Protein kinases : Role in cell signaling & implication in human
advertisement

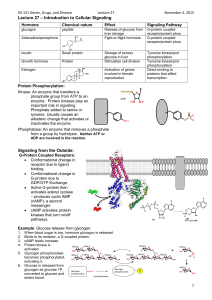
Protein kinases : Role in cell signaling & implication in human pathologies Jayanti Tokas1, Rubina Begum1, Shalini Jain2 and Hariom Yadav2 1Department 2 of Biotechnology, JMIT, Radaur NIDDK, National Institute of Health, Bethesda,MD20892, USA Email: yadavhariom@gmail.com Protein Kinase 30% of all proteins may be modified 518 protein kinase genes=human kinome space 20% of all eukaryotic genes(human genome project) Approx 30=tumor suppressor 218 genes=human diseases Approx 100 dominant oncogenes Kinases Protein phosphorylation cell signaling Reversible protein phosphorylation as a biological regulatory mechanism Edmond H. Fischer and Edwin G. Krebs (1992 Nobel Prize for Physiology and Medicine). Post-translational modification in the cell • Cell growth/proliferation • Differentiation ‘signal’ • Viability/survival • Homeostasis • Effector function (e.g. cytotoxicity, cytokine production) • Cell death Signal Transduction and Kinase Pathways Adaptor proteins Nucleus MAP kinase, • Transcription factors – Bind consensus sequence on promoter – May form complexes – May itself be transcribed following cellular activation Effector enzymes Classification On the basis of amino acid : Tyrosine kinases, Receptor (EGFR,FGFR,PDGFR) non receptor (JAK,src,Abl,MAPK) Serine threonine (PKC, Plk,Rho Kinases) Tyrosine kinase structure function: Serine threonine kinases Related pathologies Check points Related pathology Check points Structure Bioblar structure N and c N-beta sheets C-alpha helix ATP bind-cleft at intetrsection How they function: Mechanisms of Activation of Normal TKs. May oligomerise Differentiation Motility Proliferation survival Control Autoinhihibitory transmembrane interactions cytoplasmic juxtamembrane region further inhibits the enzyme by interacting with the kinase domain Autophosphorylation---. reorient critical amino acid residues increasing catalytic activity inhibitor proteins and lipids IF CONTROL LOST Loss of function Gain of function Mechanisms of TK Dysregulation oPDGF EGF VEGF FGF KL oPDGF R EGFR HER2 c-KIT FGFR3 Overexpression of receptor or ligand EGFR Superfamily with 4 receptors C-ERBB C-ERBB2 C-ERBB3 C-ERBB4 Cell proliferation Inhibition of apoptosis Angiogenesis Cell motility metastasis Carcinogenesis: colorectal cancer, lung cancer(enhanced responsiveness),glioblastoma multiforme(constitutive active) Dysregulation Cell proliferation inh of apoptosis angiogenesis metastasis Over expressed & mutated Deletions(exon 2-7:alternative splicing) or point mutations(Ile654Val) Check points FLT3 Mutation in receptor tyrosine kinase causing constitutive expression C-KIT PDGFR EGFR HER2 PDGFR Tyrosine kinase fibroblasts,smooth muscles of lung and airways Mesenchymal cell migration and proliferation Angiogenesis and blood vessel maintainance Dysfunction: Abnormal vasulature irregular diameter leakiness • Glioblastoma • Atherosclerosis • Pathological conditions:del(4q12) ; t(4;22) • Adenocarcinoma • Breast • Colon • Prostate • Stomach FGFR(1-4) Cell growth Differentiation Chemotaxis Angiogenesis Cell survival SKELETAL SYSTEM Dysfunction 60 mutations FGFR2 craniosynostosis syndrom(premature ossification of skull) Pfeiffer syndrome(additional fingers FGFR3 achondroplasia(dwarfism) Gly380Arg Gly375Cys Carcinogenesis:prostate, cervical ,bladder, colorectal cancer Check points Fusion of TK to partner protein ABL PDGFR FGFR1 FGFR3 JAK2 Bcr-Abl C-Abl Non receptor tyrosine kinase Role: Regulation of cell cycle,cellular response to genotoxic stress Apoptosis neuronal development Regulation :actin binding PI3 binding C-Bcr localised in cytoplasm during mitosis(role in cell cycle regulation) Bcr-Abl t(9:22) Related to CML(chronic myeloid leukemia) m e c h a n i s m prevent apoptosis even in the absence of growth factors Mitogenic signaling Altered adhesion to matrix TARGET-imatinim mesylate Check points A serine threonine kinase:PKC Response to •Growth factors •Hormones •Drugs 11 related kinases Unregulated in GIST Diagnostic marker therapeutic target Therapeutic targets ATP binding domain inhibitors Erbstatin Targeting Receptor Monoclonal antibodies • Herceptin, licensed for Her 2 receptor-positive • Breast cancer Small molecular inhibitors Various protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors TYRosine PHOSphorylation INhibitors tyrophosphins Competitive with substrate(eg.Itaconic acid) Competitive with ATP(Quinolines)(main thrust) ATP binding fold more specific A LOOK AHEAD 1. How many other kinase targets opened for exploration? 2. Majority of kinases remain largely uncharacterized. Current challenges and future directions THANK YOU