Growth of African Empires
advertisement

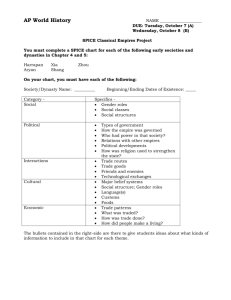
6th Grade UBD - Unit 8 - Growth of African Empires Empires Rise- In West Africa, there were three great empires. They gained power by controlling the gold and salt trades. These three empires controlled the Sahel region of West Africa for more than 900 years. Trading Kingdoms- Other kingdoms developed in Africa based on trade. Some traded in gold, others in rare goods such as ivory and leopard skins. Most participated in the slave trade as well. West Africa was an important supplier of gold during the Middle Ages. Gold was also traded internally among the African Empires. Predict how trade influenced the politics and culture of African Empires? ( 5 minutes) Work with a neighbor and compare your answer with theirs. What things are the same and what things are different? (3 minutes) The oldest fossils of human ancestors have been found in African sites ranging from Ethiopia to South Africa. Stone tools made 2.5 million years ago have also been found in Eastern Africa. Slowly, early humans spread across Africa before migrating to other continents. The humans that remained in Africa became farmers and herders. As the human population in Africa grew, societies became more complex. People began to trade with other regions. The income from trade helped build kingdoms. Gold was mined in the forests of West Africa. It was desired by markets in North Africa and Europe. Trade caravans crossed the Sahara to West Africa, carrying salt and other goods. They returned to North Africa with gold. The empire of Ghana rose in the 300s CE. It grew rich by controlling the gold–salt trade. It was at the height of its power by the 800s CE. The empire of Songhai was the largest of the West African empires. It was also the shortest-lived. It extended over most of the Sahel. Three great African empires grew and flourished between about 800 and 1800. Their strength was founded on controlling trade for the valuable natural resources of salt and gold. Salt is needed to replenish the natural salts lost through perspiration, or sweat, caused by the hot, humid climate of Africa. Salt can also be used to preserve food, or keep it from spoiling. Salt mines, which were an important part of the trade and economy of early African empires, still exist today in Africa. Video- How It's Made Salt Trade brought gold from southern Africa to northern Africa to trade for salt. By taxing this trade and benefiting from it directly, Ghana became the first great African empire, followed by Mali and Songhai. Reading Handout- Gold Mining Key Term Merchant- A person who provides materials, products, or services to a buyer, usually in exchange for money. Key Term Trade- The exchange of goods and services by sale or barter. Key Term Tax- A charge against a citizen's person or property or activity for the support of government. During this time, traders from the north brought Islam to areas in West and Southern Africa. The Mali Empire embraced Islam and built the great Muslim cultural and learning center of Timbuktu. At its largest, the Songhai Empire extended over an area as large as modern Europe and was governed by a provincial system. Empires rose in West Africa. They did this by taking control of trade routes between gold and salt mines. In many ways, these empires were more developed than cultures in western Europe at the time. Trade with Europeans allowed some Africans to gain power over its neighbors. Merchants took advantage of the seasonal monsoon winds. They used ships called dhows to travel long distances across the ocean. The Swahili had much contact with Arab traders. Swahili culture became a mixture of African and Arab culture. The city of Great Zimbabwe controlled the gold trade between gold mines in southern Africa and the city-states on Africa’s eastern coast. Reading Handout- Global Trade in Africa Several smaller cultures benefited from trade with Europe and the Arabian Peninsula, including KanemBornu, Benin, and Aksum. Swahili traders carried religion and language to areas in central and southern Africa. Key Term Dhow- A type of sailboat used in the Indian Ocean and Red Sea trade. It is still used today along the eastern coast of Africa. The great African empires were strongly influenced by the introduction of Islam there around 1000. The pilgrimage of Mansa Musa, the great Muslim leader of the Mali Empire, to Mecca showed the countries of North Africa and the Arabian Peninsula the empire’s great wealth. Video- Islam Comes to Timbuktu Timbuktu, became a center for Islamic culture and education. Later, the Songhai Empire introduced a political system of provinces and individual rulers to manage the large area under its control. The kingdoms of KanemBornu, Benin, and Zimbabwe also grew strong because of trade, and their cultures were greatly influenced by foreign traders from other areas of Africa, as well as Europe and India. Trade between Portugal and Benin resulted in exquisite brass artwork and the introduction of the first guns into Africa. Aksum on Africa’s east coast remained Christian, while trading with many other cultures and Swahili traders established citystates based on trade across the Indian Ocean and incorporated many Arabian words into their native language. The Great Zimbabwe is a spectacular stone ruin of a city made up of three parts. The Great Enclosure is the largest single ancient structure in Africa south of the Sahara. The Hill Complex, begun in 900, is the oldest section. The Valley Ruins include remnants of earthen and mud brick buildings. Key Term Great ZimbabweZimbabwe means “stone houses.” Great Zimbabwe refers to the complex stone city that became a center of trade. Video- Clues to a Culture Reading Handout- The Great Zimbabwe African empires often were built on trade. They influenced and were influenced by their trading partners. These empires were part of a complex web of trade. Trade connected them with other civilizations around the world. What has been the “muddiest” point so far in this lesson? That is, what topic remains the least clear to you? (4 minutes) Work with a neighbor and compare your muddiest point with theirs. Compare what things are the same and what things are different? (3 minutes)





![African_Kingdoms[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009434687_1-f619592414fdc11f51d76c379299de0d-300x300.png)
