Iran MUN country profile
advertisement

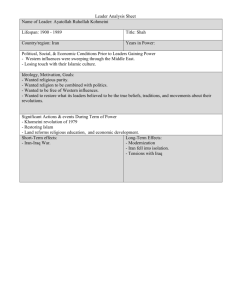
Country: The Islamic Republic Of Iran Event: Pearl-MUN Students: Abdulaziz AL Mutawa (ambassador- Environment) Abdulaziz AL Bahar (ECOSOC) Ahmed AL Mughni (Human rights) Reem AL Thekair (Disarmament) Yvette Ohanion ( SOCIAL) Country Profile Political Structure: ( Ahmed) Newly elected president Mahmoud Ahmadinejad, is a member of the “Islamic Society of Engineers”, (although he has a high rank in the Alliance of Builders of Islamic Iran). Ahmadnejad is seen as one of the top guns in the ISE alliance. Ahmadinejad ran for presidency with various views, those views by Ahmadinejad sems to attract both religious and the poverty stricken Iranians. The USA accused Ahmadinejad of being one of the leaders from the infamous hostage crisis in 1979. The responses from the Iranian government were typical denial. Iran is an Islamic Republic, with limited democracy, further accusations from the USA claiming that their type of Islamic extremism attracts terrorism. A supreme leader (Rahbar) is placed to give out “the general policies of Iran”, in other word would be the presidents boss. The supreme leader would be the only one to be able to declare ware and have the power to appoint and dismiss leaders. The president comes after the Rahbar. In total of eight vice presidents serve the president. He is the highest official in Iran and has the duty for appointing the Constitution and bowing a head boss. He is elected by the Council of Ministers, then chosen by the civilians. Then comes the Irani parliament consists that are elected by the secret ballot process from the Council of Guardians. The supreme leader Ali Khamenei, has total control of Mr. Ahmadnejad, which makes Iran a single-party state; which is very similar to communism. Iran’s president comes out as a hardliner, but he plans to appoint a government of “moderation”. Iran's governmental system is headed by a religious leader, who is basically the prime controller of power in the state. The religious leader has more power than any other political position under him, including the President. Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini, accredited to founding the Islamic Republic of Iran, believed that the conservative ideas of Shia theological schools of thought should be allowed to have evolved interpretations. He also believed that the prime cleric, or Supreme Leader, should act based on “divinely inspired guidance”. Khomeini was mainly responsible for Iran’s isolation from the Western and Eastern Blocs of the world at the time, because he banned all the Western influences such as cinema and literature, and believed in the establishment of an Islamic Nation in which all the Islamic countries would unite so as not to ally with the East or the West. He was conservative and believed the West spread corrupted ideas that influence youths. Khomeini had promised political and democratic reforms, and when they did not come he stated that Iran did not become a fully Islamic nation, and when it did then democracy would come. He believed anything that contradicted the Islamic way of thinking would be automatically considered against democracy, and that democracy would come after full adherence to Islam. The decisions that the Supreme Leader makes are final, and he has the final say in all the matters that concern the state. He alone has the power to declare war. He also appoints the Council of Guardians, which consists of 6 theological and 6 Judiciary men. They have the power to pass or fail legislative bills. This leader makes his decisions supposedly based on Islamic Shari’a law, and cannot be argued with because of that basis. The process of choosing this leader goes through 83 religious and well-educated men. The law of Islam has a salient and strong grasp over the acts that the legislative branch performs. Religion is significantly important in Iran, as it governs all the individuals that exist in this community. It is the ``long arm of the law'' in a religious sense. Geography: (Abdulaziz AL Mutawa) The Islamic Republic of Iran is consisted of rocky heavy mountains and long ranged plateaus; although oil exists the country still faces some poverty issues plus pollution. The country of Iran is located in the Middle East, bordering on the Gulf of Oman, the Persian Gulf ( also known as the Arabian Gulf) , and the Caspian Sea, between Iraq and Pakistan. Iran has access to different landscapes from lakes to gulfs and from a bit of river to straits. With these different landscapes, the Iranian people have different cultures and values. Iran consists of rough, mountainous rims surrounding high interior basins. Iran holds the rank sixteenth in size among the countries of the world. Iran's capital is Tehran and has a population of over 53,533,000 people. Iran is the second largest country in the Middle East, after Saudi Arabia. It extends over a total area of 1,648,000 sq. km (636,300 sq. mile). The country is roughly triangular in shape, with its longest side extending in a slightly outward are for 2,500 km (1,600 mile) from the border with Turkey in the northwest to the border with Pakistan in the southeast. The third point of the triangle lies in the northeast, about halfway along Iran's border with Turkmenistan. Iran's greatest extent from north to south is 1,600 km (1,000 mile) and from east to west is 1,700 km (1,100 mile). Iran is deeply affected with the mountainous land it has, it makes it hard for law enforcement to capture wanted people however we do recognize the Damavand Mountain is a very important tourist attraction. Plateaus are widely spread around the land but mostly are built upon for housing needs. Iranians are all Muslim people; however due to the very rigid terrain people over in different towns tend to have different variations of a culture and other such issues. The neighbors of Iran were very loyal at some point in the last centauries; however we are more than happy to announce that Allah protected us by giving us this terrain which protected us from the past invaders. Iran has existed since the first civilizations started and still stands today, strongly in the affirmative perspective. Iran has been around more than the Iraqi states and Iran was invaded by Iraq in the 1980's but thank Allah the mountains protected us. Natural Resources: (Abdulaziz AL Mutawa) Oil and gas are from the most important natural resources found in Iran. Natural gas and coal, chromium, copper, iron ore, lead, manganese, and zinc, sulfur are other resources found in Iran. The agricultural products are wheat, rice, other grains, sugar beets, fruits, nuts p cotton; dairy products, wool; caviar. They can not feed their own people because their imports are more than their exports by approximately 1.6 billion dollars. Electricity production is fossil fuel: 92% hydro: 7 %. Iran is sadly not interdependent today, due to heavy political pressure from nations making it hard to acquire goods from all around the world. The Islamic Republic of Iran reserves the complete rights just as any other nation does to own and develop nuclear power plants. Iran wishes to widen its perspective on power acquiring plans for the future. That may be cost efficient. Although some energy experts do not agree with Iran acquiring such nuclear technology and because Iran violated some IAEA rules does not mean we did not abide by the rules set by the organization. We simply do not want pathetic westerners to enter our sacred land and degrade its existence. The Islamic republic of Iran did clarify once that it has no real need for nuclear energy resources; however the need for upgrading our technology in building up the nation is urging us to upgrade our technological standards which are vital to our homeland's status. Culture: Since the great Persian Empire, the Iranians live with little dependence n others. The name Persia itself was taken from the Greek word Persis which was taken from Pars; the name of the region where the Persian rulers lived. The name was changed to Iran to let go of western strings still attached to the great empire. Shi’ism is only about 10%-11% of the Islamic world, 85% of muslims are Sunnis; as well as all Arab nations. Iran may regard they’re Islam, but theu do believe that the Persian Empire was the best ever formed. Although Persians shared the Islamic religon with Arabs, it wasn’t Sunnism, it was Sh’isim. Arabs were accused of stealing Persian thinkers; the thinker which could’ve easily done they’re work in Persian, and maybe even Polish if they’ve wanted too. All in all, the past still play a role in they’re governmental structure, the paranoia towards Arab (which was further enhanced at the first Gulf War). Ideology ( Aziz B) Iran's religious ideology restricts freedom of religion. It is governed by the Ja'fari Shi'ism, which is a division of Islam, the official religion of the country. Islam accounts for 99 percent of the religions in Iran. Iran’s constitution is the official protector of religious rites in Iran. It recognizes a few other religions and allows them to practice their religious rites as long as they keep them within strict limits. This means that freedom of religion is supposedly allowed in Iran, but only for some religions and only if they keep their practices secretive and to themselves. The Baha’i religion, a faith originally based on Islam but considered misguided by both Sunni and Shia sects, is not guaranteed religious freedom at all because it isn’t accepted by the constitution. The Iranian government is controversial sometimes, because in the written constitution it accepts freedom of religions and does not allow prosecution against them just for their belief, but it encourages anti-Baha'i and anti-Jewish thought at the same time because it considers them traitors for not believing in the dominant religion, Shiism. Shia Muslims even consider the major Islamic Sunni sect to be a traitor sect, so what would they do to religions that don’t have anything to do with Islam? The Bahai’s are considered by Muslims to be out of the religion of Islam and against it, because they are constructing new ideas and thoughts that are opposed by all Muslims. The Bahai’ faith is extremely hated by the Iranian Islamic government for many reasons. The Bahai’ religion was established by support of Russians, Jews and British attitudes that aimed to spread controversial ideas within the Islamic community to create hatred between Muslims and deviate them from the main topics of their religion. Their main prophet, Baha’ullah, was captured many times after trying to provoke anger between Muslims, and was sentenced to death. It is noted that the Bahai’ religion is especially despised by the Shia sect of Islam, since it is considered an extremely misguided deviant of it. They are also hated because of their concurrence with the Jewish and Christian beliefs the Jesus Christ was in fact crucified. They also prevent women from wearing the traditional Hijab. This is why the government hates them so much, it being an Islamic government, because they claim to be a Muslim sect but oppose many Islamic ideals openly, which in Islam is worse than being an enemy from a totally different religion. Economy: (Reem) Mainly Iran’s economy relies on the oil sector; Iran has no economical issues since it depends on itself for money and not other countries. Most of the economic activity is controlled by the state. During recent years, relatively high oil prices have enabled Iran to collect $30 billion in foreign exchange reserves. Despite the $30 billion, the unemployment rate is extremely high (7,618,000, 11.2%). To state a fact, the Iranian government is in for a big bomb! A bomb of unhappy, young men! A quote by the US Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice, "What we support is that the Iranian people should have a chance to determine their own future, and right now under this regime they have no opportunity to determine their own future.” Iran’s growth domestic product (GDP) is $516.7 billion with a growth rate of 6.3%. Iran's economic structure is mainly agriculture is 11.2%, industry is 40.9% and services is 48.7%. Although the labor force in Iran is 23 million, Iran still suffers from shortage of skilled labor. From the 23 million, labor, 30% work in agriculture,25% works in industries and 45% works in services. $43.34 billion represents Iran’s revenue budget and $47.7 billion, including capital expenditures of $7.6 billion, represents Iran's expenditures budget. Most of Iran’s agriculture products are wheat, rice, other grains, sugar beets, fruits, nuts, cotton; dairy products, wool; caviar. Industries include petroleum, petrochemicals, textiles, cement and other construction materials, food processing (particularly sugar refining and vegetable oil production), metal fabrication, armaments. With a growth production rate of 3.5% excluding oil. Electricity production in Iran is 129 billion kWh; Iran consumes 119.9 billion kWh and exports 0 kWh. While oil production is 3.962 million bbl/day, consumes 1.4 million bbl/day, exports 2.5 million bbl/day and has oil reserves of 130.8 billion bbl. Also, natural gas production is 79 billion cu m, consumes 72.4 billion cu m, exports 3.4 billion cu m, imports 4.92 billion cu m and has reserves of 26.7 trillion cu m. Iran’s current account balance is $2.1 billion and exports is $38.79 billion f.o.b; exports include petroleum 83%, chemical and petrochemical products, fruits, nuts and carpets. Exporting partners are Japan 20%, China 9.9%, Italy 6.3%, South Africa 6.3%, Taiwan 4.8%, Turkey 4.7, South Korea 4.7%, France 4.3%, and Netherlands 4.3%. Imports are $31.3 billion f.o.b; imports include industrial raw materials and intermediate goods, capital goods, foodstuffs and other consumer goods, technical services, military supplies. With importing partners Germany 13%, France 8.9%, Italy 8%, China 7.7%, UAE 6.4%, South Korea 6.3%, Russia 4.9%. Iran has reserves of foreign exchange and gold worth $29.87 billion. With debt external of $13.4 million and an economic aid recipient of $408 million. Iran’s currency code is Iranian Rial (IRR). From 1997 to 2001 Iran had a multi-exchange-rate system; one of these rates, the official floating exchange rate, by which most essential goods were imported, averaged 1,750 rials per US dollar; in March 2002, the multi exchange rate system was converged into one rate at about 7,900 rials per US dollar. Commercial relations between Iran and the United States are controlled by U.S. approval and consist mainly of Iranian purchases of food and medical products and U.S. purchases of carpets and food. The U.S. Government forbids most trade with Iran. Some approval was temporarily ignored in the wake of the devastating Bam earthquake of December 2003. U.S. officials and relief workers actively assisted in relief and reconstruction efforts. The U.S. Government defines its areas of objectionable Iranian behavior as the following: Iranian efforts to acquire nuclear weapons and other weapons of mass destruction; Its support for and involvement in international terrorism; Its support for violent opposition to the Middle East peace process; and its dismal human rights record. The United States has had discussions with Iranian representatives on issues of concern. The United States believes, however, that normal relations are impossible until Iran's policies change. As the US Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice said "I think our European allies agree that the Iranian regime's human rights behavior and its behavior towards its own population is something to be loathed." Defense: (Reem) Although the GDP spent on Iran’s military is only 3.3%, it is the largest and one of the strongest structures in the Middle East. Iran’s military branches include Islamic Republic of Iran Regular Forces (Artesh): Ground Forces, Navy, Air Force (includes Air Defense), Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (Sepah-e Pasdaran-e Enqelab-e Eslami, IRGC): Ground Forces, Navy, Air Force, Qods Force (special operations), and Basij Force (Popular Mobilization Army) and Law Enforcement Forces. Compared to all the countries in the Middle East, Iran has the largest navy force. The US is in a way threatened by Iran, since they have a long range of ballistic highly destructive weapons. The Iranian weapons have been built in Iran or by foreign countries such as China, Russia and the USA secretly. 18 months of military service is required of all male citizens, over the age of 18, also 200,000 men and women, age 16 and above, are on the volunteer list. During the Iraqi-Iran war soldiers as young as 9 years old was recruited to fight the war! The availability man power in Iran is 18,319,545 (males 18-49), but the man power fit for military service is 15,665,725 (males 18-49). Annually the military man power reaching military age is 862,056 (males). These numbers prove that Iran is able to defend itself. The military expenses are $4.3 billion, which is 3.3% of GDP. The Supreme National Security Council (SNSC) is an institution founded in the course of revision of the Constitution of the Islamic Republic of Iran. The SNSC has been established with an aim to watch over the Islamic Revolution and safeguard the IRI's national interests as well as its sovereignty and territorial reliability. According to Article 177 of the Constitution, the responsibilities of the SNSC are as follows: 1. To determine the national defense/security policies within the framework of general policies lay down by the Leader. 2. To coordinate political, intelligence, social, cultural and economic activities in relation to general defense/security policies. 3. To exploit material and non-material resources of the country for facing internal and external threats. Corresponding with its responsibilities, the Supreme National Security Council has established sub-committees such as defense subcommittee and national security subcommittee. The sub-committees are headed by the President or one of the members of the SNSC appointed by the President. Limits of authorities and functions of the subcommittees are laid down by law, and their organizational structures are approved by the SNSC. Approvals of the SNSC shall be enforceable after ratification of the Leader. The members of the SNSC consist of: Heads of the three Powers (Executive, Legislative and Judiciary); Chief of the Supreme Command Council of the Armed Forces (SCCAF); The official in charge of the Plan an Budget Organization (PBO); Two representatives nominated by the Leader; Minister of Foreign Affairs, Minister of the Interior, and Minister of Information (Intelligence); A minister concerned with the subject, and the highest authorities of the Army and the Islamic Revolution's Guards Corps (IRGC). Views On World Problems: (Ahmed ) Iran’s continuous project for nuclear power plants is causing controversy among the USA, UK, France and Germany. Russia is helping Iran out with their first nuclear plant at Bushehr. Israel are also opposing the building of the power plant, fearing some misusage by the Iranians, who are considered a big threat towards their community. Their contract with Russia could make them build 5 power plants in the next ten years. The main question sparked by media is why a nation with rich oil resources wants a dangerous Nuclear power plants on their soil. Iran seems determined to make at least 20 power plants during the near future. The US-Iranian relations have been weak since the 1979 US embassy hostage situation. The Bush administration accuses Iran of being a Nation supporting terrorist acts. While the Iranian government accuse them as being a threat to Islam. Tensions got heated up recently after eyewitnesses claim that Iran’s president Ahmadinejad was a mastermind in the hostage-taking act. The wittenses say that Iran has put a Terrorist to lead the Iranians, and to end the “The War on Terror”, it could only mean that action must be sought on their Islamic extremest regime. Their relationship with Syria is considerably a close one. Both nations share animosity towards the US, Israel, and in the past, Sadam Hussein (although his relationship with Syria only stopped by the year 2000). Syria’s dominance of Lebanon helped its political and militarily relationship with Hizballah. Syria also assisted Iran by allowing Iranian jets to enter Syrian airspace above northern settlements of Iraq to assault western Iraqi military bases. Iran allowed Syria free oil for shutting down Iraqi pipelines in their own territory as a gesture of great gratitude for not sliding in with its Arab neighbor. Further more Iran is one of Syrian goods buyers, mainly because of the sanctions, which has stopped them from trading with a diversity of nations (which has looked as though Syria is another Iranian province). Iran’s relationship with Saddam-less Iraq continues to be tainted. Not only because the scar is still wounded from the first Gulf War, but because of the US’ continuous developments in Iraq, making it seem like the 52nd state. Currently, Iran is subsidizing the Shia’a militias in Iraq because of the continuous attacks on Shia’a citizens by the Sunni “terrorist” groups. The EU approaches tries to approach Iran in the most peaceful approach they may well have. The Europeans keep meeting Iran to discuss issues such as suspending uranium enrichment activities. They would also provide all objective into ensuring that the nuclear program of Iran is peaceful. “Israel is a disgraceful lot to the Islamic world and as the Imam said, Israel must be wiped off the map”, these are the comments that were recently stated by Iranian president Mr. Ahmadinejad referring to Iran's late revolutionary leader, Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini. He also warned Muslim leaders that recognize the state of Israel that they faced they “faced the wrath of their own people”. These comments inevitably resulted in great controversy occurring with world leaders. Mr. Blair himself believed that he never came across such comments from a world leader. Even the Palestinian peace negotiator stated “Palestinians recognize the right of the state of Israel to exist, and I reject his comments". Ancient History The empire of Persia, currently known as the Islamic Republic of Iran, was once a mighty power by itself. As first established by Cyrus the great, this Persian empire expanded greatly and became to be known as one of the most indomitable empires in history. Many groups have tried to disable it and render it helpless over the years due to its formidable power. The Islamic control over Iran began in the 7th century AD and ended a couple of centuries later. Most of Iran's people had converted to Islam by then, the majority being of the Sunni branch and some of the Shia faith. Turkish control over Iran started in the 11th century when they defeated the current rulers and. they themselves being Muslims, established dynasties in most of the area. One of the most disastrous rulers over Iran, though, were the Mongols. The Mongols essentially worked on destroying the Iranian cities and killing the people living in some of them due to their rejection of the new rule. As if that wasn't enough, the Mongols had their differences with the Muslim people of Iran based on their religion, as the Mongols were Buddhists. One of the Mongol rulers tried desperately to revive the country, but that didn't work and cities ended up being destroyed all over again. In essence, the entire period of Mongol rule was unhelpful to the country's economy. Iran is, essentially, a non-Arab country. Therefore, it is considered different than the majority of Islamic countries that are, in fact Arab. Iran’s Shia Islamic sect, the dominant Islamic sect in the country, is known to be strong and fervent when it comes to responding to tensions or pressure. The Shia sect is also known to be stricter, when noting the extremist values that the country imposes. On the other hand, the extremist Sunni sects such as Wahabbism in Saudi Arabia is viewed at times and the Taliban regime are as radical and fervent as the Shia groups. Geographically, Iran has always been known to have decent influence, because of its strategic location acting as a bridge between the Islamic and Non-Islamic world essentially. Iran has been known to act against the norm, as the major sect in Islam is the Sunni sect, but Iran has an overwhelming majority of Shias, and therefore is the most country with that population of Shia Muslims. There are other countries in which the Shia sect holds a high percentage of the Islamic society, such as Bahrain and Iraq. After the Mongols lost control of the country, the Safavids took over, and established the rule of a single ``Shah'' title. The Safavids spread the Shia sector of the Islamic religion over the country in order to make it more prevalent. The Safavids had many arguments with the Ottoman Empire, mainly territorial disputes that lasted a fair amount of time. The primary Safavid rulers established a strong economical background for the country, but that was ruined after the second Shah ended his rule over Iran. Iran fell into a phase of peacefulness and tranquility for some time after the fall of the Safavids. In the late 17th century, the Qajar dynasty took over Iran after defeating many common rivals. They were from Turkish origins, and it just so happened that in their reign foreign entities such as Russia and Britain showed interest in the region. Russia kept getting into battles with Iran and defeating it to gain more land, and both countries showed economic interests in the country, especially after oil was discovered in 1911. The entrance of Reza Pahlavi, who later became the Shah of Iran, into the battle over the rule of Iran was crucial to Iran's development. The man had many visions for the industrialization and modernization of Iran, and the seperation of it from the more powerful foreign entities: mainly Britain and Russia. Reza Shah Pahlavi wanted more control over his country and seeked the assistance of other foreign entities such as Italy and Germany. After the second World War, Reza Shah Pahlavi was exiled and removed from his position afer Britain and the USSR invaded Iran. His son was instead replaced as the constitutional monarch of Iran. An agreement was signed between Iran and the foreign entities, and peace was reached. Political reforms were initiated and elections took place for the first time in two decades. Iran was in the beginning of an advancement in all areas. Recent History Mohammad Reza Shah Pahlavi came to his position in an interesting way that would later explain why he was deposed. During World War II, the British and Soviets forced the Shah, his father, to give up his position for his son. The forces then used the new Shah as a way of transporting British and US aid to the USSR during the war. This later came to be known as the Persian Corridor. This was basically the first major US direct involvement in Iran’s affairs. Another major event was the coup against the Iranian democratically elected Prime Minister Mohammed Mosaddegh in 1953. Due to him nationalizing the Iranian oil industry, the CIA tried to overthrow him and failed the first time, leading to the Shah’s fleeing the country. The Shah was later brought back through another successful coup and the prime minister was jailed and sentenced. Mohammad Reza Shah Pahlavi was growing increasingly unpopular due to his easy manipulation by foreign entities and governments and his modernism and marriage to an American wife. He was provided aid by eight US Presidents in exchange for oil supplies. The Iranian Shah tolerated the presence of Israel in the Middle East, receiving more hatred from the religious clerics because of that. The people began to see him as a weak leader, and eventually this led to what is called ``The Islamic Revolution''. This revolution started by some demonstrations that were linked to an exiled Iranian activist named ``Khomeini'' who was now living in Iraq. The demonstrations turned fatal, and thus began riots that spread throughout all of Iran, increasingly encouraged by Khomeini's speeches from Iraq to support an Islamic government. The shah found no other way but to impose martial law on many cities in Iran, which caused further riots that became almost uncontrollable. In the meantime, Khomeini was exiled from Iraq and he seeked refuge in France. His voice was never lost, and the shah realized it was too late to regain control after massive strikes rocked the country. The shah finally fled Iran, and Khomeini returned to find the people holding elections and vote incredibly to establish the Islamic Republic of Iran in 1979. Khomeini was mostly supported by the poor who were being mistreated more, and the country needed him because they despised the Shah’s regime and his actions. One of the most significant, and probably the most critical, turning points in U.S. Iranian relations was the hostage crisis of October 1979. A number of Iranian students basically invaded the U.S. embassy in Tehran and took 66 individuals hostage. The 15month siege ended in the release of the hostages in return for U.S. agreement to hold a trial regarding its citizens' claims against Iran. This completely ended the positive U.S. Iranian relations and resulted in relative suspicion between both sides. Mahmud Ahmedinajad, Iran’s current President, was said by the Central Intelligence Agency to be deeply involved in this hostage crisis, but the Iranian government severely denied that. Another major event in Iranian history was when Iraq launched a surprise invasion on it in 1980. Iraq did so to prevent Iran from convincing Iraqi Shia Muslims to revolt against their government. In this war, the two superpowers were essentially using Iran and Iraq as a way of indirectly fighting each other. The USA provided weapons to Saddam Hussein so he could fight Iran, while mainly Russia supplied Iran with an arsenal to fight back. The war was deadly, yielding hundreds of thousands of deaths on each side, and the two entities ended it with a cease-fire agreement. The USA is accusing Iran continuously of being involved in the continuing US occupation of Iraq. The US accuses Iran of funding militias and providing them with weapons to commit terrorists acts that would lead to the destabilization of the Iraqi State. Iran keeps refuting these statements, stating that the US is only saying that to get a stronger backing on Iran’s nuclearization issue. Iran’s president, Mahmoud Ahmedinejad, just recently fired and/or reassigned around 20 of his diplomatic staff in foreign countries. This diplomatic “shake-up” of governmental staff is the largest since the Iranian Islamic revolution of 1979. Iran's foreign relations with most countries were bumpy due to the U.S. having its power threatened by Iran's nuclear weapons almost every day. Iran signed a nonproliferation protocol that was an addition to the Non-Proliferation Treaty and gave more freedom for weapons inspectors to hunt for Iran's supposed fleet of nuclear weapons. In 2005, though, tensions were elevated due to the uranium enrichment plants that were found and might also be components of weapons. The IAEA and the three prime countries in the EU were constantly sending Iran warnings regarding its enrichment plants, and Iran actually did comply towards the end of 2004 and stopped nuclear activity for months, before resuming in August of 2005, which was considered a violation by the accusing countries. Iran’s supreme religious leader continues to assert the fact that Iran does not want nuclear weapons, but will not give up enriching uranium. The recent Iranian election that hailed President Mahmoud Ahmedinejad as the state’s new head showed an unexpected loss of candidate Khatami. The previous head of state was supported by the USA, and was willing to compromise on the nuclear issue in Iran, pleasing the US and European countries. This conservative leader, however, is increasing Iran’s isolation from the rest of the international community, leading to severe tensions between Iran and the West, something the USA would prefer to avoid.