The Effectiveness of Mass Communication to Change Public Behavior
advertisement

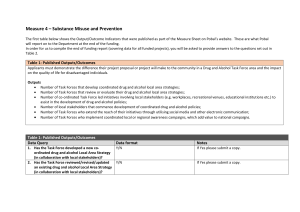
The Effectiveness of Mass Communication to Change Public Behavior Paper: Lorien C. Abroms and Edward W. Maibach Presenter: Lauralee Woods Presentation Mutual evolution of Mass Media and Population Health Proposed People and Places Framework Components of an effective campaign Mass Media’s influence on: Individual-Level Social Network Level Community Level Optimism in Harnessing Mass Media for Public Health Limits of this Review Discussion and Questions Mutual Evolution of Mass Media and Public Health Media: 1980’s broad cast was limited to fewer tools: (Less channels, broader audience) 1990’s “narrow cast/silver cast” (More channels, specific audience) Specific Demographic/psychographic targets INTERNET: Information Blast Radically Alters Business & Information Flow Lower cost and less gatekeepers Public Health: Before: Clinical focus on curing sick individuals Now: Eocological Model for Population Health Maibach’s People and Places Framework Defining Mass Media and its Components Mass media: A planned Effort that disseminates old and new messages to produce awareness or behavior change among an intended population through channels that reach a broad audience. Components: Review of Social Marketing Well-designed Message (Design) Target audience Target behavior Intended Audience Reached (Exposure) Frequency of Message (Exposure) Individual-Level Media Campaigns Extreme Success: “Truth” by Department of Health and American Legacy Foundation Result: 22% decline in teenage and adolescent smoking Exception to the Rule Normal Success: Snyder and Hamiltons meta-analysis of 48 published community-wide mass media health campaigns effects: 9% increase in short-term behavior adoption 17% increase in behavior adoption with enforceable law 5% increase in behavior adoption without enforceable law Major Players: Reach and Novelty Examples The “Truth” campaign Aim at youth feature trendy youth in public demonstration http://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=Y_56BQmY_e 8 CDC’s VERB campaign CDC’s graphic anti-smoking campaign ad Tips from former smokers Average Effects of Media Campaigns by Topic – Meta-analytic findings The Collateral Website Allows for the individually catered message: “advergames” Google also sending you specific messages based on your viewing history Few studies have been done, but promising for customer reach and brand awareness VERBnow.com Social Network Level Focuses is on types and degrees of relationship support Promotes presence of positive health leaders Target: Friends, Parents, Older Siblings, spouses… Success: “Talk to your kids about sex, everyone else is.” by North Carolina Department of Health Results: A Telephone survey showed intention and behavior increased in exposed population Social Network continued: Less Explored target: Instead of utilizing an already existing social network, building one. Example: Harvard mentoring project with a three-prong strategy Public Service Announcements Outreach to entertainment Community News Media outreach Results : Many donations and 700,000 calls to volunteers Mass Media on Community Level Subcategories: Social norms, social capital, social cohesion, collective self efficacy, income inequality, and racism. This strategy is used more for youth. Big Success: http://www.liveearth.org/ promoting Global warming Awareness Results: Most watched televised Concert…Ever Really successful? Lots of exposure, but are the ones exposed the ones who can and will make change? Place-based Field of Influence: Local and Distal Levels Range of Opportunities for interventions The Laws and Policies in the Environment The availability of products and services increased Physical structures in the environment Media and cultural messages in the environment Media Advocacy: The strategic use of mass media in combination with community organizing to advance healthy public policies Mobilization of Public and Policy Makers Lacks established methods for evaluation with environmental interventions Few studies exist Success: http://smokefreemovies.ucsf.edu/ Result: Some response from MPAA by considering smoking in R-ratings An example of this are also all of the ads on the news and on peoples houses during the elections. Optimism in Harnessing Mass Media for Public Health: Plenty of exposure Opportunities (Institutue of Medicine): Average adult is exposed 10 hours per day to media Plenty of studies on Individual level factors Paper Suggests: “Big Messy” Programs- Diverse tactics -Mass media, interpersonal communication, and outreach to policy makers More studies needed All should be explored by Public Health field Okay for groups to choose one focus or the other depending on their need Limitations: Few studies done on the subject Questions and Concerns: Are there more examples of successful or limited media campaigns? Is this framework sufficient for analyzing mass medias role effect on Public Health? Should we be optimistic about Mass media as a tool for Population health promotion or is it going to create more barriers? THE THEORY OF TRIADIC INFLUENCE Levels of Causation Intrapersonal Stream Biological/Nature BIOLOGY/ PERSONALITY Ultimate Causes 1 Social/ Personal Nexus 2 Sense of Self/Control Distal Influences 7 13 8 h Skills: Social+General 14 Proximal Predictors b c B C Others’ Beh & Atts 9 i j k l m u d e n 16 SOCIAL NORMATIVE BELIEFS o 11 w 20 q Values/ Evaluations x v 6 Interactions w/ Social Instit’s p Perceived Norms 15 5 f 10 Motivation to Comply s CULTURAL ENVIRONMENT 4 Interpersonal Bonding 19 A Nurture/Cultural 3 SELF-EFFICACY t BEHAVIORAL CONTROL Affect and Cognitions Cultural/Attitudinal Stream SOCIAL SITUATION a Social Competence g Self Determination Expectancies & Evaluations Decisions Social/Normative Stream Information/ Opportunities Knowledge/ Expectancies 17 F 18 ATTITUDES TOWARD THE BEHAVIOR 21 DECISIONS/INTENTIONS D E 12 r I 22 H G Trial Behavior EXPERIENCES: Expectancies -- Social Reinforcements -- Psychological/Physiological Experiences 23 J K Related Behaviors 18