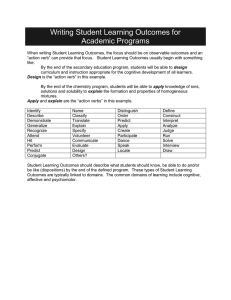
verbs for the affective and psychomotor domains
advertisement
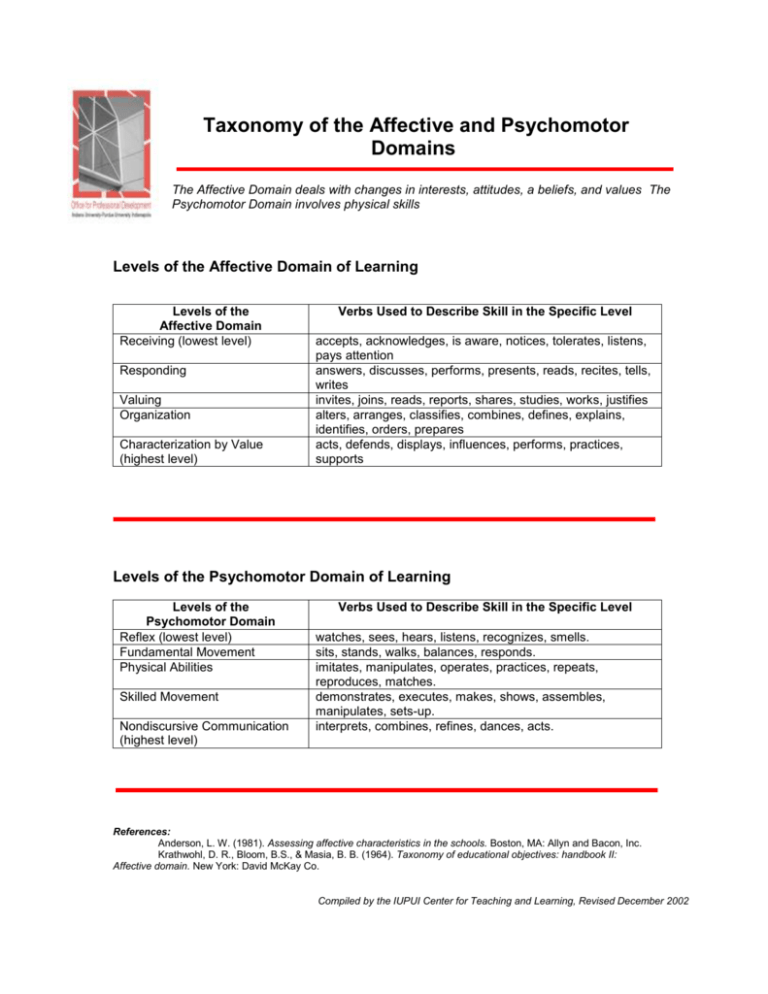
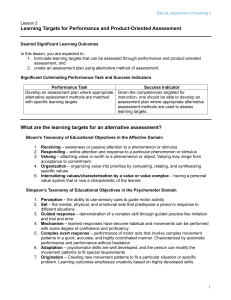
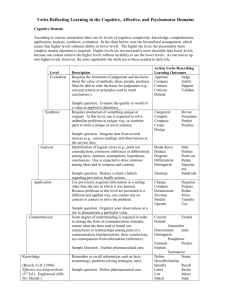
Taxonomy of the Affective and Psychomotor Domains The Affective Domain deals with changes in interests, attitudes, a beliefs, and values The Psychomotor Domain involves physical skills Levels of the Affective Domain of Learning Levels of the Affective Domain Receiving (lowest level) Responding Valuing Organization Characterization by Value (highest level) Verbs Used to Describe Skill in the Specific Level accepts, acknowledges, is aware, notices, tolerates, listens, pays attention answers, discusses, performs, presents, reads, recites, tells, writes invites, joins, reads, reports, shares, studies, works, justifies alters, arranges, classifies, combines, defines, explains, identifies, orders, prepares acts, defends, displays, influences, performs, practices, supports Levels of the Psychomotor Domain of Learning Levels of the Psychomotor Domain Reflex (lowest level) Fundamental Movement Physical Abilities Skilled Movement Nondiscursive Communication (highest level) Verbs Used to Describe Skill in the Specific Level watches, sees, hears, listens, recognizes, smells. sits, stands, walks, balances, responds. imitates, manipulates, operates, practices, repeats, reproduces, matches. demonstrates, executes, makes, shows, assembles, manipulates, sets-up. interprets, combines, refines, dances, acts. References: Anderson, L. W. (1981). Assessing affective characteristics in the schools. Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon, Inc. Krathwohl, D. R., Bloom, B.S., & Masia, B. B. (1964). Taxonomy of educational objectives: handbook II: Affective domain. New York: David McKay Co. Compiled by the IUPUI Center for Teaching and Learning, Revised December 2002