classification notes handout
advertisement

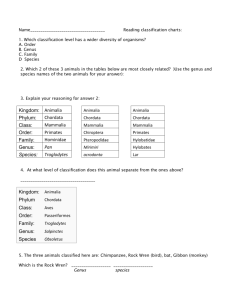
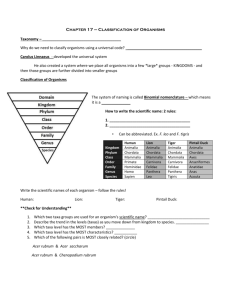
Classification Taxonomy A way of organizing living organisms Showing ancestral relationships History • Linnaeus – Swiss – lived in the late 1700’s • Devised our scheme of taxonomy – naming living organisms • Binomial naming scheme – 2 Latin-word name – Genus (small group of similar organisms) – Species (Specific name within that group) Why do we classify? • Different regions call the same animal by different names • Panther, mountain lion, cougar - all the same animal called by different names regionally – Puma concolor • What is the animal’s genus? • Species? • Organizational scheme by similar qualities into groups of related organisms Mammals • What qualities do all mammals share? Warm-blooded, nurse their young, bear live young, have fur • Homologous structures…… – Remember from before – whale, bat, cat, human forearm – we are all MAMMALS – These structures help to show common ancestry and relatedness Relationships All Mammals Lion Leopard Which are more closely related? How do we know Rabbit How classification schema show these relationships: Lion Animalia Chordata Mammalia Carnivora Felidae Panthera P. leo Leopard Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species • • • • • • • Animalia Chordata Mammalia Carnivora Felidae Panthera P. pardus Rabbit Animalia Chordata Mammalia Lagamorpha Leporidae Oryctolagus O. cuniculus How to remember the levels • Kingdom - (animal, Plant, Fungus, Archaea) Kinky • Phyum ( chordate/non-chordate) » • Class • Order • Family - • Genus – • Species – Presidents does it have a backbone? Can aves, reptilia) (mammal, (carnivore, Oftenrodentia, ungulate, Primate) (felidae [cats], canidae [dogs], Find hominidae [humans] Good (leo, panthera, felis) Panthera Sex pardus (leoplard) How many different classes are represented in this chart? How many Orders are represented in this chart? Is a catbird more like a chicken or a lion? How do you know from the classification chart? What kind of animal is a catbird – how do you know from the chart? 5- Kingdoms • Plantae – Can produce their own food from sun and carbon dioxide. Cells have cell walls for support • Animal – take in food and nutrients from other sources. No cell walls – animals have bones for support • Fungus – obtain food through decomposing other organic material • Bacteria – Single cell or unicellular. - No nucleus • Protists – single cell organisms – some are animallike, some plant-like, some fungus-like What does this cladogram show about the relationship of the 5 animals? Which Kingdom? • Make their own food • Unicellular • Decomposers 3 Domains • Eukaryotes – organisms with cells with a nucleus to hold DNA • We are eukaryotes as are plants • Prokaryotes – have no nucleus – DNA is free floating • Bacteria are prokaryotes • Archeae – Similar to prokaryotes – recently put it their own domain