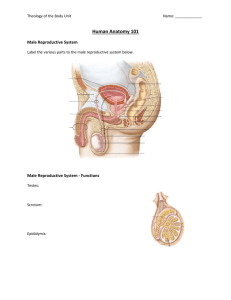
Female Reproductive System: Anatomy, Function, Health
advertisement

Unlike other body systems, the reproductive system is different for males and females In this lesson, you will learn to identify the parts of the female reproductive system. describe the functioning of the female reproductive system. identify problems of the female reproductive system. recognize the importance of early detection in the treatment of conditions of the female reproductive system. describe ways to keep your reproductive system healthy. Reproductive System The body system containing the organs that make possible the production of offspring The Female Reproductive System Three Functions of the Female Reproductive System Store egg cells Create offspring to allow fertilization to occur to nourish and protect the fertilized egg Give birth Female Reproductive Organs Internal • • • • • • ovaries fallopian tubes fimbriae uterus (womb) cervix vagina External – Vulva • • • • mons pubis labia majora (outer lips) labia minora (inner lips) vaginal opening – hymen – thin membrane partially covering the opening of vagina • clitoris Vulva the external part of the female reproductive organs ……. external genitalia • ovaries – female sex glands – two rounded organs, one on either side of the uterus – contains the ova, eggs, and hormones that cause the egg to mature • estrogen • progesterone • ova (ovum) – egg, female sex cells – a female is born with hundreds of thousands of immature ova in her ovaries – from puberty to menopause hormones cause ova mature • a few hundred will mature during reproductive years Female Reproductive Organs • fallopian tubes tubes that carry eggs, ova, from ovaries to uterus • fimbriae finger-like projections at the end of the fallopian tubes that reach out and “grab” the egg as it leaves the ovary Female Reproductive Organs uterus (womb) pear shaped hollow muscular organ that receives, holds, and nourishes the fertilized ovum during pregnancy with thick muscular walls which are – the thick muscular walls are highly elastic and can stretch many times its normal size Endometrium • the uterine lining … bloody tissue lining • thickens to prepare for the attachment of the embryo • is shed during monthly menstrual period if pregnancy does not occur Female Reproductive Organs cervix • the neck of the uterus, (lower portion) – protrudes into the top of the vagina • the passageway between the uterus and the vagina • site of glands that secret mucus to lubricate the vagina Female Reproductive Organs • vagina • an elastic, muscular tube that is a passage way between the uterus and the outside of the body, (vulva) • also called the birth canal • the female organ for intercourse – repository for semen when a male ejaculates with the penis inside the vagina during intercourse • It is possible for the sperm to enter the reproductive system if the male ejaculates near the vagina – 3 to 4 inches long – capable to stretch for birth of baby Female Reproductive Organs • Vulva the external part of the female reproductive organs ……. external genitalia ovulation when a mature ovum,(egg) is released from the ovaries • it travels along the fallopian tubes to the uterus • usually once a month … from one ovary • an ovum can live about a day in a fallopian tube ova (ovum) – egg, female sex cells – a female is born with hundreds of thousands of immature ova in her ovaries – from puberty to menopause hormones cause ova mature • a few hundred will mature during reproductive years IF A SPREM IS PRESENT AND ONE SUCCESSFULLY PENETRATES THE OVUM Fertilization union of a sperm and an egg to form a single cell – PREGNANCY Female Reproductive Organs Fimbriae Fimbriae Ova Ovary (inside) Menstruation The menstrual period the process of shedding the uterine lining (discharging blood and tissue out of the female body) Occurs only when an ovum is not fertilized Page 38 in Human Sexuality Book menstrual cycle • the time from one menstruation to another – first day of period to first day of next period – usually 28 days • starts at puberty and continues until menopause – due to increase levels of hormones • purpose is to prepare the body for fertilization … get ready to have a baby 4 stages of the cycle 1. Days 1-8 menstruation … menstrual period about 5-7 days average … not always 2. Days 9-13 … days before release egg hormones cause an egg to mature in one ovary body is preparing for egg 3. Day 14 … ovulation … egg is released into one fallopian tube 14 days before menstrual period 4. Days 15-28 … days after egg is released – egg travel through the fallopian tube to the uterus waiting to be fertilized IF EGG NOT FERTILIZED CYCLE BEGINS AGAIN 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 1. 2. 3. 4. menstruation body is preparing for egg ovulation egg travel through the fallopian tube to the uterus waiting to be fertilized IF EGG NOT FERTILIZED CYCLE BEGINS AGAIN THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW • the average length of the menstrual cycle is 28 days, however …… • it is normal for the cycle to be longer or shorter • Blood passing out of the body is about 3-10 table spoons • This is blood the body does not need so it does not make the women ill or weak • the most likely time to get pregnant is around ovulation time • ovulation occurs on or about 14 days before your period starts regardless of the length of your cycle • to count the days of the menstrual cycle: day 1 – first day of menstrual period last day of cycle – day before your period starts again • Menstruation continues until menopause Menstrual Problems A variety of menstrual problems can affect girls. Some of the more common conditions are: Cramps … uterus is contracting mood swings or sadness … hormones Less often …… painful periods very heavy periods with excess bleeding. missed or infrequent periods, even though she's been menstruating for a while and isn't pregnant. Problems of the Female Reproductive System Infertility: This is the inability to get pregnant. It may be due to blocked fallopian tubes, a failure to produce eggs, endometriosis, or and STD left untreated. Ovarian cysts: These are growths on the ovary. Symptoms of ovarian cysts include a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen and abdominal pain, swelling, and bloating. Infections - Vaginitis – inflammation of vaginal tissue, Yeast infections symptoms inflammation of vaginal tissue, discharge, burning, itching, and painful urination Toxic shock syndrome - Associated with tampon use and some contraceptive devises symptoms include: fever, chills, vomiting, diarrhea, rash Cancer – Breast – Cervical Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) These are diseases spread through sexual contact. Gynecologist GYN a physician who specializes in caring for the female reproductive system women should start to see a gynecologist by about age 18 or when they begin to be sexually active Caring for The Female Reproductive System • Practice abstinence from sex - this can prevent infections with HIV and other STDs • Bathe or shower daily - keep the external reproductive organs clean especially during menstruation. • Sanitary pads and tampons should be changed often - every four hours. • Perform self breast examinations - a way to check your own breast for lumps or tenderness. • Have regular medical checkups – Pap Test - a physician can answer any question she has. Gynecologist. • Get medical attention for signs of infection - lumps, sores, rashes, or a discharge that require medical attention. What happens if an egg is not fertilized? It is eliminated from the body through menstruation ... Woman has her period What happens if it is fertilized? An egg that is fertilized moves down into uterus and implants in the endometrium and develops into a baby….. No period What are the three most important functions of the female reproductive system? – to store eggs – to allow fertilization to occur – to nourish and protect the fertilized egg until it is ready to live outside the female’s body