N1822
advertisement

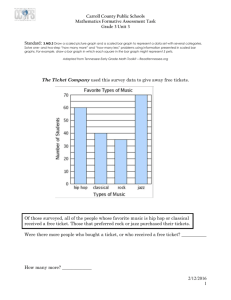
TS 18661 Part 4 Supplementary Functions WG 14 N1797 2014-04-07 Math functions IEC 60559:2011 specifies and recommends these math functions: exp exp2 exp10 [−∞, +∞] expm1 exp2m1 exp10m1 [−∞, +∞] log log2 log10 [0, +∞] logp1=log1p log2p1 log10p1 [−1, +∞] hypot(x, y) [−∞, +∞] × [−∞, +∞] rSqrt = 1/√x [0, +∞] compound(x, n) = (1 + x)n [−1, +∞] × Z Math functions (2) rootn(x, n) = x1/n pown(x, n) = xn pow(x, y) = xy powr(x, y) = xy sin cos tan sinPi(x) = sin(π × x) and cosPi(x) = cos(π × x) tanPi(x) = tan(π × x) [−∞, +∞] × Z [−∞, +∞] × Z [−∞, +∞] × [−∞, +∞] [0, +∞] × [−∞, +∞] (−∞, +∞) (−∞, +∞) [−∞, +∞] Math functions (3) atan2Pi(y, x) asin acos atan atan2(y, x) sinh cosh tanh asinh acosh atanh [−∞, +∞] × [−∞, +∞] [−1, +1] [−∞, +∞] [−∞, +∞] × [−∞, +∞] [−∞, +∞] [−∞, +∞] [+1, +∞] [−1, +1] Math function binding • Some IEC 60559 math functions already in C11 • TS adds the rest, in Library 7.12 Mathematics and Annex F • Also, for completeness tanpi asinpi acospi [−∞, +∞] [−1, +1] • TS does not require IEC 60559-specified correct rounding • Names with cr prefixes reserved for correctly rounded verisons, e.g., crsin for correctly rounded sin function Math function binding (2) • Added tgmath macros for new functions • Reserved names for complex versions of new functions, for binary floating types Math function names • Added logp1 equivalent to log1p – For consistency with log2p1 and log10p1 – And to avoid the confusing log21p and log101p • Used compoundn for compound(x, n) – Because of existing compound(x, y) extensions – Fits with scalbn(x, n) and others • Otherwise used IEC 60559 names, without camelCase (IEC 60559 does not require using its names) Math function special cases • IEC 60559 and C11 Annex F treat special cases the same • New functions follow same principles • TS follows C11 style for specifying math errors in 7.12 Sum reductions IEC 60559:2011 specifies and recommends sum reduction operations on vectors p and q of length n: sum(p, n) Σi=1,npi dot(p, q, n) Σi=1,npi × qi sumSquare(p, n) Σi=1,npi2 sumAbs(p, n) Σi=1,n|pi| Scaled products IEC 60559 specifies and recommends scaled product reduction operations: compute without over/underflow pr = scaled product and sf = scale factor such that result product = pr × radixsf scaledProd(p, n) scaledProdSum(p, q, n) scaledProdDiff(p, q, n) ∏i=1,npi ∏i=1,n(pi + qi) ∏i=1,n(pi – qi) Reduction function names IEC 60559 sum dot sumSquare sumAbs scaledProd scaledProdSum scaledProdDiff TS 16881-4 reduc_sum reduc_sumprod reduc_sumsq reduc_sumabs scaled_prod scaled_prodsum scaled_proddiff Reduction function interfaces double reduc_sum ( size_t n, const double p[static n] ); double scaled_prod ( size_t n, const double p[static n], intmax_t * restrict sfptr ); Arrays indexed 0 to n - 1 IEC 60559 reductions • Result values not fully specified like other IEC 60559 operations • Implementation can (re)order operations and use extra range and precision, for speed and accuracy • Must avoid over/underflow, except if final result of sum reduction deserves over/underflow Reduction special cases • Follows general principles for special cases, e.g., – reduc_sum(n, p) returns a NaN if any member of array p is a NaN. – reduc_sum(n, p) returns a NaN and raises the “invalid” floating-point exception if any two members of array p are infinities with different signs. – Otherwise, reduc_sum(n, p) returns ±∞ if the members of p include one or more infinities ±∞ (with the same sign). Reduction special cases (2) • For scaled product: – scaled_prod(n, p, sfptr) returns a NaN if any member of array p is a NaN. – scaled_prod(n, p, sfptr) returns a NaN and raises the “invalid” floating-point exception if any two members of array p are a zero and an infinity. – Otherwise, scaled_prod(n, p, sfptr) returns an infinity if any member of array p is an infinity. – Otherwise, scaled_prod(n, p, sfptr) returns a zero if any member of array p is a zero. – Otherwise, scaled_prod(n, p, sfptr) returns a NaN and raises the “invalid” floating-point exception if the scale factor is outside the range of the intmax_t type.