Prevention Wellbeing - North East Lincolnshire Clinical
advertisement

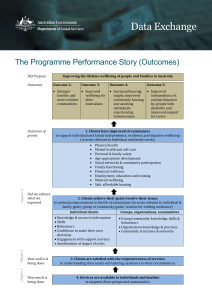
CARE ACT SEMINAR PREVENTION & WELLBEING Correct as at March 2015 THE CARE ACT http://youtu.be/NKEm83eUBzM WHAT THE ACT SAYS ABOUT PREVENTION AND WELLBEING • Duty to promote wellbeing • Duty to prevent or reduce the need for care and support • Duty to provide information and advice Wellbeing Care Act definition • The wellbeing principle applies in all cases where the council is either carrying out a care and support function or making a decision in relation to a person • Applies to adults, carers, children, their carers and young carers • It applies equally when the council has delegated the responsibility SO WHAT IS WELLBEING....... • • • • • • • A persons whole welfare Common expectations across all agencies delivering Local Authority functions It forces a shift from “fitting” people into services towards “meeting a need” it involves thinking differently. No hierarchy unless dictated by the individual Applies to every function delivered by all statutory and related commissioned services Underpins the whole Care Act Need a preventive “system" to be able to deliver WELLBEING MUST DO’S • LA’s MUST promote wellbeing when carrying out any care and support function in respect of a person, “this is any process, activity or broader responsibility that LA’s performs”. • LA’s MUST have regard to any other key principles when carrying out care and support functions e.g.. Mental Health Act, • The wellbeing principle/key principles apply equally to those with care and support needs, and their carers (and in some circumstances to those in transition) • LA’s must consider how to meet each person’s specific needs rather than simply considering which service they will fit into. • The wellbeing principle/key principles should inform the delivery of universal services which are provided to all people in the local population. Identifying gaps and smart commissioning. • Although the wellbeing principles/key principles apply specifically when LA’s perform an activity /task , or make a decision in relation to a person, the principles should also be considered when LA undertake broader strategic functions e.g. town planning KEY WELLBEING AREAS IMPORTANT TO PEOPLE: • • • • • • • • • personal dignity (including treatment with respect) physical and mental health and emotional wellbeing protection from abuse and neglect control by the individual over day-to-day life (including over care and support provided and the way it is provided) participation in work, education, training or recreation social and economic wellbeing domestic, family and personal relationship suitability of living accommodation the individual’s contribution to society EXERCISE 1: What does Wellbeing mean to your job role? • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Customer and business support services Strategy and policy Commissioning and procurement Street cleansing Housing Social case work Mental health activity Community Nursing Home Care Support staff Residential and Nursing Care providers Intermediate Tier assessment and provision staff Finance Safeguarding Carers Single Point of Access and Triage WHY IS THIS DIFFERENT? • Shift of emphasis from providing services to meeting needs • Places individual’s wishes at the centre of decision making • Enables co-production when meeting need SOME IMPLICATIONS FOR SOCIAL CARE FUNCTIONS • A local authority should be able to evidence that it has considered each case on its own merits, considered what the person wants to achieve, and how the action which the local authority is taking may affect the wellbeing of the individual • During the assessment process, for instance, the local authority should be able to evidence that it has explicitly considered the most relevant aspects of wellbeing to the individual concerned, and assess how their needs impact on them. THE BLOBS AND THE SQUARES • http://vimeo.com/42332617 • http://vimeo.com/42332617 WHAT IS PROMOTING WELLBEING? • actively seeking improvements in the principles Connect to people around you… 5 WAYS TO WELL-BEING Be active, discover an activity that matches your ability… Give… Keep learning… Take notice of what is going on in your community… 5 WAYS TO WELL-BEING • Connect with everyone around you. With family, friends, neighbours and colleagues. Invest time in developing these cornerstones of life. • Be Active go for a walk or run. Step outside. Cycle. Play a game, garden, dance. Exercising makes you feel good. Discover a physical activity that suits your mobility and level of fitness. • Take Notice Be curious. Catch sight of the beautiful. Remark on the unusual. Notice the changing seasons. Savour the moment. Enjoy what you eat. Be aware of the world around you. • Keep learning Try something new. Rediscover an old interest. Sign up for that course. Take on a different responsibility at work. Fix a bike. Learn to play an instrument. Learn to cook something new. Set a challenge you will enjoy achieving. • Give Do something nice for a friend or a stranger. Thank someone. Smile. Volunteer your time. Join a community group. Look out as well as in. Seeing yourself and your happiness, linked to the wider community can be incredibly rewarding and creates connections with the people around you. PREVENTION • • • Duty of councils to prevent the need for care and support Linked to duty to provide information and advice Prevention can be: Primary e.g. providing access to universal services. Secondary – targeted to groups at higher risk Tertiary – minimising the effect of disability PREVENTION – SCOPE • • • Includes carers Guidance suggests that councils need to be clear about what is already provided Identification of the access points and those individuals most in need of support • Recently bereaved people Adults returning from hospital Admissions/returns from prison Benefit recipients People who have changed housing Those accessing private health care and support Need to prepare a clear local approach to prevention – agenda is much wider than adult social care Includes public health, transport, housing, leisure PREVENTION MUST DO’S A local authority MUST take steps, which it considers will: (a) (b) (c) (d) contribute towards preventing or delaying the development by adults in its area of needs for care and support contribute towards preventing or delaying the development by carers in its area of needs for support reduce the needs for care and support of adults in its area reduce the needs for support of carers in its area A local authority MUST have regard to: • • • the importance of identifying services, facilities and resources already available in the authority’s area and the extent to which the authority could involve or make use of them in performing that duty; the importance of identifying adults in the authority’s area with needs for care and support which are not being met (by the authority or otherwise); the importance of identifying carers in the authority’s area with needs for support which are not being met (by the authority or otherwise). PREVENTION • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=18549Ifz Lzw&sns=em PREVENTION CATEGORIES Preventing, reducing and delaying needs • Primary: Universal, relates to services aimed at individuals who have no particular health or social care needs, they are services which could help an individual to avoid developing needs by maintaining their health and independence. • Secondary: More targeted interventions aimed at individuals and their carers who have an increased risk of developing needs, where a provision may help to slow down or reduce further deterioration. • Tertiary: These services are aimed at individuals and their carers to minimise an impact of a disability or deterioration in health. Includes supporting people to regain skills, includes re ablement and supporting carers to be able to continue to care. PREVENTION • At every intervention, must consider how to prevent, reduce or delay “need” • In order to promote wellbeing we must focus on delaying and preventing care and support needs, and supporting people to live as independently as possible for as long as possible. HEALTHY LIVES HEALTHY FUTURES “SHIFTING TO THE LEFT” WHAT ARE WE DOING LOCALLY TO MEET PREVENTION AND WELLBEING AGENDA • • • • • • • • Personal asset based and solution focussed approach – “Connect programme” focus Health and Wellbeing Board – partnership Public Health - NELC Building and releasing community capacity - NELC and CCG Improving access to information and advice – NELC and CCG Development of S4Me and e-market place - joint Single Point of Access and Information - joint approach Healthy Lives Healthy Futures: HLHF DISCUSSION POINTS • What do these requirements mean for the council, CCG and wider partners? • What are the key areas we need to strengthen? • Do we have the infrastructure to do this? • Do you have any suggestions? • What else can we do locally? TO TAKE AWAY WITH YOU..... • • • • Care Act slides Couple of scenarios Building and releasing community capacity Services4me leaflet TO TAKE AWAY...... BUILDING COMMUNITY CAPACITY • • • • • • Change Champions Preventive Services Market Reshaping Board (PSMRB) market reshaping for community and voluntary sector Good Neighbours Board - Good Neighbours and Good Friends – stay young and stay together in North East Lincolnshire Health and Wellbeing Collaborative - voluntary led - encourage people to improve their health and well-being and overall lifestyle Employability – supporting people into employment Hope Street Rehabilitation Service RELEASING COMMUNITY CAPACITY & GOOD NEIGHBOURS • • • • • • • • Multi agency and community membership Increasing community capacity Croft Baker Haverstoe Humberston and New Waltham Park Scartho Waltham PREVENTIVE SERVICES MARKET RESHAPING • Foresight – Gym • Red Cross – first call • YMCA Counselling Service CHANGE CHAMPION COURSE HIGHLIGHTS • • • A three day over three month intensive and practical course. Gives the participants the skills and confidence to set up and deliver interventions in their area. 12 Change Champion Cohorts have started up with almost 200 participants to date and a range of new initiatives. 9 cohorts have now graduated and are continuing to use their skills to bring about improvement and to support others. Programmes they are working on: • Time Banking • Older People’s activities • Dementia education for practices, dementia friendly surgeries and a sleep pilot for people with dementia and their carers • Family support training - managing stress, cooking • A reminiscence project • Raising awareness of dementia services in the community • Inter – cultural older people activities • Developing a social enterprise to fund subsidised activities to develop sewing skills. Working with Mental Health services and the private sector. • Developing young people’s clothing recycling. Developing musical activities for young people • Pulmonary rehab services for people in the community & a falls service in sheltered accommodation Change Champion graduates in calendar photo shoot. Presented by: Ros Davey Head of Demand Management & Communities (FOCUS) Caroline Barley Prevention and Well Being Manager (NELC) For further comments / queries: NELCCG.workforce-FAQ@nhs.net