Document
advertisement

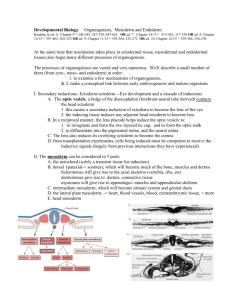
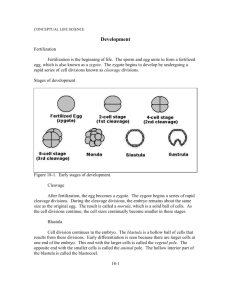
Embryology Review Embryology Embryology – study of origin and development in utero—prenatal formation, growth and differentiation Prenatal period Embryonic period – first 8 weeks Fetal period – remaining 30 weeks Embryonic Period Fetal Period The Embryonic Period Week 1 – from zygote to blastocyst Fertilization (Conception) – in lateral third of uterine tube Zygote (fertilized oocyte) moves toward the uterus Blastomeres – daughter cells formed from zygote through mitotic division called cleavage Morula – solid cluster of 12–16 blastomeres Blastocyst – fluid-filled embryonic stage– ~ 60 cells The Embryonic Period Events in first week Zygote 4-cell Morula Early blastocyst Late blastocyst— implantations occur at this stage Fertilization and the Events of the First 6 Days of Development Week 2 – Blastulation Two-layered embryo formation Bilaminar embryonic disc – inner cell mass divided into two sheets Epiblast and the hypoblast Together they make up the bilaminar embryonic disc Week 2 – Blastulation Amniotic sac – formed by an extension of epiblast Outer membrane forms the amnion Inner membrane forms the amniotic sac cavity The cavity is filled with amniotic fluid Week 2 – Blastulation Yolk sac – formed by an lateral extension of hypoblast Digestive tube forms from yolk sac NOT a major source of nutrients for embryo Tissues around yolk sac gives rise to earliest blood cells and blood vessels Implantation of the Blastocyst Implantation of the Blastocyst Implantation of the Blastocyst Disorders of implantation Ectopic pregnancy Tubal— 95% Peritoneal Douglas pouch Pracental previa -Placenta forms at the inner cervical os -Characterized with uterine bleeding Week 3 – Trilaminar embryo Primitive streak – raised groove on the dorsal surface of the epiblast Gastrulation – a process of invagination of epiblast cells Begins at the primitive streak Forms the three primary germ layers Week 3 – Tri-laminar embryo Three Germ Layers Endoderm – formed from migrating cells that replace the hypoblast Mesoderm – formed between epiblast and endoderm Ectoderm – formed from epiblast cells that stay on dorsal surface Note that all layers derive from epiblast cells Week 3: The Primitive Streak Week 3 – Tri-laminar embryo Week 3: Notochord formation Primitive node – a swelling at one end of primitive streak Notochord forms from primitive node and endoderm Notochord – defines body axis Is the site of the future vertebral column Appears on day 16 Week 3: Notochord and Mesoderm Week 3: Notochord and Mesoderm Week 3: Neurulation Neurulation – ectoderm starts forming brain and spinal cord Neural plate – ectoderm in the dorsal midline thickens Neural groove – ectoderm folds inward Week 3: Neurulation Neurulation (continued) Neural tube – a hollow tube pinches off into the body Cranial part of the neural tube becomes the brain Folic acid deficiency at this stage causes neural tube defects Week 3: Neurulation Neural crest Cells originate from ectodermal cells Forms sensory nerve cells Induction Ability of one group of cells to influence developmental direction of other cells Week 3: Mesodermal differentiation Somites – Body segementation Paraxial mesoderm Intermediate mesoderm – begins as a continuous strip of tissue just lateral to the paraxial mesoderm Week 3: Mesodermal differentiation Lateral plate – most lateral part of the mesoderm Coelom – becomes serous body cavities Somatic mesoderm – apposed to the ectoderm Splanchnic mesoderm – apposed to the endoderm Parts of the mesoderm Neurulation and notocord Neuralation and notocord Week 4 – Embryonic folding Folding of embryo laterally and at the head and tail Embryonic disc bulges; growing faster than yolk sac Primitive gut – encloses tubular part of the yolk sac Site of future digestive tube and respiratory structures Week 4 – The Body Takes Shape Week 4 – Folding Derivatives of the germ layers Ectoderm forms Brain, spinal cord, and epidermis Endoderm forms Inner epithelial lining of the gut tube Respiratory tubes, digestive organs, and urinary bladder Notochord – gives rise to nucleus pulposus within intervertebral discs Week 4 – Folding and systemic development Mesoderm – forms Muscle Bone Dermis Connective tissues Mesoderm differentiates further and is more complex than the other two layers Week 4 – System development Mesoderm (continued) Somites divides into Sclerotome Dermatome Myotome Intermediate mesoderm forms Kidneys and gonads Week 4 – System development Mesoderm (continued) Splanchnic mesoderm Forms musculature, connective tissues, and serosa of the digestive and respiratory structures Forms heart and most blood vessels Somatic mesoderm – forms Dermis of skin Bones Ligaments Derivatives of Germ Layers Figure 3.10 The Germ Layers in Week Four Week 5-8 – Organogenesis Limb buds form Embryo first looks recognizably human (week 8) Head is disproportionately large All major organs are in place Fetal period- summary Fetal period- summary Fetal period- summary