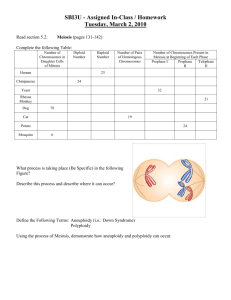
When things go wrong in meiosis
advertisement

When things go wrong in meiosis Review of meiosis Errors during crossing over (Prophase I) • Block mutations happen during meiosis and involve the rearrangement of whole blocks of genes. • It can happen either spontaneously or due to radiation. • Block mutations include: – – – – Deletion Inversion Translocation Duplication Block mutations Original sequence Mutated sequence Deletion ABCDEFGHMNOPQRST ABGHMNOPQRST Inversion ABCDEFGHMNOPQRST ABFEDCGHMNOPQRST Translocation ABCDEFGHMNOPQRST 1234567890 GHMNOPQRST ABCDEF1234567890 Duplication ABCDEFMNOPQ ABCDEABCDEFMNOPQ FMNOPQ Errors in Independent Assortment • Non-disjunction = failure of homologous chromosomes to separate (Anaphase I and Anaphase II) Definitions • Aneuploidy: condition that results when one cell has a different chromosome number to the normal chromosome number. • Monosomy: a condition in which an individual has only one half of a specific pair of homologues. • Trisomy: a condition in which an individual has three of a specific chromosome. • Polysomy: a condition in which an individual has more than three of a specific chromosome. • Haploid (n): having half of an entire chromosome (eg. Sex cells) • Diploid (2n): having double of an entire chromosome (eg. Somatic cells) • Triploid (3n): having three of an entire chromosome • Polyploidy: a condition in which an individual has one or more extra of an entire chromosome. Polyploidy Triploid Tetraploid Octaploid Hexaploid Faulty Gamete Production