Mesopotamia Vocabulary Terms
advertisement

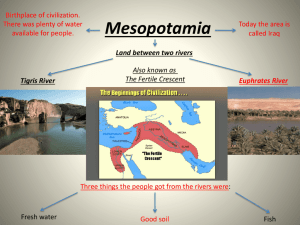
Mesopotamia Vocabulary Terms Ms. Smith World History Chapter Objectives Describe how religion, family life, and government influenced Sumerian civilizations. Chapter 3 Mesopotamia Vocabulary City-state: a Sumerian city and the farmland around it. Each one had its own god and government. Ziggurat: the temple at the center of each Sumerian city. Artisans: skilled workers. Members of the Sumerian middle class. Chapter 3 Mesopotamia Vocabulary Cuneiform: Sumerian writings on clay tablets. Made up of hundreds of markings shaped like wedges. Priest-kings: Sumerian priests who were also kings. Scribe: Sumerian writer Hereditary: passed down from parent to child. The Rise of Sumer Sumerians grew wheat, barley, sesame, flax, fruit trees, and vegetables. The Sumerians set up a government and laws. As the population grew, they built cities. Important great city was Ur. City-states Surrounded by a wall Wall kept out lions and bandits Went to war with each other Religious and Family Life Ziggurat was at the center of each city- state. Only priests could enter. Ziggurat: Farmers, artisans, traders stored goods. Poor were fed Children went to school Events were celebrated. Sumerians believed they were on earth to please the gods. 3000 gods Sons of rich went to school Sons of poor worked in fields or learned a trade. Writing developed to keep track of trade. Women could buy and sell property, run businesses, own and sell enslaved person. Priests and Kings Epic of Gilgamesh – story of a great flood that covered the earth. Section 1 Review The Sumerians gained control of the twin rivers by building levees. The center of Sumerian life was the ziggurat the courts. The lives of Sumerian women compared with today’s women would be described as having the ability to sell property and own businesses. Sumerian accomplishments Cuneiform Levees City of Ur Government Irrigation Epic of Gilgamesh Section 2: Later Empires Empire- groups of states under one ruler. Culture – the way of life of a group of people. Reform – improvement reign – period of power Sargon I Created the world’s first empire. Reign lasted 50 years. Strong ruler United the cities of Mesopotamia and Akkad. Hammurabi of Babylon Conquered Akkad and Sumer and became ruler in 1800 B.C. The Babylonians took many parts of the culture of the people they conquered. (language, Gods) Brought about changes in: religion, irrigation, and the tax system. Hammurabi of Babylon Best known for Hammurabi’s Code. Each city-state had it’s own code. Believed in FAIR LAWS. Innocent until proven guilty. Punishment ranged from fines to death. During his reign, Babylon became an important center for trade.