Unit 9*Evolution
advertisement

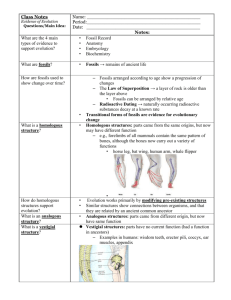
V. Evidence of Change Over Time Resources Bozeman—Evidence for Evolution http://www.bozemanscience.com/004-evidence-for-evolution Campbell Textbook Ch. 22.3 V. Evidence of Change Over Time A. Fossils– show organisms in historical sequence; show intermediate and extinct forms of organisms V. Evidence of Change Over Time B. Biogeography—Use of biology and geography to describe relationships Closely related species tend to be found in same geographic region; whereas, same ecological niches tend to be occupied by very different species (though sometimes similarlooking) i.e/ Marsupials vs. Eutherians IV. Evidence of Change Over Time C. Comparative Anatomy i. Homologous Structures– same structure; different function V. Evidence of Change Over Time Analogous Structures—same function; different structure (i.e., butterfly and bird wing)– doesn’t show a relationship ii. Vestigial Structures—No longer use (i.e., appendix, tailbone) Vestigial Analogous vs Homologous ii. V. Evidence of Change Over Time iv. Embryology—similarities in embryos that aren’t found in adult forms (i.e., gill slits in mammal embryos) V. Evidence of Change Over Time C. Comparative Molecular Biology– similarities and differences in DNA sequences and proteins VI. Microevolution Resources: Bozeman—Genetic Drift http://www.bozemanscience.com/003-genetic-drift Bozeman—Solving H-W Problems http://www.bozemanscience.com/solving-hardy-weinbergproblems Campbell Textbook Ch. 23 VI. Microevolution A.Conditions that Result in Change in Gene Frequency over Time i. Mutation-Random, permanent changes in DNA Usually bad Often small effects Usually covered up by sexual reproduction VI. Microevolution ii. Non-Random Mating– changes in gene pool because some organisms mate more/less or not all iii. Gene Flow– change in gene pool due to immigration/emigration VI. Microevolution iv.Genetic Drift– change in gene pool due to chance VI. Microevolution 1. Bottle Neck– population size is drastically reduced and eliminates certain alleles 2. Founder Effect– the “founders” of a population contribute their alleles which may or may not represent the entire population VI. Microevolution iv. Natural Selection (Modes)– See Worksheet B. No Evolution– Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium 1908—See Lab