West Africa - ANDREWSGEOGRAPHY
advertisement

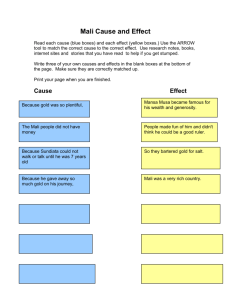
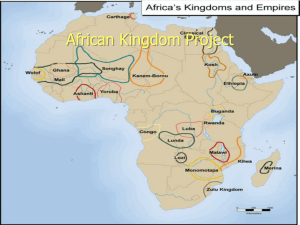
17 Countries 1. Benin 2. Burkina Faso 3. Cape Verde 4. Chad 5. Gambia 6. Ghana 7. Guinea 8. Guinea Bissau 9. Ivory Coast (Côte d'Ivoire) 10. Liberia 11. Mali 12. Mauritania 13. Niger 14. Nigeria 15. Senegal 16. Sierra Leone 17. Togo Atlantic Ocean Sahel Sahara Niger River Senegal River Volta River Benue River Lake Chad West Africa 1/5th of Africa Sahara Sahel Western Sudan Forests General similarities Geography Wetter and more humid than the north Sahel Mauritania, Mali, Senegal, Burkina Faso, Niger, Chad Highest point: Mount Cameroon The rest of W. Africa only reaches heights of 900 feet above sea level Four Main Rivers Senegal River Niger River (longest) 10 countries 7.5% Volta River Benue River Lakes Lake Volta Reservoir that has the largest surface area of any in the world Akosombo Dam Ghana Lake Chad Drying up! Lake Chad Lake Chad Very important Chad, Cameroon, Niger, Nigeria 20 million people Fishing Water Shrank as much as 95% since 1963 Human population expansion Water Stress Overuse of water without being replenished! http://articles.cnn.com/2011-0302/world/shrinking.lake.chad_1_lakechad-lake-regionlocals?_s=PM:WORLD Population Density Highest populations around areas with abundant rainfall and vegetation Slave Trade Nigeria Most populated country in West Africa Geography and Climate History Five sections Prehistory – 12,000 BCE Empires! ○ Internal African Empires Slavery and European Conquest Colonialism Post-Colonial Era Pre-History Drying of West Africa cut the civilizations off from each other Legends, traditions, stories Often unreliable! Empires Ibos ○ Lineage system, family groups, religion ○ Established major economic system Benin Three Trading Kingdoms Ghana Mali Songhai Empires of West Africa Wolof Ghana Mali Ashanti Yoruba Kanem-Bornu Songhai Characterization of Kingdoms No separation of power King, counselors, advisors carried out all levels of government Power based on ability to collect revenue and tribute ○ Sovereignty Centralized states Concentrated in the hands of few people City-States What caused the rise and fall of the West African Kingdoms? What makes a kingdom great? Most of the information that we have about the early African civilization is based on oral traditions. Why should this be so? What advantages are there to oral history as compared to written accounts? What other historical sources might be found to confirm or dispute oral accounts? Natural Resources Salt Gold Cloth Weapons Timber Ghana on the Map AD300 to about 1100 Ghana developed in West Africa between the Niger (NIjhur) and the Gambia Rivers. The rivers helped Ghana to grow rich because they were used to transport goods and develop trade. Ghana also collected taxes from traders who passed through the kingdom. The people called their nation Wagadu; we know it as Ghana --that was the word for war chief. The kingdom of Ghana probably began when several clans of the Soninke people of west Africa came together under the leadership of a great king named Dinga Cisse. Ghana had few natural resources except salt and gold. They were also very good at making things from iron. Ghanaian warriors used iron tipped spears to subdue their neighbors, who fought with weapons made of stone, bone, and wood. Ghana became a rich and powerful nation, especially when the camel began to be used as a source of transport. Ghana relied on trade and trade was made faster and bigger with the use of the camel. THE SILENT TRADE Salt/gold trade savanna areas poor in salt Sahara, rich in salt. Taghaza, salt mining village traders from there carried salt to Jenne and Timbuktu Silent trade took place near the Niger river Arab traders would lay slabs of salt in neat rows pound on drums and invite gold merchants to trade ride off on camels Gold/Salt silent trade Gold merchants would arrive leave a fair amount of gold and withdraw into hiding Arabs would return and if they felt the gold was a fair amount they would take it and leave If not, they would beat their drums and a second round of trading would begin both groups probably wanted to keep the sources of their goods a secret. "The King . . .(wears). . . necklaces round his neck and bracelets on his forearms and he puts on a high cap decorated with gold and wrapped in a turban of fine cotton. He (meets people) in a domed pavilion around which stand ten horses covered with gold-embroidered materials…and on his right, are the sons of the (lesser) kings of his country, wearing splendid garments and their hair plaited with gold. At the door of the pavilion are dogs of excellent pedigree. Round their necks they wear collars of gold and silver, studded with a number of balls of the same metals.“ – Al-Bakri What does this quote tell us about life in Ghana? Islamic Mosque in Ghana blankbluesky.com/ travel/ghana/ After 700 AD, the religion of Islam began to spread over northern Africa. Muslim warriors came into Ghana and fought with the non-Islamic people there. This weakened the great civilization of Ghana. Local warriors then decided to break away from the power of Ghana and form their own local kingdoms. This ended many of the trade networks. This eventually weakened the civilization of Ancient Ghana. Empire of Mali 1235 Mali emerges as a major kingdom Located south of Ghana This kingdom became important when resources became scarce and trade routes shifted This made them wealthy and helped Mali to obtain more power. gold earrings Land of Gold & Griots A griot of today Sundiata: The Lion King Prince of the Mandinka people, who were conquered by Susu In 1230, he conquered the Susu people Ruled from 1230-1255 Under Sundiata, Mali prospered He led the people in conquering and expanding his kingdom to be as great as Ghana had been. Perhaps the greatest king of Mali was Mansa Musa (1312-1337). He developed the gold and salt trade of Mali and his kingdom became very powerful and rich. Mansa Musa MiniFact: Mansa means Emperor or King Several kings ruled after Sundiata’s death Mansa Musa was grandson of Sundiata’s half brother He became the greatest king of Mali in 1312 Under Mansa Musa, Mali became a great trading center Mansa Musa was a Muslim and built many beautiful mosques or Islamic temples in western Africa. This is the mosque at Djenne in Mali. It’s built of mud! The Hajj Mansa Musa was a devout Muslim Muslims must make a journey to Mecca called a ‘hajj’ Mansa Musa crossed Africa to reach Mecca He took a huge caravan with him in 1324 60,000 servants and followers and 80 camels carrying more than 4,000 pounds of gold to be distributed among the poor. Of the 12,000 servants 500 carried a staff of pure gold. After that, everyone knew about the wealth of Mali Mali Five times larger than Ghana! Niger and Senegal Rivers Gold and Salt Trade routes through Middle East, Europe and Asia Niani – capital Timbuktu – major city Timbuktu A very important city in Mali Center of learning for Muslims Universities and schools Largest trading center in Mali On the Niger River ○ Trade ○ Food ○ Washing Timbuktu 19th century traders in Timbuktu What did Mali trade? Gold The dotted lines are trade routes from Mali to other parts of Africa What else did they trade? Camels, the ships of the desert, traveled in caravans bringing to Mali: Salt Copper Ivory Cloth Kola Nuts Slaves Books Shells MiniFact: This was before Columbus even sailed to the New World! Why was Salt Important? The man is holding a slab of salt mined recently near Timbuktu Mali often traded its gold for salt Salt was sometimes more valuable than gold! People’s bodies need salt to live In the desert heat, salt is lost through perspiration Salt was used to preserve food Salt was brought in large slabs (coins) Mali Ancient Religion Animistic Spirit of the Land Increase the growth and quality of the crops. Still followed by Mali people. They believed that the chief of the village had direct contact with the spirit The leader of the village was the secular religious head of the community. They believed through this connection that the land would always provide them enough food and resources to trade Slowly and gradually, Islam became the dominant religion of the country. Several Islamic universities started being established throughout the country and Islam became an integral part of culture, education and trade. The Griots This is a 19th century griot of Mali with his instrument Storytellers were called Griots or djeli They were important people in Mali They told the land’s history Most of what we know about ancient Mali came from the storytellers They were advisors to the kings Griots Storytelling Call and Response Musical phrases Sound Effects Pantomime Scenery/Props When Mansa Musa died there were no kings as powerful as he was to follow. The great kingdom of Mali weakened. Eventually a group of people known as Berbers came into the area and other people came up from the south to claim territory that was once part of the kingdom. Although Mali fell, another advanced African kingdom took its place, the kingdom of Songhai. The Berbers still live in North Africa. This picture, taken in 1893, shows a Berber group. Sunni Ali saw that the kingdom of Mali was weakening and he led his soldiers to conquer the area. He began the kingdom of Songhai. He also set up a complex government to rule all the lands he had conquered. Sunni Ali died in 1492 CE. His son took over the rule of Songhai but he did not accept Islam as a religion. One of Sunni Ali’s generals, named Muhammad Ture, overthrew the new king and made himself king of Songhai. Ture was a follower of Islam (Muslim) and so he made Islam the religion of his kingdom. This is a photo of a mosque in western Africa. Many mosques were built of local materials. Mosques Bobo Dioulasso Songhai remained a rich and strong kingdom under Muhammad Ture’s rule. It had a complex government centered in the city of Gao, and great centers of learning. But later rulers were not as powerful. In the late 1500s, Morocco invaded Songhai to take its rich trade routes. Moroccans had a new weapon, the gun, and the army of Songhai did not. This led to the fall of Songhai. Moroccans Sunni Ali Askia Muhammed continued spread of Islam Judar Pasha – led Moroccans to victory Guns, Germs, and Religion Guns Malaria Islam This map was created in 1375. The same trade routes were used by the merchants of the Songhai kingdom. What kinds of pictures do you see on the map and why do you think the mapmaker put them there? All three kingdoms of West Africa relied on trade for their strength and wealth. Silk, Ceramics, Beads, Islam from Europe and Asia Salt Timbukt Gao u Jenn e Gold, Ivory, Wood, Slaves Coming into West Africa Coming from Africa and going to Europe and Asia Three Trading Empires Ghana, Mali, Songhai Ghana - AD 800 Conquered Ghana Sundiata ○ Warrior king Trade routes across Sahara Gold and salt Mansa Musa ○ Economics and Trade “Ghana” or war chief Traders began to refer to 1235 – Mali the area as “Ghana” Around 1400, Songhai replaced Mali Sunni Ali 1591, Moroccan army invades Colonialism 1472 – Portuguese Trade route to India Encountered Benin empire Pepper, ivory, timber, gold, slaves Ivory Coast, Gold Coast, Slave Coast Niger River Slavery 14-24 million slaves Nigeria Slavery Europeans transported slaves over long distances under inhumane conditions Slaves in Africa had well-defined rights/privileges Slaves in European societies had little to no rights. European slavery affected four continents and lasted for centuries! Europe, Africa, North America, South America Slavery Slave trade began on the Atlantic side of Africa Goree Island (20 million slaves) House system Caused warfare between tribes Age of Enlightenment Question of natural rights of man Somersett v. Knowles (1772) An Inquiry into the Wealth of Nations by Adam Smith (1776) 1807 – Slave trade illegal for British Empire Relations with Europe after Slavery European countries began to make treaties with chiefs NOT to provide slaves Three strategies Attempted to substitute goods from Africa Took over parts of Africa to get the goods Sent in missionaries to “Westernize” Africa Franco-Prussian War of 1870 “Scramble for Africa” European Imperialism What is imperialism? What is a major reason a country would want to colonize another? Imperialism: foreign government governs a territory without significant settlement; Formation of an empire Colonialism: exploiting the resources of the conquered country for the benefit of the conqueror with significant settlement Return to Colonialism Imperialism Colonialism Goods, not people Establish political control “Indirect Rule” “Chiefs” Chiefs Musa Mburi — a village elder — remembered, Before the coming of Europeans we had no chiefs, but when they came they installed chiefs. When they waged wars against any village, the person that stayed behind and did not run away was installed the chief. Another elder recalled, When asked who was their Chief, the people sometimes put forward a man who was the most important man in their village; sometimes (most often) they just looked blank; and sometimes they put forward the village idiot, to see what happened to him. The new chiefs became rich and powerful but, for the average native, colonialism brought forced labor, the loss of land, and taxation. Involvement in World Wars World War I Nigeria “World War I awakened the political consciousness of colonial people” ○ Ideas of liberty and freedom 1918, the first Pan-African Congress issued a resolution: The natives of Africa must have the right to participate in the government as fast as their development permits, in conformity with the principle that the government exists for the natives, and not the natives for the government. Colonial Relations Great Depression Really hurt Africa! World War II Nigerians were called to support Great Britain Atlantic Charter (FDR and Winston Churchill) “the right of all peoples to choose the form of government under which they will live.” Nigerian Trades Union Congress October 1, 1970 Political Crisis Legacy of Colonization Political Instability Modern Borders No consideration for ethnic/linguistic groups Nigeria Religions Islam Christianity (Nigeria, Ghana) Indigenous Religious influence (syncretism) Allegiance to clan’s god African traditional religion Griot West African historian Poet, praise-singer, musician Great Mosque of Djenne Games/Sports/Music Oware Soccer World Cup! Genres Mbalax ○ Jazz, soul, rock Highlife Fuji Afrobeat Kente Boubou – attire Djembe drum Kora Harp-lute West Africa Today: ECOWAS Economic Community of West African States All countries except Mauritania Treaty of Lagos Promote region’s economy West African Monetary Union Stateless Societies Whereas old kingdoms were centralized, today many countries are decentralized Decentralization ruled by elders “Democracies of age” Igbo of Southeast Nigeria Problems of West Africa Sierra Leone 31% literacy rate Civil wars Ghana Economic Map Review Porto Novo, Benin Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso Praia, Cape Verde N’Djamena, Chad Yamoussoukro, Cote d'Ivoire Banjul, Gambia Accra, Ghana Conakry, Guinea Bissau Guinea-Bissau Monrovia, Liberia Bamako, Mali Nouakchott, Mauritania Niamey, Niger Abuja, Nigeria Dakar, Senegal Freetown, Sierra Leone Lomé, Togo Map Review