Animal Classification, Phylogeny and Organization
advertisement

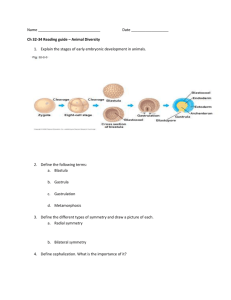
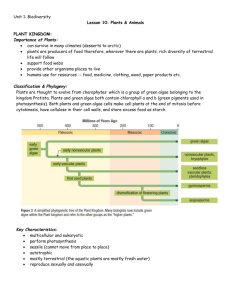
Animal Classification, Phylogeny and Organization Chapter 7 Why do we need Nomenclature? Taxons • • • • • • • • Domain – Eubacteria, Archaea and Eukarya Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Question? • How is DNA evidence of common ancestry? VGT vs HGT • Vertical Gene Transfer – genes transfer from parent to offspring • Horizontal Gene Transfer – genes transfer from one species to another • Base of the tree of life is a net Animal Systematics • Arranging animals into groups to show evolutionary relationships Vocabulary Phylogeny Body Symmetry • • • • • What sort of symmetry do humans have? Asymmetry Bilateral symmetry Radial symmetry Cephalization • How did evolution play a part in this? Patterns of Development • Major stages: fertilization, cleavage, gastrulation, organogenesis • Master control genes: Hox , Pax Cleavage • An embryonic stage that follows fertilization • Characterized by rapid cell division • Ends when cells form a hollow ball called a blastula Gastrulation • Embryonic stage that follows cleavage and blastula formation • Cell movement generates additional inner layers Differentiation • After gastrulation, development begins to differentiate, depending on the organism Vocabulary • Ectoderm – gives rise to the epidermis • Endoderm – gives rise to the tissue that lines the gut cavity • Mesoderm – gives rise to supportive (bone), contractile (muscle) and blood cells • Coelom – gives rise to viscera Protostomes vs Deuterostomes