Program Evaluation
advertisement

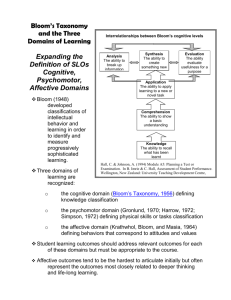
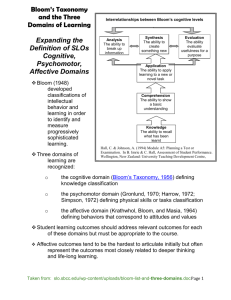
Setting Goals and Objectives CHSC 433 Module 2/Chapter 6 L. Michele Issel, PhD UIC School of Public Health Learning Objectives What you ought to be able to do by the end of this module: 1. 2. 3. 4. Develop a measurable objective. Determine an appropriate target value for the outcome. Distinguish between process and outcome objectives. Explain the connection among program theory, program objectives, and the evaluation plan. Outline of this ppt Writing Goals and Objectives Process versus Effect Objectives Setting Targets Goals and Objectives Differences between Goal and Objective Setting Objective targets Goals and Objectives Goals are broad, not measurable, are related to the distal outcome and the conceptual hypothesis. Objectives are specific, measurable. • Process objectives are related to the organizational and service utilization plan. • Outcome objectives are related to the action hypotheses and impact theory. Comprehensive Program Theory in Two Phases Program Theory Planning and Thinking Foundation Program Delivery and Implementation Reality Process Theory Impact Theory Organizational Plan Service Utilization Plan (Inputs, capacity) (Activities, Interventions) Outputs (Products) Process Objectives Initial OUTCOMES (Impact) Longer term OUTCOMES Impact and Outcome Objectives Process - Efect Questions Who does it with or to clients How many clients receive the program How often do it with or for clients How much intervention clients get What do with or for clients What is different about clients because of the program How much or great is the difference clients experience How soon and long do clients experience the benefits Set Target Numbers for Process Objectives Based on past experience with program Based on budget constraints Based on mandates, requirements For critical elements of organizational plan For critical elements of the service utilization plan Attention to Process Process Evaluation is important Process Evaluation is distinct from Impact or Outcome Evaluation Process Evaluation is more like QI, TQM, CQI, QA combined Set Target Numbers for Effect Objectives Based on past experience with program Based on published norms Based on community norms Based on local and national trends data Based on pie-in-the-sky hopes and estimates Based on synthetic estimates using epi data Making Objectives Measurable State a target number, such as a %, rate, number, a score. Each objective is related to a distinct, unique action or outcome; contains only one idea. Replace “increase” with “will be” Formula for Objectives Statement written in the following format is an ideally stated objective: By when, Who Will do What by How much Examples of Effect Objectives By 9/02, 80% of clients will achieve a [score on] ADL level of independence. • Indicator of physical impact is ADL level By 10/03, 80% of clients not have serious depression for at least six months after treatment. • Indicator of psychological impact is depression Setting Targets Review the detailed information in the textbook on setting targets, especially for effect objectives Synthetic Estimates Apply known rates to target population • Basically just doing the math Less accurate with smaller target population From Objectives to Data Outcome Objective #1 Indicator A Indicator B Indicator C Data Collection Method Data Collection Method Data Collection Method Data Source Data Source Data Source Create a table based on the above connections. Can add a time line for data collection. Measure Program Impact Across the Pyramid Direct Health Care Services ____________________ Enabling Services ___________________________ Population-Based Services ___________________________________ Infrastructure Services For Educational Objectives When you write curriculum for health program, here are tips to writing student learning objectives (also good for your practicum objective writing) Learning objectives Learning domains Model of Relationships Pedagogy (Content, Learning Strategies, Activities) Student Learning Objectives Test Achievement of Learning Objectives Student Learning Generic Learning Objective By the end of this course, the student will be able to: • [Use a cognition verb] • [Use an affective verb] • [Use a psychomotor verb] Learning Objectives Express: Student outcomes Results from the course Changes in the students NOT What the student does (process) What the faculty does (process) Cognition Levels (simple to complex) Knowledge Comprehension Application Analysis Synthesis Evaluation Affective Levels (Simple to Complex) Receiving phenomenon Reacting to phenomenon Valuing Organizing values into priorities Internalizing values Psychomotor Levels (simple to complex) Perception Readiness to act Guided response Mechanism Complex overt response Adaptation Origination Learning Objectives: Find the 2 Good and 1 Bad Example By the end of this course, students will Be able to write a paper on the relative importance of social factors contributing to health disparities (cognition) Be able to conduct multivariate statistical analysis on secondary data sets (psychomotor) Engage in advocacy activities designed to address health disparities (affect) Resources for Writing Objectives Right click on hyperlink, then click on “Open in new window” Overview of cognitive, affective and psychomotor domains: http://www.nwlink.com/~donclark/hrd/bloom.html Bloom’s taxonomy along with possible verbs for use in testing: http://www.kcmetro.cc.mo.us/longview/ctac/blooms.htm http://www.coun.uvic.ca/learn/program/hndouts/bloom.ht ml http://www.kcmetro.cc.mo.us/longview/ctac/blooms.htm http://www.teachers.ash.org.au/researchskills/dalton.htm All together now… From Objectives to Data to Evidence of Program Value