Dr. Elisar Barbar's Lab - Oregon State University
advertisement

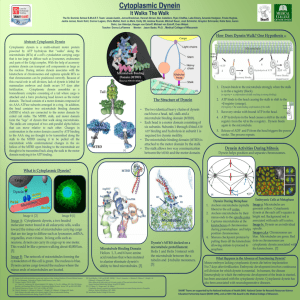
Structural Analysis of Cytoplasmic Dynein Marcus A. Chiodo Dr. Elisar Barbar Biochemistry and Biophysics Department Importance • Dynein transports cargo throughout the cell • Assists organization of cellular components • Plays a major function in cellular division – Segregation of chromosomes Motor Proteins • Motor proteins are the cell’s transportation system • Dynein and Kinesin are the two primary classes of motor proteins – They are powered by ATP and “walk” along microtubules transporting their cargo • Dynein and Kinesin transport cargo in opposing directions and are different structures Dynein • Two classes of dynein – Axonemal dynein • propels beating of cilia and flagella – Cytoplasmic dynein • transports membrane bound vesicles, protein complexes, chromosomes • Cellular organization • Cell Division Cytoplasmic Dynein • A large multi-subunit molecular motor protein – Heavy chains contain the ATP and microtubule binding sites • Cytoplasmic dynein is responsible for transporting cellular cargo to the minus end of microtubules (i.e. toward the centrosome) Light Chain 8 (LC8) • 10.3 kDa subunit of Dynein found in all eukaryotes • Connects the cargo binding proteins to the mobile proteins (heavy chains) • Assists in assemblage of Dynein complex • Free form structure is known Drosophila Swallow (Swa) • Swa is an example of a natural occurring cargo protein in Drosophila cells – Role in localizing bicoid mRNA of the oocyte during oogenesis • Focused on the 206 to 297 amino acid domain of Swa Project Objective • Grow, purify and collect 30mg of LC8/Swa protein • Screen LC8/Swa protein for promising crystallization conditions • Optimize conditions of promising leads from screens • X-Ray diffraction on LC8/Swa crystal to determine protein structure Recombinant Protein Growth Insertion of LC8 & Swa DNA into vector (coexpression) Vector inserted into E. coli bacterium Cell Replication Centrifuge 1. Induction with IPTG 2. Lyse Cells Purification: Affinity Column • The protein has a His-tag that has an affinity towards the divalent Ni ions in the column’s resin • Untagged proteins either have a weaker or no affinity for the Ni compared to the His-tagged protein • Imidazole also has an affinity for Ni and can compete with the protein with the His-tag Affinity Column Process www.bio.davidson.edu/Courses/genomics/method/ Affinity Column Data Size Exclusion Column (SEC) •SEC’s take advantage of porous particles to separate molecules by different sizes and shapes •Smaller molecules can enter the porous particles and therefore have a longer travel path and elution time LC8/Swa SEC Data Intensity (uV) 3600 uV 63 minutes 71 minutes 2000 uV 60 minutes Time (minutes) Crystal Screens •Used Hampton Crystal Screens I and II •Allows 96 different combinations of various salt, precipitant and buffer types, concentrations and pH •Assists in determines starting point for crystallization Crystal Screen Optimization •Determine best lead from the screen •Optimize the selected condition •Let crystallize •Locate best crystal •X-Ray Diffraction What Remains? • Check for crystal on optimized crystal condition • Perform X-Ray Diffraction study • Determine 3-D structure of the LC8/Swa complex Thank You! • • • • • • • • Howard Hughes Medical Institute Dr. Kevin Ahern Dr. Elisar Barbar Dr. Gregory Benson Gretchen Clark-Scannel Yujuan Song Dr. Karplus’ Lab Grant Farr