File - Mr. Westwater's History Class
advertisement

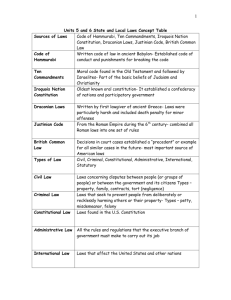
UNIT 3: COURT SYSTEM There are five independent but interrelated parts of the court system. They are…. 1. Judge 2. Prosecution 3. Defense 4. Jury 5. Probation Department SYNONYMS IN THE COURT SYSTEM 1. “Prosecution” District Attorney (D.A.) State People Prosecutor 2. “Defense” Accused Defendant 3. “Attorney” Counsel Lawyer Representation Latin nolo contendere habeas corpus modus operandi First Step in Process #1 Arraignment *your initial (1st) hearing *happens ASAP after arrest *very brief proceeding WHAT HAPPENS AT ARRAIGNMENT? 5 things 1. Charges are read to the accused 2. Rights are explained in detail 3. Attorney requested if already not done so 4. Bail is determined/set 5. Plea is entered MA Law states all accused must first plead not guilty! WHAT EXACTLY IS BAIL? • Definition- money paid to the courts to insure you will make your next and every required court hearing: • Synonym-> “collateral” • Could be required to pay percentage of full amount, payments • Options if can’t afford to pay? BAIL OPTIONS Bond Agent/Bond Company -Agent pays the bail, you are released, you then pay back money with an additional fee. Fee is how they profit. “comparison”-home loan with interest WHAT COULD HAPPEN IF YOU DON’T SHOW UP FOR A COURT APPEARANCE? One possibility is…….. CONDITIONS ASSESSING DENIAL OF BAIL 1. prior record (1st time or lengthy?) 2. circumstances of crime (violent, child) 3. likelihood to flee 4. dangerousness to community 5. likelihood to recommit PERSONAL RECOGNIZANCE What kind of things would “tie” an individual to an area charged with a crime? 1. family 2. job or career/profession? 3. community involvement 4. residence? 8TH AMENDMENT SAYS…… “Excessive bail shall not be required, nor excessive fines imposed, nor cruel and unusual punishments inflicted”. What would you consider cruel and unusual? WHAT IF YOU GOT THE CHANCE TO PLAY THE ROLE OF……… In 4-6 sentences, simulate a statement from one of the following talking about your style as a Judge. Be accurate to your personality! 1. defendant 2. defense attorney 3. prosecutor 4. court reporter PRE-TRIAL PROCEDURES/HEARINGS #1”Arraignment” Then depending what state you are in…… #2 Grand Jury Indictment Or #2 Preliminary Hearing Majority of states Preliminary Hearing Massachusetts? Grand Jury Indictment GRAND JURY INDICTMENT 1. 2. 16-23 people serve on jury Only prosecution presents facts/evidence. Defendant is not present. 3. Majority percentage vote sends to trial process 4. The jury votes whether police had probable cause to arrest. Confirmation of Probable Cause In other words, is there enough evidence against accused to go to trial? PRELIMINARY HEARING 1. Both prosecution and defense present evidence. 2. No jury, judge confirms if law enforcement had probable cause. 3. Defendant is not present. What system would you rather have for Massachusetts? Why? NEXT STEP IS…… DEPENDING ON WHAT STATE.. “Plea Hearing” • Not guilty set date for trial • Guilty immediately to sentencing • Nolo Contendere (“no contest”) can’t be taken to civil trial for same crime, immediately to sentencing WHAT ARE PRE-TRIAL MOTIONS? -They are requests for a separate hearing that either the Prosecution or Defense makes that are not done unless granted. For example.. 1. Continuance- more time to prepare case 2. Examination of Competency- evaluation of defendant if competent to stand trial 3. Change of Venue- change of location of trial because fairness of trial is compromised 4. Suppress Evidence- certain pieces of evidence can not be introduced to jury What word is associated with this??????? JARED LEE LOUGHNER USA TODAY REPORTS • Update at 3:40 p.m. ET January 8th • Rep. Gabrielle Giffords, D-Ariz., has been shot in the head and is in critical condition following a shooting earlier today at an event outside of a Tucson grocery store in her district. • C.J. Karamargin, a spokesman for Giffords, told the Associated Press that the congresswoman was in surgery as of 1 p.m. Arizona time. Karamargin said an unspecified number of Giffords' staff members were injured in the shooting. Karamargin said he had no other information on the conditions of the injured or on the circumstances of the shooting. PLEA BARGAINING PROCESS -Both sides (prosecution/defense) come together and make compromise to avoid going to trial. Prosecution Advantages 1. guilty verdict (victory) 2. save time and money (tax payers/budget) 3. concentrate on cases going to trial Defense Advantages 1. reduced sentence 2. some charges dropped 3. reduced severity of charge(s), for example… ATTORNEY’S RESPONSIBILITIES BETWEEN PLEA HEARING AND 1ST DAY OF TRIAL 1. Review entre police report 2. Review all evidence 3. Interview all witnesses 4. Study case history (precedents set) 5. Interview relevant expert witnesses 6. Background check on all relevant people Months, months, months…..Years? “APPEAL PLEA AGREEMENT 2012” • Supreme Court Ruling 5-4 • Precedent/Case Law set *Any convicted offender can appeal his/her sentence if guilty verdict was reached in spite of plea agreement being offered and refused, and can prove legal counsel did not provide best defense possible with use of the plea agreement. Violation of 6th Amendment • Offender must prove….. 1. offender would have accepted plea agreement if not for legal advice given 2. reasonable probability prosecutor would not have withdrawn offer before trial 3. judge would have accepted offer GIDEON V. WAINWRIGHT (1963) *Clarence Earl Gideon 1961 *arrested on charges of B & E and petty larceny *defended himself in court *5 year sentence in prison *appealed from prison that he was imprisoned illegally Case Law Established: Any indigent defendant cannot be denied the right to counsel. If they request legal representation, they must be provided with. 6th Amendment STEPS OF THE TRIAL Step 1 Opening StatementsBoth sides explain to the judge and jury the evidence to be presented as proof of the allegations against the defendant, or to deny/discredit/create doubt about the allegations Who goes 1st? Prosecution> Burden of Proof STEP 2 Direct Examination by the Prosecution: -Each one of the Prosecution’s witnesses (such as police, experts, eyewitnesses) is questioned. Their testimony is proof against the defendant. STEP 3 Cross Examination by the Defense -The defense will ask questions of the Prosecution’s witnesses. Their goal is to discredit the witness, or create doubt in the minds of the jurors. STEP 4 Motion to Dismiss- At this point, the Defense can request a “motion to dismiss” or ask the judge to render a “directed verdict”, therefore ending the case by dismissing the charges. Not often done. STEP 5 Direct Examination by the Defense: Each defense witness is questioned and evidence is submitted in favor of the defense. Witnesses such as: 1. experts 2. eye witnesses 3. character witnesses STEP 6 Cross Examination by the…….. Prosecution Each defense witness is cross examined. The goal of the questioning is to discredit the witness, or to create doubt in the minds of the jury about the credibility of the witness. STEP 7 Closing Statements by Prosecution then Defense Reviews all evidence, states how the evidence proves or denies allegations, then asks for a guilty or not guilty finding STEP 8 Rebuttal Argument Prosecutor has the right to make additional closing statements Why doesn’t the defense get this????? Burden of Proof falls where? STEP 9 Jury Instructions The judge instructs the jury as to the law(s) that apply to that particular case. He/she also explains their responsibilities in reaching a verdict STEP 10 Jury Deliberations The jury, behind closed doors, discusses the case until they can collectively come to a decision of a guilty or not guilty verdict. Vote must be unanimous STEP 11 Sentencing The Judge issues length of sentence to be served by convicted offender. *Sometimes as a separate hearing TRIAL OBJECTIONS • Leading • Ambiguous or Unintelligible • Compound • Argumentative • Calls for Narrative Answer • Calls for Speculation • Assumes Fact in Dispute or Not in Evidence • Irrelevant • Hearsay • Inadmissible Opinion