managerial accounting
advertisement

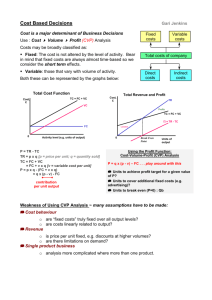
MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING ZCMA 6022 Managerial Accounting Decision Making Managerial accounting process: 1. IDENTIFY 2. MEASURE 3. ANALYZE Controlling Management Accounting Activities 4. INTERPRETE 5. COMMUNICATING Directing Operational Activities Planning OVERVIEW SKILLS TO ACQUIRE • Decision Making • Plan • Directing Operation • Control and Review TOOLS TO BE USED • Costing • Budgeting • Performance Measurement Case Study Group Project Industry of Your Choice 1. F&B Service 2. Manufacturing 3. Healthcare 4. Public Sector 5. Telecommunication 6. Theme Park 7. Plantation & Agriculture 8. Construction 9. Hospitality 10. Transport 11. Energy & Utilities 12. Oil & Gas 13. Retail Content of Report & Presentation 1. Background • Industry • Company 2. 3. 4. 5. Decision making (Based on Individual Assignment) Planning Operation Directions Control **Please note that case study report and presentation is just for illustrative purpose, the amounts need not to be accurate or true however assumptions must be stated clearly Individual Project Industry of Your Choice (Based on Group Project) 1. F&B Service 2. Manufacturing 3. Healthcare 4. Public Sector 5. Telecommunication 6. Theme Park 7. Plantation & Agriculture 8. Construction 9. Hospitality 10. Transport 11. Energy & Utilities 12. Oil & Gas 13. Retail 14. Non Profit Organization Content of Report & Presentation 1. Background (different from group project) • • Industry Company 2. Decision making techniques 3. Role Play Report • • • • • Chairman CFO Manager Assistant Manager Preparer **Please note that case study report and presentation is just for illustrative purpose, the amounts need not to be accurate or true however assumptions must be stated clearly Managerial Accounting • Be creative • Be imaginative BALANCEDSCORECARD Financial Perspective Goals Measurements Customer Perspective Goals Internal Business Process Perspective Measurements Goals Learning and Growth Perspective Goals Measurements Measurements PORTER VALUE CHAIN COSTING Product Cost Product Cost vs Period Cost Product Cost ` Product Cost Type of Production Process Job Shop •Low production •Little standardization •One of a kind product •Eg Film production (Universal Studio) Batch •Multiple products •Low volume •Eg: Heavy Equipment (Caterpillar) Assembly •Few Major Products •Higher Volume •Eg: automotive assembly (Ford) Continuous Flow •High Production •High Standardized commodity products •Eg: production of gasoline (Exonmobile) Production Process Job Order Costing Process costing POR = allocated overhead ($) / anticipated direct labour ($) Job Order Costing Average cost for each distinct production costs Predetermined Overhead Rate = Budgeted Manufacturing Overhead costs Difference in decimal points only __________________________________ Budgeted amount of Cost Driver (or activity based Commonly used cost driver is direct labour hour It can be implemented on company level or department level Difference in decimal points only Process costing Average cost over large number of identical units of product COST CLASIFICATION COST CLASIFICATION COST OBJECT Direct cost Indirect Cost CONTROLLABILITY Controllable cost Uncontrollable cost Cost Behavior Mapping Cost Cost Classification Cost Object Direct Cost Indirect Cost Managers/ PIC Controllability over Cost Controllable Cost Opportunity Cost Sunk Cost Differential Cost Cost In Relation to End Product/ Service Uncontrollable Cost Variable Cost Variable Cost In Tandem Semi Variable = FC + VC Step Variable Cost Fixed Cost Unchanged Marginal Cost & Average Cost Distinction between Cost Fixed Cost Curvilinear Costs Step Fixed Cost Engineered Cost Committed Cost Discretionary Cost Cost Behavior Mapping Cost Behavior : Semi Variable Cost Prediction 1. Account Classification : • Classifies ledger accounts to either a. b. c. Fixed cost Variable cost Semi-variable cost 2. Visual-Fit Method • Suitable for semi-variable cost a. b. c. d. Plot observation Scatter diagram Intercept = FC VC = Semi-Variable Cost (-) FC Cost Estimation 3. High-Low Method • Use for semi-variable cost approximation a. Variable Cost Per unit = (HIGHEST COST - LOWEST COST ) / (HIGHEST ACTIVITY - LOWEST ACTIVITY 4. Least Square Regression Method a. Y = a + b1X1 5. Multiple Regression Method a. Y = a + b1X1+ b2X2 6. Engineering Method a. b. How much needed and how much it cost Not relying so much on historical data AccountClassification Visual-Fit Method High-Low Method Least Square Regression Method Multiple Regression Method Engineering Method Cost Estimation Visual-Fit Method Account Classification Method Note: ACM and VFM main different is ease of explanantion, however, both method are not objective, as professional judgement differs for analyst Cost Estimation Visual-Fit Method High-Low Method Note: HLM and VFM are almost similar, the differences are: (1) use of available data, (2) objectivity of report outcome Cost Estimation Note: LSRM and VFM are almost similar, the differences are: (1) approach to draw a line (statistical vs visual), (2) objectivity of report outcome Visual-Fit Method Least Square Regression Method Cost Estimation Least Square Regression Method Y = a + b1X1 Multiple Regression Y = a + b1X1+ b2X2 Cost Estimation Account Classification easy to use for simple organization more complex to explain without in depth experience on the expenditure may get varied analysis due to dependencies of professional judgement Engineering Method forward looking comprehensive information of activities involved and cost involved lack of objectivity : eg: two cost analyst may give to different report Time Consuming and expensive Cost Estimation Account Classification easy to use for simple organization more complex to explain without in depth experience on the expenditure may get varied analysis due to dependencies of professional judgement Visual-Fit Method Easy to explain with sufficient knowledge, analyst is able to spot outliers lack of objectivity : eg: two cost analyst may give to different report Cost Estimation High-Low Method easy to use for simple organization only uses high and low points of data lack of objectivity Visual-Fit Method Easy to explain with sufficient knowledge, analyst is able to spot outliers lack of objectivity : eg: two cost analyst may give to different report Cost Estimation Least Square Regression Method Y = a + b1X1 Easy to explain with sufficient knowledge, analyst is able to spot outliers Make use of all available data objective outcome economic plausibility Goodness of fit (R2) Visual-Fit Method Easy to explain with sufficient knowledge, analyst is able to spot outliers Make use of all available data lack of objectivity : eg: two cost analyst may give to different report Cost Estimation Least Square Regression Method Y = a + b1X1 Easy to explain with sufficient knowledge, analyst is able to spot outliers Make use of all available data objective outcome economic plausibility Goodness of fit (R2) Multiple Regression Y = a + b1X1+ b2X2 Easy to explain with sufficient knowledge, analyst is able to spot outliers Make use of all available data objective outcome more complex and requires more statistical capabilities economic plausibility Goodness of fit (R2) Prediction Sales Prediction Cost Prediction Engineered Cost Discretionary Cost Committed Cost Cost Changed in total as the level of activity/ production varies Unchanged in total as the level of activity/ production varies Variable Cost Material Fixed Cost Labour Labour Support Activities Overhead Manufacturing Overhead Manufacturing Overhead COST Cost of Goods/ Services Direct Material Direct Labour Raw Material WIP Indirect Material Finished Goods Manufacturing Overhead Indirect Labour Other Manufacturing Cost Service Dept cost Premium overtime Idle time Setup cost etc NOTE: the same concept as manufacturing can be replicated with service industries with relevant customization to type of service COSTING ADVANCED COSTING METHODS Activity Based Costing (ABC) Target Costing Life Cycle Costing Stage : Implementation Back-Flush Accounting Throughput Accounting Variable Cost vs Fixed Cost Total Cost Cost Per unit 6,000 Fixed Cost 5,000 Variable Cost 1 Material Cost 2 Labour Cost 5 10 5000 4,000 4000 3,000 3000 2,000 2000 1,000 1000 Units Produced 6000 15 Manufacturing Overhead Cost 0 1 2 3 4 5 Units Produced Material Cost Labour Cost Manufacturing Overhead Cost 6 Financial Accounting Reporting to interest Organization Cost Stakeholders Managerial Accounting Cost Management Service Raw Material Manufacturing Conversion Cost Cost of Goods Sold Raw Material WIP Inventory Finished Goods Cost of Goods Sold ABC vs Traditional ABC Traditional ABC vs Traditional ABC Traditional • Volume based costing system • Over costing high volume product lines • And under costing complex line Traditional product costing system • Volume based costing system • Or Throughput based costing system • BASED ON BUDGETED LABOUR HOURS MANUFACTURING OVERHEAD RATE = Total Budgeted Manufacturing Overhead ---------------------------------------Total Budgeted Labour Hours ABC system • Technique that allocates overheads based on the activities that drives the cost Cost Pool 1 Manufacturing Overhead Cost Pool 2 Total Overhead Cost Pool 1 Customer Overhead Cost Pool 2 Cost Driver Rate = Total Cost Pool Overheads -----------------------------------Total COST DRIVERS ABC Cost Pool Cost Drivers ABC & ABM Preparer (ABC) Reviewer (ABM) • To decide • To identify: • new product or services to develop • existing products/services curtail or drop • products/ services should be promoted • overhead costs to target • Non value added activities • Non value added costs • Customer Profitability Analysis CVP analysis • Breakeven Point (BEP) (units and $) doesn’t convey how profit changes as activity changes • Graph 1. CVP graph – over FC 2. CVP graph – over VC 3. Profit-Volume graph shows BEP Shows Profit and Loss areas • Sensitivity Analysis • Safety Margin (MOS) • Operating Leverage CVP analysis BEP Sensitivity Analysis Margin of Safety CVP Income Statement Traditional Income Statement doesn’t disclose breakdown between FC / VC/ Semi-Variable Cost Contribution Income Statement highlights distinct values of FC/ VC/ Semi-VC Highlights CVP relationships Able to identify Cost Structure (Cost domination – VC or FC) CVP Analysis - Breakeven Breakeven Point ($) 1. Contribution Margin Approach Breakeven Point (unit) 1. Contribution Margin Approach 2. Formula 2. Formula CVP Analysis - Breakeven Breakeven Point ($) 1. Contribution Margin Approach Breakeven Point (unit) 1. Contribution Margin Approach 2. Formula 2. Formula CVP Graph CVP graph over FC CVP graph over VC CVP Graph CVP graph over FC Profit Volume Graph CVP Analysis – Income Statement CVP Analysis – Income Statement - ABC Cost Behavior Mapping Industry Cost Estimation Method(s) Complexity of Processes Cost Behavior Mapping Value Chain Production Process Mapping CVP analysis Assignment Group Assignment: Organization of your choice 1. All the steps are for Final Presentation Project, unless otherwise stated Industry Cost Estimation Method(s) Complexity of Processes Cost Behavior Mapping Value Chain Production Process Mapping Individual Assignment: 1. Cost Estimation Methods Other Semi Individual Assignment: 1. Role Play 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. BOD CEO Operation Manager Financial Controller External Stakeholder CVP analysis