01-Skeletal System PP
advertisement

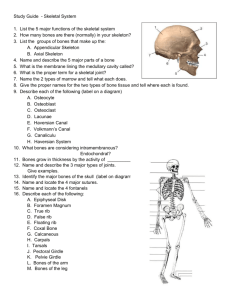
Skeletal System Objectives: A. Recognize the interdependence of major systems of an animal’s body; B. Describe types of bones and connective tissue along with their function C. Classify types of joints in a skeleton D. Label bones on a skeleton diagram OBJECTIVE A- Recognize the interdependencies of major systems of an animal’s body What makes a car run? OBJECTIVE A- Recognize the interdependencies of major systems of an animal’s body The secret is… there are several systems. If one system fails, the automobile will not function properly or may not function at all. Animals are much like cars in that they are composed of a variety of interdependent systems. OBJECTIVE A- Recognize the interdependencies of major systems of an animal’s body What does interdependent mean? Systems that mutually depend on each other to work. OBJECTIVE A- Recognize the interdependencies of major systems of an animal’s body Can only one system function on it’s own? Why or Why Not? Read article on Boneless Chicken and discuss. OBJECTIVE B-Describe types of bones and connective tissue along with their function The Skeletal System • Provides the frame and support for all the other systems and organs. • What is the purpose of a skeletal system??? This system is made up of cartilage, bones, and connective tissue. OBJECTIVE B-Describe types of bones and connective tissue along with their function Cartilage • is composed of firm tissue that is not as hard as bone and is somewhat flexible. EXAMPLES: Nose & Ears OBJECTIVE B-Describe types of bones and connective tissue along with their function Long Bones • Are the longest bones • Provide support for the body giving it the rigidity (hardness) necessary to stand and move. EXAMPLES: Leg Bones OBJECTIVE B-Describe types of bones and connective tissue along with their function Where are short bones located? OBJECTIVE B-Describe types of bones and connective tissue along with their function Short Bones • Are mostly found in the joints and serve as hinges. • They help cushion shock and protect long bones by being flexible • Are often as big around as they are long EXAMPLES: ankles OBJECTIVE B-Describe types of bones and connective tissue along with their function What is an example of an irregular bone? OBJECTIVE B-Describe types of bones and connective tissue along with their function Irregular Bones • Function as support and protection • Are irregularly shaped. EXAMPLE: Vertebrae These bones make up the backbone, which is not a single bone, but a series of irregular bones. They flex and bend to give the animal movement. The vertebrae are divided into several different areas: Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral, and Coccygeal OBJECTIVE B-Describe types of bones and connective tissue along with their function Cervical Vertebrae-The section in the neck from the skull to the first rib. Thoracic-extends along the rib cage. Each of these has a rib attached to each side. For Your Information: Cattle have 13, Horses have 18, and Pigs have 13-14 dependent on breed. OBJECTIVE B-Describe types of bones and connective tissue along with their function Lumbar-The area of the spinal column from the last rib to the pelvis. Also referred to as the loin. For Your Information: If you have ever judged sheep, you may have measured this region with your hand. Animals with a long lumbar region are desirable, as this is where some of the most valuable cuts of meat come from. OBJECTIVE B-Describe types of bones and connective tissue along with their function Sacral-Extends through the pelvic area. The bones in this region are fused together to form a rigid section called the sacrum- providing an attachment for the pelvis. Coccygeal- The vertebrae that continue from the pelvis to the end of the tail. For Your Information: The bones at the top of the tail are larger than the bones at the end. The size tapers until the ones at the end have no channel. OBJECTIVE B-Describe types of bones and connective tissue along with their function Flat Bones: • are relatively thin and flat • They usually help to protect organs • Usually multiple bones fused together EXAMPLE Skull- is composed of flat bones. These bones encase the brain and protect it. Pelvis- OBJECTIVE B-Describe types of bones and connective tissue along with their function On the Cow Skeleton, color the following: Red- Long bones Green- Short bones Grey- Flat Bones Irregular Bones: Purple- Cervical Pink- Thoracic Blue- Lumbar Orange- Sacral Yellow- Coccygeal OBJECTIVE C-Classify types of joints in a skeleton How are joints classified? OBJECTIVE C-Classify types of joints in a skeleton Joints are connections of bone in the animal’s body to make up the skeletal system. The connections are held together by bands of tough tissue called ligaments that bind the bone to the joints. Ligaments give the joints flexibility and serve as shock absorbers to protect the ends of bones. They are classified by the way they move… OBJECTIVE C-Classify types of joints in a skeleton Classifications of Joints: Hinge Gliding Ball & Socket Joint Video Clip OBJECTIVE C-Classify types of joints in a skeleton On the Horse Skeleton, draw a shape around the following joints: Triangle- Hinge joint Circle- Ball & Socket joint Square- Gliding OBJECTIVE C- Label bones on a skeleton diagram OBJECTIVE C- Label bones on a skeleton diagram OBJECTIVE C- Label bones on a skeleton diagram Bell Quiz 1- What is the definition and purpose of a flat bone? 2- Describe a long bone and give an example. 3- What is the definition of interdependence? Give an example of 2 interdependent systems. 4- What type of bones give movement and flexibility? 5- What is the name of the vertebrae that are found in an animal’s loin.