development ppt2
advertisement

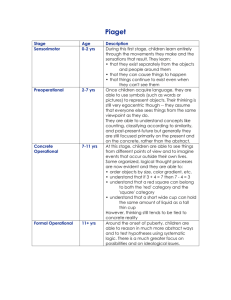
* Developmental Psychology * prenatal development * physical development * cognitive development * social/moral development * * 3 phases * germinal stage = first 2 weeks * conception, implantation, formation of placenta * embryonic stage = 2 weeks – 2 months * formation of vital organs and systems * fetal stage = 2 months – birth * bodily growth continues, movement capability begins, brain cells multiply * age of viability * *Jean Piaget (1920s-1980s) *Assimilation/ Accommodation *4 stages and major milestones *Sensorimotor *Object permanence *Preoperational *Centration, Egocentrism *Concrete Operational *Decentration, Reversibility, Conservation *Formal Operational *Abstraction * cognitive development through stages * driving force behind development: making sense of our experiences * schemas * assimilation * accommodation * *sensorimotor stage * birth to 2 years * infants know the world mostly in terms of their sensory impressions and motor activities * object permanence * the awareness that things continue to exist even when not perceived *preoperational stage * age 2 to 6-7 * child learns to use language but does not yet comprehend the mental operations of concrete logic * conservation * properties such as mass, volume and number remain the same despite changes in the form of objects * lacking in the preoperational stage * centration * the tendency to focus on just one feature of a problem, neglecting other important aspects * egocentrism * the preoperational child’s difficulty taking another’s point of view *concrete operational stage * age 6 to 7-11 * children gain the mental operations that enable them to think logically about concrete events * understand conservation and mathematical transformations *formal operational stage * beginning at age 12, person can think logically about abstract concepts * thinking about actual experience to thinking about imagined reality and symbols * children construct their knowledge * development can not be separated from its social context * learning can lead development * language plays a central role in mental development * scaffolding * zone of proximal development * *attachment * * : an emotional tie with another person, shown in young children by their seeking closeness to the caregiver and showing distress on separation intense parent/child bond * stranger anxiety * * infants’ fear of strangers 8 months * critical period * an optimal period shortly after birth when an organism’s exposure to certain stimuli or experiences produces optimal development * * secure attachment * 60% of infants * explore environment in mother’s presence, distressed when she leaves, seek contact when she returns * insecure attachment * less inclined to explore environment * persistent distress when she leaves and/or indifference when she returns * temperament * a person’s characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity * *parenting styles * authoritarian * parents set rigid rules, enforce strict punishments, and rarely listen to their child’s point of view * authoritative * parents set firm rules, make reasonable demands, and listen to their child’s viewpoint while still insisting on responsible behavior * permissive * parents set few rules, make minimal demands, and allow their children to reach their own conclusions * * Stage theories, three components * progress through stages in order * progress through stages related to age * major discontinuities in development * Erik Erikson (1963) * Eight stages spanning the lifespan * Psychosocial crises determining balance between opposing polarities in personality * social tasks and challenges of adolescence * psychosocial stages: * Erikson’s theory that individuals pass through eight developmental stages, each involving a crisis that must be successfully resolved * * trust vs. mistrust * a totally dependent infant will develop an optimistic, trusting attitude toward the world depending on whether his biological needs are adequately met by his caregivers and sound attachments are formed * autonomy vs. doubt and shame * child aged 2-3 years must begin to regulate some behavior, taking some personal responsibility for feeding, dressing, and bathing. The child will develop a sense of self-sufficiency or a sense of personal shame and self-doubt depending on whether his efforts are met with approval or dissatisfaction * initiative vs. guilt * a child aged 3-6 years begins to take initiative that conflicts with parental wishes. Overcontrolling parents may instill feelings of guilt and damage self-esteem. Supportive parents encourage emerging independence while providing appropriate controls. * industry vs. inferiority * a child aged 6 – puberty extends social functioning beyond the family. The child must learn that productivity is valued in this sphere to achieve a sense of competence, or he will develop a sense of inferiority. * identity vs. role confusion * from ages 12- 20, the major task is to build a consistent identity, a unified sense of self. Failure of teens to achieve a sense of identity results in role confusion and uncertainty about the future * intimacy vs. isolation * from ages 21 – 40, the major task is to achieve intimacy (deeply caring about others and having meaningful experiences with them). Otherwise, we experience isolation, feeling alone and uncared for in life. * generativity vs. stagnation * from age 45 – 65, adults need to express their caring about future generations by guiding/mentoring others or producing creative work that enriches the lives of others. Failing this, people become stagnant and preoccupied with their own needs and comforts. * integrity vs. despair * from age 65 to death, people who look back on their lives with satisfaction develop a sense of wholeness and integrity. Those in despair look back with regret and disappointment in the lives they have led. * * Kohlberg (1976) * Reasoning as opposed to behavior * Moral dilemmas * Measured nature and progression of moral reasoning * 3 levels, each with 2 sublevels * Preconventional * Conventional * Postconventional * nature and nurture * continuity and stages * stability and change *