Phylogeny and Systematics

Phylogeny and
Systematics
Chapter 10
Taxonomy
Taxonomy produces a formal system for naming and classifying species to illustrate their evolutionary relationship.
Taxonomy & Systematics
Taxonomy
Formal system for naming and classifying species.
Systematics
Broader science of classifying organisms based on similarity, biogeography, etc.
Systematic zoologists have three goals:
To discover all species of animals.
To reconstruct their evolutionary relationships.
To classify animals according to their evolutionary relationships.
Taxonomy
Introduction of evolutionary theory into animal taxonomy changed taxonomist ’ s role from one of classification to systematization.
Classification denotes the construction of classes.
Grouping of organisms that possess a common feature called an essence used to define the class.
Taxonomy
Systematization places groups of species into units of common evolutionary descent.
Character variation is used to diagnose systems of common descent.
No requirement that an essential character be maintained throughout the system for its recognition as a taxon.
Taxonomy
In classification
Taxonomist asks whether a species being classified contains the defining feature of a particular taxonomic class.
In systematization
Taxonomist asks whether the characteristics of a species confirm or reject the hypothesis that it descends from the most recent common ancestor of a particular taxon.
Linnaeus and Classification
Carolus Linnaeus designed our hierarchical classification scheme.
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Linnaeus and Classification
All animals are placed in Kingdom Animalia.
Names of animal groups at each rank in the hierarchy are called taxa (taxon).
Each rank can be subdivided into additional levels of taxa.
Superclass, suborder, etc.
Linnaeus and Classification
Linnaeus and Classification
Binomial nomenclature is the system
Linnaeus used for naming species.
Genus and species
Names are latinized and italicized, only the genus is capatilized.
Sitta carolinensis
Linnaeus and Classification
A trinomial name includes a subspecies epithet.
Ensatina escholtzii escholtzii
E. e. klauberi
Species
Defining a species can be difficult.
Criteria:
Common descent
The smallest distinct groupings of organisms sharing a pattern of descent.
Morphological & molecular techniques
Members of a species must form a reproductive community that excludes other species.
Species
The geographic range of a species is its distribution in space.
Evolutionary duration of a species is its distribution in time.
A worldwide species is cosmopolitan .
One with a very localized range is called endemic .
Typological Species Concept
The typological or morphological species concept relies on type specimens that represent the ideal form for the species. When trying to name a specimen, the type specimens were compared.
Scientists still name species by designating a type specimen.
The Biological Species
Concept
The biological species concept emerged during the evolutionary synthesis.
“ A species is a reproductive community of populations (reproductively isolated from others) that occupies a specific niche in nature.
” Mayr 1982
Sibling species fit this category, but can only be differentiated with molecular techniques.
Lacks a temporal dimension.
Degree of reproductive isolation necessary?
Species that reproduce asexually?
Evolutionary Species Concept
The evolutionary species concept states that a single lineage of ancestor-descendant populations that maintains its identity from other such lineages and that has its own evolutionary tendencies and historical fate.
Definition accommodates both sexual and asexual forms as well as fossils.
Phylogenetic Species
Concept
The phylogenetic species concept is defined as an irreducible (basal) grouping of organisms diagnosably distinct from other such groupings and within which there is a parental pattern of ancestry and descent.
Both asexual and sexual groups are covered.
Phylogenetic Species
Concept
Main difference in practice between the evolutionary and phylogenetic species concepts:
The latter emphasizes recognizing as separate species the smallest groupings of organisms that have undergone independent evolutionary change.
Discerns the greatest number of species but may be impractical.
Disregards details of evolutionary process.
Investigating the Tree of Life
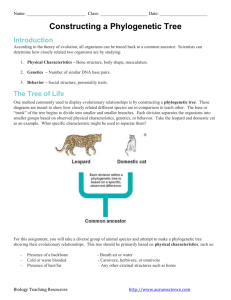
A major goal of systematics is to infer the evolutionary tree or phylogeny – the evolutionary history of a species or group of related species.
Phylogeny
Phylogenies are inferred by identifying organismal features, characters , that vary among species.
Morphological
Chromosomal
Molecular
Behavioral or ecological
Phylogeny
Shared characters that result from common ancestry are homologous .
Independent evolution of similar characters that are
NOT homologous is called homoplasy .
Sorting Homology from
Analogy
A potential misconception in constructing a phylogeny is similarity due to convergent evolution , called analogy , rather than shared ancestry.
Sorting Homology from
Analogy
Convergent evolution occurs when similar environmental pressures and natural selection produce similar (analogous) adaptations in organisms from different evolutionary lineages.
Sorting Homology from
Analogy
Analogous structures or molecular sequences that evolved independently are also called homoplasies .
Shared Primitive and Shared Derived
Characteristics
A shared primitive (ancestral) character :
Is a homologous structure that predates the branching of a particular clade from other members of that clade.
Is shared beyond the taxon we are trying to define.
Example – mammals all have a backbone, but so do other vertebrates.
Shared Primitive and Shared Derived
Characteristics
A shared derived character is an evolutionary novelty unique to a particular clade.
All mammals have hair, and no other animals have hair.
Phylogeny
The form of the character that was present in the common ancestor of the entire group is called ancestral .
Variant forms of the character arose later and are called derived character states .
Determining polarity of a character involves determining which state is ancestral.
Phylogeny
Polarity is determined by using outgroup comparison .
An outgroup is closely related, but not part of the group being examined (the ingroup ).
If a character is found in both the study group and the outgroup, it is considered ancestral for the study group.
Character groups found in the study groups but not the outgroups are derived .
Phylogeny
Clades are organisms or species that share derived character states and form a subset within a larger group.
A synapomorphy is a derived character shared by the members of the clade.
A clade corresponds to a unit of evolutionary common descent.
A nested hierarchy is formed by the derived states of all characters in a study group.
Phylogeny
Ancestral character states for a taxon are called plesiomorphic .
Sharing these ancestral characters is called symplesiomorphy .
Symplesiomorphies, unlike synapomorphies, do not provide information on nesting of clades – groups with derived characters get left out.
Phylogeny
The nested hierarchy of clades can be represented as a cladogram that is based on shared synapomorphies.
Phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree is another way of representing evolutionary relationships.
Branches represent real lineages that occurred in the evolutionary past.
Includes information about ancestors, duration of evolutionary lineages, amounts of evolutionary change that has occurred.
Sources of Phylogenetic Information
Characters used to construct cladograms can be found using:
Comparative morphology – examine shapes and sizes of organismal structures, including developmental origins.
Comparative biochemistry – examine sequences of amino acids and nucleotides to identify variable characters.
Comparative cytology – uses variation in numbers, shapes, and sizes of chromosomes and their parts.
Taxonomy
A theory of taxonomy allows us to rank taxonomic groups.
Two popular theories
Evolutionary taxonomy
Phylogenetic systematics
Both based on evolutionary principles, sometimes results conflict.
Cladistics
A valid clade is monophyletic .
Signifying that it consists of the ancestor species and all its descendants.
Cladistics
A paraphyletic clade is a grouping that consists of an ancestral species and some, but not all, of the descendants.
Cladistics
A polyphyletic grouping includes numerous types of organisms that lack a common ancestor.
Traditional Evolutionary Taxonomy
Evolutionary taxonomy utilizes common descent and the amount of adaptive evolutionary change to rank higher taxa.
Sometimes this type of classification includes paraphyletic groupings.
Phylogenetic Systematics
Phylogenetic systematics , or cladistics , emphasizes common descent and is based on cladograms.
All taxa must be monophyletic.
Cladistic taxonomists have moved chimpanzees, gorillas, and orangutans into the family Hominidae with humans.
Humans and chimps form a sister group , as do the human/chimp group and gorillas.
Theories of Taxonomy
Both evolutionary and cladistic taxonomy:
Accept monophyletic groups.
Reject polyphyletic groups.
Differ on accepting paraphyletic groups.
Traditional evolutionary taxonomy does.
Phylogenetic systematics does not.
Difference has important evolutionary implications.
Theories of Taxonomy
Current State of Animal Taxonomy:
Modern animal taxonomy was established using evolutionary systematics and recent cladistic revisions.
PhyloCode
New taxonomic system
Being developed as an alternative to Linnean taxonomy.
Replaces Linnean ranks with codes that denote the nested hierarchy of monophyletic groups conveyed by cladograms.
The terms “ primitive, ” “ advanced, ” “ specialized ” and “ generalized ” are used for specific characteristics and not for groups as a whole.
Maximum Parsimony and Maximum
Likelihood
Systematists can never be sure of finding the single best tree in a large data set.
Narrow the possibilities by applying the principles of maximum parsimony and maximum likelihood .
Parsimony
Among phylogenetic hypotheses the most parsimonious tree is the one that requires the fewest evolutionary events to have occurred in the form of shared derived characters.
Occam ’ s Razor
Parsimony
The principle of maximum likelihood states that, given certain rules about how DNA changes over time, a tree can be found that reflects the most likely sequence of evolutionary events.
Phylogenetic Trees as Hypotheses
The best hypotheses for phylogenetic trees are those that fit the most data: morphological, molecular, and fossil.
Molecular Systematics
Much of an organism ’ s evolutionary history is documented in its genome.
Comparing nucleic acids or other molecules to infer relatedness is a valuable tool for tracing organisms ’ evolutionary history.
Major Divisions of Life
Aristotle ’s two kingdom system included plants and animals.
One-celled organisms became a problem
Haeckel (1866) proposed Protista for singlecelled organisms.
R.H. Whittaker (1969) proposed a five-kingdom system to distinguish prokaryotes and fungi.
Major Divisions of
Life
Woese, Kandler and Wheelis
(1990) proposed three monophyletic domains above kingdom level —Eucarya,
Bacteria and Archaea —based on ribosomal RNA sequences.
Major Divisions of Life
More revisions are necessary to clarify taxonomic kingdoms based on monophyly.
“ Protozoa ”
Neither animals nor a valid monophyletic taxon.
“ Protista ”
Not a monophyletic kingdom.
Most likely composed of seven or more kingdoms.
Major Subdivisions of the Animal
Kingdom
Traditional groupings based on embryological and anatomical characters:
Branch A ( Mesozoa ): phylum Mesozoa, the mesozoa
Branch B ( Parazoa ): phylum Porifera, the sponges and phylum Placozoa
Branch C ( Eumetazoa ): all other phyla
Major Subdivisions of the Animal
Kingdom
Branch C ( Eumetazoa ): all other phyla
Grade I ( Radiata ): phyla Cnidaria, Ctenophora
Grade II ( Bilateria ): all other phyla
Division A ( Protostomia ): Protostome characteristics
Acoelomates : phyla Platyhelminthes,
Gnathostomulida, Nemertea
Pseudocoelomates : phyla Rotifera, Gastrotricha,
Kinorhyncha, Nematoda, Nematomorpha,
Acanthocephala, Entoprocta, Priapulida, Loricifera
Eucoelomates : phyla Mollusca, Annelida,
Arthropoda, Echiurida, Sipunculida, Tardigrada,
Onychophora.
Major Subdivisions of the Animal
Kingdom
Division B ( Deuterostomia ): Deuterostome characteristics
phyla Phoronida, Ectoprocta, Chaetognatha,
Brachiopoda, Echinodermata, Hemichordata,
Chordata
Major Subdivisions of the Animal
Kingdom
Recent molecular phylogenetic studies have challenged traditional classification of Bilateria.
Grade II: Bilateria
Division A: ( Protostomia ):
Lophotrochozoa : phyla platyhelminthes, Nemertea,
Rotifera, Gastrotricha, Acanthocephala, Mollusca,
Annelida, Echiurida, Sipunculida, Phoronida, Ectoprocta,
Entoprocta, Gnathostomulida, Chaetognatha, Brachiopoda
Ecdysozoa : phyla Kinorhyncha, Nematoda,
Nematomorpha, Priapulida, Arthropoda, Tardigrada,
Onychophora, Loricifera
Division B ( Deuterostomia ):
phyla Chordata, Hemichordata, Echinodermata