Development of Instructional Objectives
advertisement

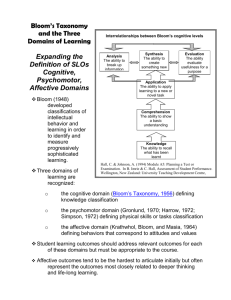
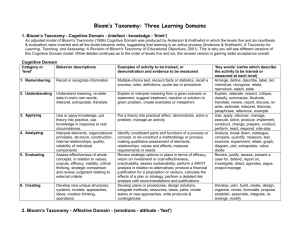
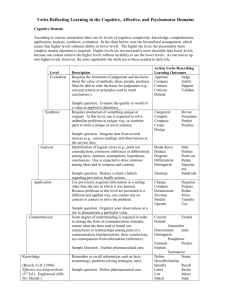
Behavioral Objective After a 5 minute therapy session, the client will be able to completely eliminate her presenting problem. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ow0lr63y4Mw ED 880.629.9B Evidence-Based Teaching Session 3 Anne Belcher, Ph.D. Linda Adamson, Ed.D. Objectives Compare educational taxonomies for the cognitive, affective and psychomotor domains. Generate measureable objectives in each of the domains. Align measureable objectives with potential evidence of accomplishment. What is an Objective? An outcome statement that captures specifically what knowledge, skills and attitudes the learner(s) should be able to exhibit following instruction What is the Value of Objectives to the Teacher? What is the Value of Objectives? From the teacher perspective, they help us to keep our teaching: On target Learner-centered Focused on content/behaviors Organized with regard to methods and materials What is the Value of Objectives to the Learner? . What is the Value of Objectives? From the learner’s perspective: Knowing what is expected of them/what they should learn Understanding what KAS they should have at the end of the experience Guiding them in organizing their reading/studying Levels of Objectives Program Course – Where did your Teaching Goal Inventory results fit in terms of types of objectives? Class/module/clinical Key Components of an Objective Should be SMART Specific Measurable/observable Attainable for target audience within scheduled time and specified conditions Relevant and results-oriented Targeted to the learner and to the desired level of learning Teacher & Educational Development, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, 2005 An Overarching Objective for Your Evidence-Based Teaching project Think and write… Then pair Pairs share with the group (Strategy: Think – Pair – Share; variation: Think – Pair – Square – Share) Educational Taxonomies A taxonomy is a system that describes, identifies, and classifies groups Organized by levels of complexity In education, three domains of learning are classified: Cognitive Psychomotor Affective Value of Taxonomies? . Value of Taxonomies Useful for writing objectives and developing test items/evaluations Ensure that important categories of learning are not overlooked Cognitive Domain Old Version Bloom et. al. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives: The classification of educational goals. Handbook I: Cognitive domain. NY: David McKay New Version Anderson et. al. (2001). A taxonomy learning, teaching and assessing: A Revision of Bloom’s taxonomy of Educational objectives. NY: Longman Explore Further! http://www4.uwsp.edu/education/lwilson/ curric/newtaxonomy.htm Bloom’s Taxonomy: Learning in Action http://community.thinkfinity.or g/thread/3591 Psychomotor Domain Harrow’s categories: Involuntary movement—reaction Fundamental movements—basic movements Perception—response to stimuli Physical abilities—stamina that must be developed for further development Skilled movements—advanced learned movements No discursive communication—effective body language Harrow, A.J. (1972). A taxonomy of the psychomotor domain: A guide for developing behavioral objectives. NY: David McKay Psychomotor Domain Simpson’s categories Perception Set Guided responses Mechanism Complex overt response Adaptation Origination Simpson, E.J. (1972). The classification of educational objectives in the psychomotor domain. In M.T. Rainier, (Ed). Contributions of behavioral science in instructional technology: The psychomotor domain. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Gryphon Press, Prentice Hall. Psychomotor Domain Dave’s levels of psychomotor learning Imitation Manipulation Precision Articulation Naturalization Dave, r. (1070). Psychomotor levels in developing and writing objectives. Tucson, AZ: Educational Innovators Press. Psychomotor Objective: What is the desired end-state? How would you evaluate? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vYwypSLiaTU Challenges of Writing Psychomotor Objectives Affective Domain Describes the way learners react emotionally; typically targets awareness and growth in attitudes, values, beliefs and feelings Receiving Responding Valuing Organizing Characterizing Motivational Interviewing http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dm-rJJPCuTE Identify affective objective(s) How would you evaluate level of success? Challenges of Writing Affective Objectives Universal Design for Learning A way of thinking about the design of learning in order to maximize the success of all learners 3 components of learning are addressed: The WHAT: what is the new content, what are varied ways I can experience it, and how do I fit it into my existing schema? The HOW: what are varied ways I can interact with the new content and put it to use? The WHY: why does this new content matter to me??? http://cast.org/udl/index.html UDL … Taking It Further! http://www.cast.org/pd/institute/june8.html http://www.cast.org/research/index.html Revisit the Beginning Re-examine your own overarching EBT objective. Talking with a partner: IDENTIFY… your learners and the domain(s) in which your objective fits. some of the multiple means of representing the new content that you might be able to use some of the multiple means of application and expression that might be appropriate some of the multiple means of engagement available to you for these learners Class Feedback On your post-it, please respond to the following: Share at least one thing you learned tonight that you did not already know. Offer one suggestion that would have improved your learning in this session. Next Steps ON-LINE SESSION!! (Enjoy Valentine’s Day!)