handout_phasing
advertisement

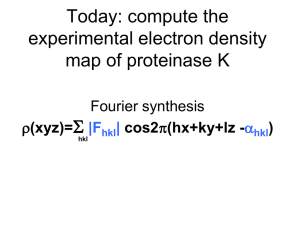
Phasing Goal is to calculate phases using isomorphous and anomalous differences from PCMBS and GdCl3 derivatives --MIRAS. How many phasing triangles will we have for each structure factor? For example. FPH = FP+FH for isomorphous differences For example. FPH* = FP+ FH* for anomalous differences -h-k-l hkl -h-k-l 4 Phase relationships PCMBS FPH = FP+FH for isomorphous differences PCMBS FPH* = FP+ FH* for anomalous differences -h-k-l GdCl3 GdCl3 hkl -h-k-l FPH = FP+FH for isomorphous differences FPH* = FP+ FH* for anomalous differences -h-k-l hkl -h-k-l PCMBS FPH = FP+FH for isomorphous differences Imaginary axis |FPH| |Fp | Real axis FH Harker construction for SIR phases. FP –native measurement FH (hkl) calculated from heavy atom position. FPH(hkl)–measured from derivative. Point to these on graph. SIR Phasing Ambiguity PCMBS FPH* = FP+ FH* for anomalous differences -h-k-l hkl -h-k-l Imaginary axis Isomorphous differences Anomalous differences FH(-h-k-l)* Fp (hkl) Real axis FH(hkl) We will calculate SIRAS phases using the PCMBS Hg site. FP –native measurement FH (hkl) and FH(-h-k-l) calculated from heavy atom position. FPH(hkl) and FPH(-h-k-l) –measured from derivative. Point to these on graph. Harker Construction for SIRAS phasing (Single Isomorphous Replacement with Anomalous Scattering) GdCl3 FPH = FP+FH for isomorphous differences Imaginary axis Isomorphous Deriv 2 Anomalous Deriv 1 Fp (hkl) Real axis Isomorphous Deriv 1 Harker Construction for MIRAS phasing (Multiple Isomorphous Replacement with Anomalous Scattering) GdCl3 FPH* = FP+ FH* for anomalous differences -h-k-l hkl -h-k-l Imaginary axis Isomorphous Deriv 2 Anomalous Deriv 1 Isomorphous Deriv 1 Fp (hkl) Real axis Anomalous Deriv 2 Harker Construction for MIRAS phasing (Multiple Isomorphous Replacement with Anomalous Scattering) Barriers to combining phase information from 2 derivatives 1) Initial Phasing with PCMBS 1) Calculate phases using coordinates you determined. 2) Refine heavy atom coordinates 2) Find Gd site using Cross Difference Fourier map. 1) Easier than Patterson methods. 2) Want to combine PCMBS and Gd to make MIRAS phases. 3) Determine handedness (P43212 or P41212 ?) 1) Repeat calculation above, but in P41212. 2) Compare map features with P43212 map to determine handedness. 4) Combine PCMBS and Gd sites (use correct hand of space group) for improved phases. 5) Density modification (solvent flattening & histogram matching) 1) Improves Phases 6) View electron density map Center of inversion ambiguity Remember, because the position of Hg was determined using a Patterson map there is an ambiguity in handedness. The Patterson map has an additional center of symmetry not present in the real crystal. Therefore, both the site x,y,z and -x,-y,-z are equally consistent with Patterson peaks. Handedness can be resolved by calculating both electron density maps and choosing the map which contains structural features of real proteins (Lamino acids, right handed a-helices). If anomalous data is included, then one map will appear significantly better than the other. Patterson map Use a Cross difference Fourier to resolve the handedness ambiguity With newly calculated protein phases, fP, a protein electron density map could be calculated. The amplitudes would be |FP|, the phases would be fP. r(x)=1/V*S|FP|e-2pi(hx+ky+lz-fP) Answer: If we replace the coefficients with |FPH2-FP|, the result is an electron density map corresponding to this structural feature. r(x)=1/V*S|FPH2-FP|e-2pi(hx-fP) What is the second heavy atom, Alex. When the difference FPH2-FP is taken, the protein component is removed and we are left with only the contribution from the second heavy atom. This cross difference Fourier will help us in two ways: 1) It will resolve the handedness ambiguity by producing a very high peak when phases are calculated in the correct hand, but only noise when phases are calculated in the incorrect hand. 2) It will allow us to find the position of the second heavy atom and combine this data set into our phasing. Thus improving our phases. Phasing Procedures 1) Calculate phases for site x,y,z of PCMBS and run cross difference Fourier to find the Gd site. Note the height of the peak and Gd coordinates. 2) Negate x,y,z of PCMBS and invert the space group from P43212 to P41212. Calculate a second set of phases and run a second cross difference Fourier to find the Gd site. Compare the height of the peak with step 1. 3) Chose the handedness which produces the highest peak for Gd. Use the corresponding hand of space group and PCMBS, and Gd coordinates to make a combined set of phases. Lack of closure e=(FH+FP)-(FPH) FH-calculated from atom position FP-observed FPH-observed e is the discrepancy between the heavy atom model and the actual data. Why is it not zero? Phasing power |FH|/ e = phasing power. e=(FH+FP)-(FPH) The bigger the better. Phasing power >1.5 excellent Phasing power =1.0 good Phasing power = 0.5 unusable Rcullis e/|FPH|-|FP|= Rcullis. e=(FH+FP)-(FPH) Kind of like an Rfactor for your heavy atom model. |FPH|-|FP| is like an observed FH, and e is the discrepancy between the heavy atom model and the actual data. Rcullis <1 is useful. <0.6 great! Figure of Merit 0 270 0 + + 90 180 270 + + 90 180 0 + + 270 180 Phase probability distribution How far away is the center of mass from the center of the circle? 90 Density modification A) Solvent flattening. • Calculate an electron density map. • If r<threshold, -> solvent • If r>threshold -> protein • Build a mask • Set density value in solvent region to a constant (low). • Transform flattened map to structure factors • Combine modified phases with original phases. • Iterate Density modification B) Histogram matching. • Calculate an electron density map. • Calculate the electron density distribution. It’s a histogram. How many grid points on map have an electron density falling between 0.2 and 0.3 etc? • Compare this histogram with ideal protein electron density map. • Modify electron density to resemble an ideal distribution. Number of times a particular electron density value is observed. Electron density value HOMEWORK