lecture6
advertisement

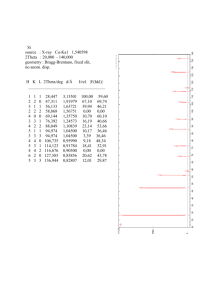
1. Diffraction intensity 2. Patterson map Lecture 6 2-1-2006 Calculation of the electron density r(x,y,z) We already know: This is equivalent to: Because: F is a Fourier synthesis of r The reverse is also true: or r is a Fourier synthesis of F This two Fourier syntheses form the mathematic foundation for all crystallographic calculation Physical meaning of Fourier synthesis Scattering --First Fourier Transform Focusing ----Second Fourier Transform An simple example of Fourier transform f=2 + By superimposing three cosine waves, we have f=3 = + If we have more higher frequency terms, we have f=5 Symmetry in diffraction pattern • A diffraction pattern possesses at least the same or higher symmetry than the crystal – Remember that reciprocal lattice rotates with the crystal itself. • All diffraction patterns have a center of symmetry I(h,k,l) = I(-h, -k, -l) These two reflections are called a Friedel pair. • From diffraction intensity, we should be able to determine space group symmetry in most cases (symmetry of diffraction pattern, systematic absences) Symmetry in diffraction pattern: a center of symmetry Therefore, Symmetry in diffraction pattern: a center of symmetry - electron density r is a real quantity Because The implication is: Which means r is real, as expected for a physical quantity. Space groups with screw axes, glide planes, F, C, I centered lattices will have systematic absences. Effect of the size of the unit cell on the diffraction intensity V is the volume of unit cell Vcr is the size of crystal l is wavelength Experimental data look like this … h k l F 0 1 2 25 1 0 3 14 -1 2 3 14 -2 1 2 11 1 2 1 10 3 -2 0 23 3 1 3 19 a h,k,l are miller indices, F is structure factor amplitude No phase information. Intensity statistics: Rmerge • Only a small number of reflections are collected on each photograph • To construct the reciprocal space, we need to merge reflections from different frames. • Measurement error is quantitatively described by Rmerge R = I (hkl) - / I (hkl) Where hkl are miller indices of a particular reflection, and i is the ith measurement of that reflection • Rmerge varies from a few percent in low resolution ranges to over thirty percent in high resolution ranges Intensity statistics: what are the important quantities Intensity statistics: Wilson plot • • After data merging, the first thing to do is to calculate the Wilson plot Wilson provide an estimation of temperature factor Because we have If ri ≠ rj, 2pi(ri-rj)S will vary from 0 to 2p, resulting in 0 value for I(abs, S) Therefore, and we know then we have With some adjustments, then we have Intensity statistics: Wilson plot • • After data merging, the first thing to do is to calculate the Wilson plot Wilson provide an estimation of temperature factor Slope => B factor Y intercept => absolute scale C However, for 2pi(ri-rj)S to vary from 0 to 2p, S has to be at least 1/3Å-1 What is phase problem? Electron density can simply be calculated as: However, we can only measure I(hkl), and we can only get |F(hkl)|=sqrt(I). The phase information a(hkl) is missing. Structure determination is all about phase determination. Methods for phase determination Molecular replacement (MR) • Only one native crystal is needed. One homologous structure must be available. Quick and simple. Multiple isomorphous replacement (MIR) • Use heavy atom to perturb diffraction intensities Hg Pt • At least one native crystal and two crystals soaked in U two heavy atom solutions must be available. • Need no information about the unknown structure. Multiwavelength anomalous dispersion (MAD) Se (S Se) • As X-ray wavelength approaching absorption edge, anomalous scattering occurs – Friedel pairs are no longer equal in intensities. • Only one crystal is needed but multiple data sets must be collected at three different wavelengths. • Se-Met protein is usually needed. Excellent electron density map. The first crystal structure of a protein molecule • 1962: Max Ferdinand Perutz and Sir John Cowdery Kendrew win the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their studies on the structures of globlular proteins. • The structure of myoglobin was solved by MIR. (Max Perutz, 1914-2002) Patterson function In 1934, Patterson published a paper suggesting that the Patterson function: giving rise to a map showing interatomic vectors (not individual atomic positions, though) The three variables u, v, w vary from 0 to1 within the crystal unit cell. No phase information is needed for Patterson synthesis Pattern map shows intermolecular vectors There are a total of N2 vectors, of which N are located at the origin, and N2-N are distributed throughout the volume of the unit cell. If atom i contains Zi electrons and atom j contains Zj electrons, the corresponding vector rij will have a weight proportional to ZiZj. Patterson map has a center of symmetry. The space group of patterson map may be derived from crystal space group by adding a center of symmetry and losing translational elements associated with screw axes or glide planes. Pattern map shows intermolecular vectors By definition: Because: we have: Pattern map shows intermolecular vectors another example Patterson maps often have serious overlapping of peaks 1-D 1. Peaks are generally broad 2. N2 –N peaks in total 2-D Simple structures can be solved from Patterson maps Space group Pm: (x,y,z) and (x,-y,z) There will be a set of vectors between symmetry-related atoms at: (0,2y, 0) in Patterson map. Simple structures can be solved from Patterson maps • Space group symmetries usually give rise to concentrated vector points in the forms of Harker lines or Harker planes • Example: space group P21 – General positions are: (x,y,z), (-x, y+1/2, -z) – Interatomic vector for symmetry-related atoms is: (2x, ½, 2z) – There will be a lot of vector on v=1/2 section in Patterson map – v=1/2 is called Harker section – From Harker peaks, we can obtain x and z coordinates for every atom Patterson map in protein crystallography • Locate heavy atom positions for multiple isomorphous replacement method or multiwavelength anomalous dispersion method • Rotation and translation function searches for molecular replacement method