Meiosis - Mrs. Shelly Jackson
advertisement

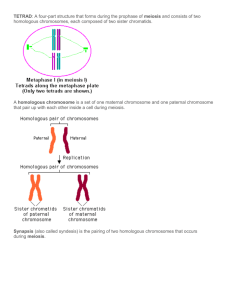
Meiosis Genetic Diversity Meiosis Vocabulary Somatic cell- a body cell (liver, skin, testis, ovary). Diploid- chromosomes are paired (2 # 9 chromosomes) 2n- symbol for diploid Gamete- sex cells (only 2 types: sperm & egg) Haploid- a single chromosome n- symbol for haploid Homologous chromosomes- same (all # 9 chromosomes) Homologous Chromosomes Homo= same • Same length • Centromere same location • Same position of genes How many different chromosomes are Represented in the image above? Chromosome #1 – Mom and its copy Chromosome #1 – Dad and its copy Significance of Meiosis Increases the genetic diversity of a gene pool. Gene pool- all the possible genetic possiblities with a population. 1. Crossing over- Prophase I 2. Independent Assortment- Metaphase I 3. Random fertilization - Meiosis is Reduction Division What is reduced? Meiosis Amoeba sisters - 7 min Same parents: Different children? Genetic Diversity- Meiosis • Crossing – Over • Independent Assortment As a result of Meiosis: • Random fertilization Genetic variation- Meiosis I Crossing Over- Prophase I Homologous chromosomes – exchange genes. This process is random -- occurs with all 23 different homologous pairs- different Every time! Crossing Over Enzymes cut genes out of the two different versions homologous chromosomes and exchange them. Independent Assortment Homologous chromosomes line up randomly on the equator. During Anaphase- they will “sort out” differently into cells. Independent assortment can generate up to 223 genetic variations in the gametes. Genetic variation- Meiosis I Independent Assortment- Metaphase I Gametes are all genetically different! Remember- each child is a product of a separate meiotic event for both the sperm and the egg (ovum). Each child was the result of a different meiosis event for Mom & Dad Genetic Variation - Gametes Random Fertilization Which sperm will fertilize the ovum. Review the Process What type of reproductions is Meiosis? How many times will the cell divide? How many times will the DNA replicate? How many cells are produced? Are the daughter cells clones? Diversity is the raw material of Evolution What would happen to the offspring is suddenly an alien came to their community and devoured people with white hair? Why is “sex” (the exchange of genetic information) more important than life? Evolution Variations in a species- makes it more likely that some organisms will survive in a changing environment! How does Meiosis factor into the evolutionary process? Evolution Genetic Variation is the raw material for evolution!! Differentiate between Crossing over and Independent assortment: 1. What happens with homologous chromosomes in crossing over? • When does it occur (very specific)? • What is the result? 2. What happens with homologous chromosomes in Independent Assortment? • When? • What is the result? Chromosome Mutations Crossing Over Cutting and Pasting Errors: Errors in Anaphase What happens to the chromosomes in Anaphase? Have you ever been told to move to the right but you moved to the left? Sometimes this happens to the chromosomes! Non-disjunction Disorders Chromosomes fail to separate properly! Creates some cells with : • too many chromosomes! • too few chromosomes! Down’s Syndrome