Acids and Bases 2 - MAH-SBHS
advertisement

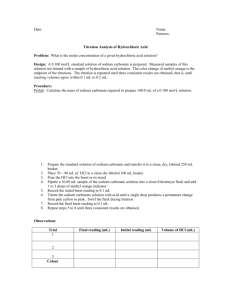
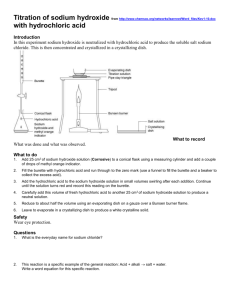
How would you write the name of the following compounds ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Zn(OH)2 NaOH HCl Mg(NO3)2 What does an acid do to red litmus? What does an acid to do blue litmus? How can we tell the pH of a substance? Ions – table of ions open in work book Flame test The Lab Everyday Life ACIDS: Hydrochloric acid – HCl Nitric acid – HNO3 Sulfuric acid – H2SO4 Ethanoic acid – CH3COOH ACIDS: Tartaric acid Citric acid DNA Carbonic acid BASES: Sodium hydroxide – NaOH Potassium hydroxide – KOH Calcium hydroxide – Ca(OH)2 Ammonia – NH3 BASES: Magnesium hydroxide Limestone Garden lime Baking soda Indicator COLOUR In acidic solution In neutral solution In alkaline solution Litmus Paper (red or blue) Red stays red Blue turns red Red stays red Blue stays blue Red turns blue Blue stays blue Universal Indicator Red, orange, yellow Green Blue, purple (B FOR BLUE & BASIC) When an acidic solution is mixed with an alkaline solution a NEUTRALISATION reaction occurs H+ ions in acid, react with OH- of the base forming water H+ + OH- H2O HCl solution – mixed with NaOH Some H+ reacted not all – solution still acidic Complete neutralisation when all the H+ have reacted with OHFINAL SOLUTION WILL CONTAIN Na+ and Clions – evaporation = NaCl crystals In your lab group ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ At least 8 test tubes Two beakers Universal Indicator Test tube rack ◦ Challenge: Create the best looking rainbow of pH using your acids (HCl) and base (NaOH) ◦ Use the neutralisation reaction Acid + Base = ??? What is an ionic compound? When writing ionic formula does the metal change its name of the non-metal? Acid + Base = ???? + ???? Write the salts formed from the following reactions (word equation) ◦ Sulfuric Acid + Sodium Hydroxide ◦ Hydrochloric acid + Potassium Hydroxide ◦ Nitric Acid + Sodium Hydroxide ◦ Write ionic formula for the salts produced ◦ ION QUIZ ACID + BASE → SALT + WATER e.g. hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide → sodium chloride + water HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H 2O e.g. sulfuric acid + potassium hydroxide → potassium sulfate + water H2SO4 + 2 KOH → K2SO4 + H20 Acid Formula Salts Hydrochloric HCl Chlorides Sulfuric H2SO4 Sulfates Nitric HNO4 Nitrates Ethanoic CH3COOH Ethanoates 1.Nitric acid + Sodium hydroxide Sodium nitrate 2.Sulfuric acid + Potassium hydroxide Potassium sulfate 3.Hydrochloric acid + Magnesium oxide Magnesium chloride 4.Ethanoic acid + Sodium hydroxide Sodium ethanoate ACID + BASE → SALT + WATER Question: What sorts of compounds act as bases in this case Answer: Metal oxides and metal hydroxides MgO CuO Fe2O3 ZnO Mg(OH)2 Cu(OH)2 Ca(OH)2 NaOH KOH (1) Hydrogen chloride + Magnesium oxide → Magnesium chloride + Wa 2 HCl + MgO → MgCl2 + H2O (2) Nitric acid + Sodium hydroxide + → Sodium nitrate + Water HNO3 + NaOH → NaNO3 + H2O (3) Sulfuric acid + Calcium hydroxide → Calcium sulfate + Water H2SO4 + Ca(OH)2 → CaSO4 + 2 H2O 1. Hydrochloric acid + Zinc oxide → Zinc chloride + wate 2. Nitric acid + Copper oxide → Copper Nitrate + water 3. _____ + Sodium hydroxide → Sodium sulfate + water 4. Hydrochloric acid + Iron oxide → ___________ + water 1. Hydrochloric acid + Zinc oxide → Zinc chloride + wat 2 HCl + ZnO → ZnCl2 + H2O 2. Nitric acid + Copper oxide + → Zinc nitrate + water 2 HNO3 + CuO + → Cu(NO3)2 + H2O 3. Sulfuric Acid + Sodium hydroxide → Sodium sulfate + wa H2SO4 + 2 NaOH → Na2SO4 + 2H2O Iron chloride 4. Hydrochloric acid + Iron oxide + → ___________ + wa 6 HCl + Fe2O3 → 2 FeCl3 + 3 H2O 1. Antacid (“anti-acid”) tablets • Stomach acid (HCl) causes heartburn • “Quick-eze” contain a base, magnesium hydroxide - Mg(OH)2 • The base neutralises the stomach acid, relieving the symptoms of hear Hydrochloric acid + Magnesium hydroxide → Magnesium chloride + water 2. Toothpaste and tooth decay Bacteria on our teeth produce acids as part of their metabolism The acid wears away the enamel on our teeth Toothpaste is basic, this helps to neutralise the acid and prevent tooth d Past exam paper: Epsom salt has the chemical formula MgSO4. It can be prepared by reacting an acid with magnesium hydroxide a) Give the chemical name for MgSO4 b) Name the acid used in this reaction c) Write the word equations for the preparation ofMgSO4 d) This reaction is described as a neutralisation reaction: Explain what is meant by neutralisation reaction Past exam paper: Epsom salt has the chemical formula MgSO4. It can be prepared by reacting an acid with magnesium hydroxide a) Give the chemical name for MgSO4 Magnesium sulfate b) Name the acid used in this reaction Sulfuric acid c) Write the word equations for the preparation of MgSO4 Magnesium hydroxide + sulfuric acid = magnesium sulfate + water a) This reaction is described as a neutralisation reaction: Explain what is meant by neutralisation reaction 1. H+ 2. red 3. litmus 4. atomic number 5. ion 6. metal 7. CO328. NO39. sulfate 10. sulfuric acid 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Sodium hydroxide alkali base OHpositive CH3COOH (NH4)2CO3 negative HCO3Al2O3 ClLi+ Mg2+ Zn2+ Fe3+ NH4+ Ca2+ O2- CO32- SO42- HCO3- OH- Cl- O2- CO32- SO42- Li+ LiCl Li2O Li2CO3 Li2SO4 Mg2+ MgCl2 MgO MgCO3 MgSO4 Mg(HCO3)2 MgOH2 Zn2+ ZnCl2 ZnO ZnCO3 ZnSO4 Zn(HCO3)2 Zn(OH)2 Fe3+ FeCl3 Fe2O3 Fe2(CO3)3 Fe(HCO3)3 Fe(OH)3 NH4+ NH4Cl (NH4)2O (NH4)2CO3 (NH4)2SO4 NH4HCO3 NH4OH Ca2+ CaCl2 CaO CaCO3 CaSO4 Ca(HCO3)2 Ca(OH)2 Fe2(SO4)3 HCO3- OHLiHCO3 LiOH ACID + CARBONATE → SALT + WATER + CARBON DIOXIDE e.g. Hydrochloric acid + Calcium carbonate → Calcium chloride + w + carbon dioxide NB – This also occurs with BICARBONATES (Hydrogen carbonates) ACID + REACTIVE METAL → SALT + HYDROGEN GAS e.g. Sulfuric acid + Magnesium → Magnesium sulfate + hydrogen 1. Hydrochloric acid + Calcium carbonate → Calcium _____ + water + 2. Nitric acid + Copper carbonate → Copper _____ + water + CO2 3. Sulfuric acid + Sodium carbonate → Sodium _____ + water + CO2 4. Ethanoic acid + Zinc carbonate → Zinc _____ + water + CO2 Below is an example of what? Blue is for.... Red is for... Acid + Carbonate -- Write the colour changes when copper carbonate was heated. Exam question in the past Heat Copper carbonate in a test tube Heat till colour change Add Sulfuric Acid (up to first article) Filter Solution we will leave to evaporate so put in evaporation dish Clean Up Baking powder This contains baking soda (sodium hydrogen carbonate) and an acid (usually tartaric acid) in powder form. When the baking powder is added to water, the baking soda and the acid react, producing CO2 gas and making the cake rise! Fizzy tablets – like Berocca These contain an acid and a carbonate in powder form When the tablet gets wet, the acid and carbonate react together to form CO2 – the fizzy bubbles Limestone caves: Limestone is composed of calcium carbonate Caves form when acidic rainwater dissolves the limestone, forming cracks and fissures The limestone reappears underground as stalactites and stalagmites Acid + Carbonate demo Equations from the experiments (EVERYONE NEEDS TO GET!!) Mark using marking sheet Once finished: Mind map of atoms and acids and bases topic Team Quiz