PPT slides
advertisement

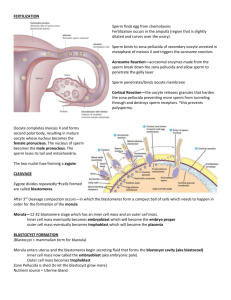
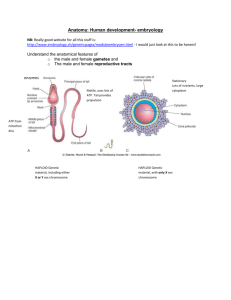
Neurulation in the chick, after the node regresses Typical vertebrate organization of the chick embryo (and >200 selector gene domains) “Somatic mesoderm” “Visceral mesoderm” Notochord **Or wait until the embryo lifts off the yolk sac Extra-embryonic membranes of the chick Amnion and chorion: contain ectoderm and somatic mesoderm Yolk sac and allantois: contain enododerm and visceral mesoderm Chick development: Formation of the allantois Human or mouse embryo: pre-implantation stages 2. 2Blastocyst cavity formation 3. Cell sorting (hypo vs. epi) 4. hatching 128 cell Day 7-human Day 5.5-mouse 1. compaction gene expression starts 128-cell blastocyst compaction 128-cell blastocyst Mouse pre-implantation stages: compaction, apical-basal polarization, cleavage, blastocyst cavity formation Compaction at the late 8-cell stage, With apical-basal polarization of cells Human 128cell blastocyst before/during hatching Oct4 gene expression in epiblast “zona” Holding pipet Injection pipet Injection of ES cells into the blastocyst cavity Mouse embryonic stem cells (ES cells) from the inner cell mass, growing in a culture dish Dr. Mario Capecchi-1984 Univ. of Utah (random) (e.g., GFP with promoter) Mouse transgenesis (insertion of a foreign gene into the mouse genome) non-homologous integration FOSTER MOTHER (2x) Green ES cells Gene for red fluorescent protein (RFP) Gene for green fluorescent protein (GFP) from jellyfish Implantation of the human blastocyst in the uterine wall. Mouse implantation is also invasive, like human Syncytiotrophoblast Maternal tissue Uterine fluid Role of the AVE (anterior visceral endoderm) in establishing the anterior-posterior axis of the mouse embryo Day 5.25 Day 5.5 Day 6.25 Cylindrical Symmetry Otx2 Anterior neural ectoderm Nodal, Vg1, Cripto (co-receptor For Nodal and Vg1) Endo-mesoderm induction Cerberus (anti-Nodal) Dkk (anti-Wnt) Lefty (anti-Nodal) Bilateral Symmetry A P or hypoblast Epiblast ectoderm Endo-mesoderm induction, Primitive streak Nodal, wnt, brachyury, fgf expressed