File
advertisement

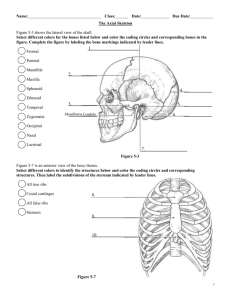
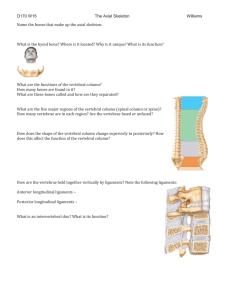
Axial Skeleton Vertebral Column/ Spine supports the skull /transfers weight • Structure: • 26 irregular bones • (33 pre-birth) • • • • • 7 cervical 12 thoracic 5 lumbar 1 sacrum 1coccyx • Intervertebral foramenBetween each vertebrae For spinal nerves Intervertebral discsCushion/absorbs shock Provides flexibility Hardens with age Herniated Disc • When the annulus wall weakens, the disc will press against the spinal nerve = PAIN curvatures • • • • • • Primary curvatureWhat you are born with Posterior = Convex Secondary curvatureWhat develops Cervical becomesposterior concave when baby lifts head • Lumbar becomes posterior concave when baby walks Abnormal Curvatures • Scoliosis- abnormal side to side • Kyphosis-Exaggerated posterior curvature of thoracic vertebraeosteoporosis • Lordosis-exaggerated posterior curve of lumbar • Pregnancy, pot belly Typical Vertebrae • Body- weight bearing anterior • Vertebral Arch- join the laminae and pedicles posterior • Vertebral Foramencanal that spinal cord passes • Transverse Process- 2 lateral projections from the arch Typical vertebrae • Spinal Processsingle projection from posterior arch • Superior and Inferior Articular Processes- paired projections lateral to the foramen allows the vertebrae to join each other Cervical Vertebrae - neck C1 - ATLAS • No body • receives the occipital condyles • Allows the “yes” nod Cervical vertebrae C-2 - AXIS • Has an upright pivot called dens or odontoid process • Allows rotation“no” Cervical vertebrae C-3 to C- 7 • Small • Short bifid spinous process • Transverse processes contain foramen for arteries Thoracic Vertebrae T1 – T12 • Larger heart shaped body • Long spinous process-points downward • 2 costal facets on either side for ribs Thoracic Vertebrae Lumbar vertebrae L1 – L5 • Massive body • Hatchet like spinous process • Takes most stress Sacrum 5 fused vertebrae • Posterior Pelvis • wing like • Lateral articulation with hip • Medial Sacral Crest- posterior fused spinous processes Sacrum • Sacral foraminalateral to crest • Sacral Canaldown the center • Sacral Hiatusinferior opening Coccyx 3-5 fused vertebrae • tailbone Bony Thorax • Ribs • Sternum • Thoracic vertebrae Sternum • Manubrium- jugular notch • Body- sternal angle (3rd rib) • Xiphoid Processsmall point at bottom Xiphoid • The Xiphoid process can cause damage because of the location of the liver Costal Cartilage • The costal cartilage attaches the ribs to the sternumhyaline cartilage Ribs- 12 pairs • True ribs-are connected to the sternumvertebrosternal # 1-7 • Posterior – attached to thoracic vertebrae 1-7 • Anterior- attached to sternum • False Ribs- are not connected directly to the sternum • Ribs 8-10 are called false • Ribs 8-10 are called vertebrochondral • Posterior- attaches to vertebrae • Anterior- attaches to cartilage • Floating Ribs- ribs 11 & 12 • They are not connected in the anterior, only the posterior • Posterior- vertebrae • Anterior- nothing Ribs- flat bones • Head- meets with the body of the thoracic vertebrae • Neck- meets with the transverse process of the thoracic vertebrae • Shaft- angles downward