January 26-27, 2012: Life Cycle
advertisement

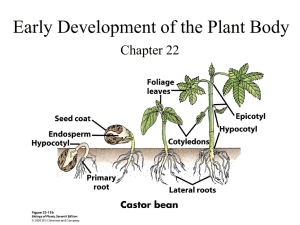
Behavior = the manner in which a person behaves in reacting to social stimuli or to an inner need or to a combination thereof; OR = good manners OR = an activity of a defined organism, especially observable activity when measurable in terms of quantifiable effects on the environment whether arising from internal or external stimuli OR = anything that an organism does that involves action and response to stimulation OR = the response of an individual, group, or species to the whole range of factors constituting its environment Plant Life Cycle: includes stages of dormancy processes of mitosis, cell expansion, differentiation, fertilization (twice!) Plant Development is flexbile: indeterminate, cells toti-potent Corn (Zea mays) produces male flowers (tassel) and female flowers (many make up the ear) the plants can ‘self’ or outcross a pollen grain germinating on a style must extend its tube down the length of the style (12 inches or so) and fertilize the embryo at the end of the style in order to make a kernel (ovule) develop Once and embryo is formed, it can undergo mitosis (cell division), and differentiation to make all the different cell types, tissues and organs of a plant. This process is called development. Development is regulated at three levels: Genetic – by control of the pattern of gene expression, cells determine which proteins, structures and processes are active Internal signaling – signals include ‘hormones’ other metabolites (sugars, peptides) hydraulic and electric signals External signaling light temperature water nutrient biotic interactions Plant ‘hormones’ or growth regulators are active at nM levels. Their activity depends on: 1) rate of synthesis 2) rate of transport to active site 3) receptivity of target/presence of receptor 4) rate of degradation Seeds are like tiny space ships, launched from their mother into space, packed full of food, primed to germinate if or when they land on suitable substrate. Germination: • dormancy must be broken • seed imbibes water • tissues rehydrate • embryo releases GA • aleuroce cells respond to GA • endosperm digested • embryo begins to grow • root elongation followed by shoot/leaves Some seeds require light as a cue for germination. The photoreceptor responsible for this sensory process is Phytochrome – red (660 nm)/far red (730 nm) photoreceptor ‘switch’ phytochrome is a protein with enzyme activity (kinase), bound to a chromophore; when the chromophore absorbs R or FR light, it changes the protein conformation, thus activating/inactivating the enzyme