practices/Behaviors
Increased quality of…
Increased availability/ access to…
Improved social / policy environment…
Strategies: Strategies: Strategies:
Strategies (Sub IR):
Example: Result Framework for a
Family Planning Project
GOAL: REDUCED FERTILITY
SO: Increased FP use and improved FP/RH practices
Increased knowledge of, improved attitudes toward, and acceptance of key services and behavior
Strategies:
Increased quality of FP counseling and services for
Increase availability of educational materials at clinic and community level
•
Community mobilization (using
PRA and PDI) including men
• Implement mass media strategy
• Mobilize opinion leaders at national and local level
Design/ implement supportive supervision
System
• Train service providers
(in-service and preservice in FP counseling and management of side effects
•
Remodel clinic to allow for privacy
•
Design and implement quality improvement program
Increased availability/access to
FP/RH
Strengthen logistics management
• Mobilize private sector providers
•
Mobilize CHWs/CBDs
• Encourage socially marketed pills
Improved social and policy environment for
FP
Advocate for community based distribution of pills
Promote addition of
Depo injections to EPI outreach strategy
Pilot social marketing of pills
Basic Logic Model
INPUTS
Nurses
Lab techs
Govt. funds
GAP funds
Other donor funds
HIV test kits
Counseling protocol
Referral system for prevention &
Tx services
ACTIVITIES
Train nurses & lab techs in VCT
Provide pre-test counseling
Conduct HIV test
Provide post-test counseling to all clients tested
Refer pregnant
HIV+ women to
PMTCT svcs
Refer HIV+ clients to Tx services
OUTPUTS
Nurses & lab techs trained
Clients are counseled for
HIV testing
Clients are tested
Clients receive results and posttest counseling
Pregnant HIV+ women referred to PMTCT svcs
HIV+ clients referred to ARV, support & HBC
IMMEDIATE
OUTCOMES
Quality of VCT increased
Access to VCT increased
Knowledge of
HIV status increased
Knowledge about & access to prevention resources increased
Access to HIV treatment resources increased
26
INTERMEDIATE
OUTCOMES
Risk behaviors decreased
HIV treatment increased
IMPACTS
HIV transmission rates decreased
HIV prevalence decreased
HIV morbidity & mortality decreased
PROJECT DESIGN FRAMEWORK LABELS
Project Design Level
Labels Used By Various Organizations
USAID Others
Level A:
Improvement in Health
Status
Impact Impact Goal
Level B:
Use of
Services
Strategic Objectives Purpose
Level C:
Demand for
Services
Capacity to
Deliver
Services
Level D:
Interventions
Intermediate Results (IR)
Specific Objectives
Startegies (Sub-IR)
Outputs
Activities
Outputs
Activity Clusters
Activities
Inputs
Case 1: To decrease maternal mortality, a 10-year program plan to improve to train midwifes to Delivery and ANC services at health facilities, and to train and deploy CHWs to increase the community’s awareness about, and use of the improved services at the health facilities.
Case 2: To reduce high fertility, a 5-year program plans to work with the Government to change policies in order to allow and promote use of modern family planning methods, train family planning providers to provide better FP services, and to launch public campaigns that promote family planning methods.
Case 3: To reduce HIV infection among adolescents, a five-year program plans to implement income generation activities for the youth, provide and promote universal secondary education, and build adolescent-friendly reproductive health service delivery points.
Exercise
• Identify and state is the Public Health problem implied in the case study.
• What are population level factors will the program target to change in order to alleviate the public health problem
• Prepare a Program Framework for the scase study
Monitoring and Evaluations
Framework
M&E Questions
• Monitoring questions
– What is being done?
– By whom?
– Target population?
– When?
– How much?
– How often?
– Additional outputs?
– Resources used? (Staff, funds, materials, etc.)
M&E Questions
• Evaluation Questions?
– Is the content of the intervention or the activity being delivered as planned?
– Does the content of the intervention or the activity reflect the requisite standards?
– Have the intervention achieved the expected results?
What do we need to answer these questions…?
INDICATORS
…to take measurements.
Indicators: Definition
• Markers that help to measure change by showing progress towards meeting objectives
• Observable, measurable, and agreed upon as valid markers of a less well-defined concept or objective
• Indicators differ from objectives in that they address specific criteria that will be used to judge the success of the project or program.
See comment for examples
Type and Level of Each Indicator
• Type
– Input/Process (Monitoring)
– Outcome / Impact (Evaluation)
• Level
– Global level
– Country level
– Program level
Exercise: Group work
• Use your case study and identify at least two indicators for program monitoring and two indicators for program evaluation.
What Is a Good Indicator?
• Valid : Measures the effect it is supposed to measure
• Reliable: Gives same result if measured in the same way
• Precise: Is operationally defined so people are clear about what they are measuring
• Timely: Can be measured at an interval that is appropriate to the level of change expected
• Comparable: Can be compared across different target groups or project approaches
Criteria for Indicator Selection
• Consistent with project design —measure the desired result
• Useful —contributes to project design, management, and evaluation
• Available
• Affordable
Standard Indicators
Where possible, a project should select standard indicators.
• They have been tested for validity and reliability.
• They allow comparison between projects or sites.
• They tend to be available for SOs and some IRs.
How Many Indicators?
• Choose at least one or two indicators per intermediate result, as well as the SO for evaluation purposes.
• Choose one or two indicators per result for program monitoring.
• Choose indicators that may be able to “cover” more than one element.
• For management, think about basic activities that you need to monitor to judge if you are implementing activities as planned; include indicators that help you make decisions.
Exercise: Group work
Refer to the indicators you selected..
• Were the good indicators ?
• Did you select a minimum number recommended given the type and size of your program?
M&E Framework
Sample M&E Framework
Preventing Post Partum Hemorrhage :
Increase Active Management of the Third Stage of Labor
Result Indicator Definition Data source
Collection
Method
Frequency
Responsible Party
Active
Management of the Third
Stage of labor increased
Proportion of trained clinicians performing
AMTSL to standard
# of trained midwives performin g all steps of AMTSL on all patients/
AMTSL observation checklist
Clinical observation
Annual Zambia
JHPIEGO staff
See comment for examples
M&E Plan
• The plan is a managerial tool that specifies the schedule, resources, responsibilities, for your M&E activities (data collection, data quality control, reporting, dissemination and use of data)
• Note:
– The plan should specify the time points when evaluations will be carried out, for example: Midterm, and End term.
– Outcome/Impact evaluation is reserved for large longer term programs that can make impact at public health status level.
– Your plan should include activities to monitor and evaluate the implementation, as planned, of the M&E plan.
Strategic Planning for M&E: Setting Realistic
Expectations
Monitoring and Evaluation Pipeline
Number of
Projects
All
Input/Output
Monitoring
Most
Process
Evaluation
Some
Outcome
Monitoring/
Evaluation
Few *
Impact Monitoring/
Evaluation
* Supplemented with impact indicators from surveillance data.
Levels of Monitoring & Evaluation Effort
Adaptation of Rehle/Rugg M&E Pipeline Model, FHI 2001
Source: CDC. Global AIDS program monitoring and evaluation (M&E) field guide
Question
If funding for your case study program was cut off and the program closed in two years.
What changes would you make to you M&E
Plan?
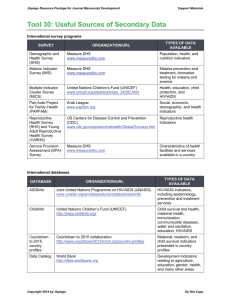
Sources of Information
• http://www.cpc.unc.edu/measure
• http://www.unaids.org/DocOrder/OrderFor m.aspx
• http://www.fhi.org/en/Publications/index.ht
m