Non-Ruminant Digestion
advertisement

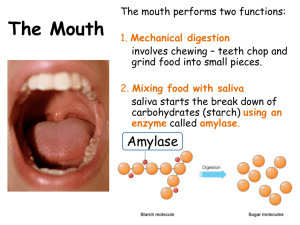
Non-Ruminant Digestion What are Non-Ruminants? • Animals with digestive systems that have a simple stomach structure, also called a monogastric system – Most animals are classified as omnivores or carnivores The Non-Ruminant System Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine Anus The Non-Ruminant System • Mouth – Collects and chews feed and vegetation – Teeth • Carnivores – Sharp teeth for tearing and ripping • Omnivores – Sharp teeth and flat molars for tearing and grinding The Non-Ruminant System • Salivary Glands – Secretes digestive enzymes – Provide lubrication for swallowing The Non-Ruminant System • Esophagus – Connects mouth to stomach – Unidirectional • Forceful regurgitation may occur in some animals when sick The Non-Ruminant System • Stomach – Glandular pouch that mixes and churns feed – Secretes gastric juices and enzymes to aid in food particle breakdown The Non-Ruminant System • Pancreas – Produces and secretes enzymes • Aids in the digestion of carbohydrates and fats • Liver – Lobed reddish brown organ – Produces bile (greenish in color) • Aids in the digestion of fats • Gall Bladder – Storage sac for bile from liver • Secretes bile into small intestine The Non-Ruminant System • Small Intestine – Secretes intestinal juices • Pale watery substance from the intestinal wall – Protein digestion – Buffers hydrochloric acid from the stomach – Digests and absorbs nutrients The Non-Ruminant System • Small Intestine Sections – Duodenum • Secretion of intestinal juices, pancreatic enzymes and bile to further digest food – Jejunum • Digestion • Absorption of nutrients – Ileum • Absorption of nutrients The Non-Ruminant System • Cecum – Non-functioning blind pouch found in-between the small intestine and large intestine • Large Intestine – Absorbs water and adds mucus to undigested feed The Non-Ruminant System • Rectum – Internal sphincter which controls excretion • Anus – External sphincter which controls excretion The Non-Ruminant System Large Intestine Small Intestine Anus Pancreas Duodenum Stomach Salivary Glands Ileum Mouth Rectum Jejunum Cecum Gall Bladder Liver Esophagus Lobed reddish brown organ, produces bile (greenish in color), aids in the digestion of fats Secretes intestinal juices digests and absorbs nutrients Secretes digestive enzymes provides lubrication for swallowing Secretion of intestinal juices, pancreatic enzymes and bile to further digest food, 1st section of small intestine Connects mouth to stomach unidirectional Glandular pouch that mixes and churns feed, secretes gastric juices and enzymes Collects and chews feed and vegetation Produces and secretes enzymes, aids in the digestion of carbohydrates and fats Who has sharp teeth for tearing and ripping? Absorbs water and adds mucus to undigested feed Storage sac for bile from liver, secretes bile into small intestine Who has sharp teeth and flat molars for tearing and grinding? Internal sphincter which controls excretion Absorption of nutrients 3rd section of small intestine Non-functioning blind pouch found in-between the small intestine and large intestine External sphincter which controls excretion Digestion and absorption of nutrients nd 2 section of small intestine The Non-Ruminant System