Master Chef: Chicken In this investigation, you will dissect a chicken
advertisement

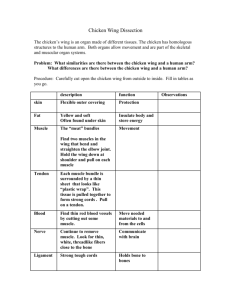
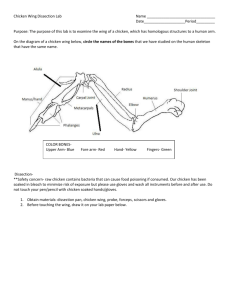
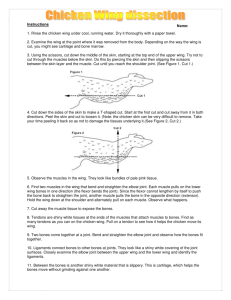
Master Chef: Chicken In this investigation, you will dissect a chicken wing. Your goal is to observe, locate, compare and remove tissues as nearly whole as possible. Do not cut parts into small pieces. Be sure to carefully read the lab before asking a question. Each group (5 – 6 people) will hand in one completed lab packet. One to three people who do not want to handle the chicken should be the scribes (write down the answers). These people should also underline each step as they read it to ensure they do not miss anything. Each group will have three dissectors who will handle the chicken. Anybody handling the chicken or anything the chicken has touched must wear gloves. Anybody using a sharp object must wear goggles while using it. Materials: Chicken wing, dissecting pan, dissecting kit, gloves, goggles Procedure Place a chicken wing in your dissecting tray. Pick up the wing and imagine it is still on the chicken. Do you think your wing is from the right or left side of the chicken? _________________ 1. Skin - tough tissue that covers the outside of the wing. Before you begin the dissection, study the outside of the wing. Examine the web-like skin between the bones. What evidence do you see that the skin was covered with feathers? 2. Joints – Joints are defined as _____________________________________________________________. Joints in the human body are similar to joints on the chicken wing. Label the joints on the diagram below. Include the joint where the wing was attached to the rest of the chicken. For each joint you labeled, include what type of joint it is (fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial). If it is synovial, write what kind of synovial joint it is. Carefully cut the skin with scissors along the entire length of the chicken wing. Be careful not to cut through the muscles below the skin. Remove the skin and fat tissue (yellow tissue under the skin) from the wing. This is difficult. It works best if you slide your finger under the skin to break some of the connective tissues then grab the skin and cut it away. You do not need to remove the skin from the section of the wing furthest from the chicken’s body. This is the hardest step in the lab; be patient. 3. Muscles – muscles can do two things: _____________ and _____________. There are three types of muscles in the body: 1. 2. 3. Which muscle type are the muscles you are observing on the chicken wing? ____________________________ Use a blunt (not sharp) probe to separate the individual muscles from each other without tearing them. With a pencil, sketch the different muscles onto the diagram on the first page of this lab packet. Many muscles in the body come in pairs: the first muscle moves the body in one direction while the second muscle in the pair moves the body in the opposite direction. In the case of the chicken wing, flexors bend the wing while extensors straighten it out. Straighten the chicken wing and hold it horizontally above the tray. Pull on each of the muscles and note the movement that each muscle causes. You can also pinch each muscle to see what movement it causes. Both of these actions are similar to that muscle flexing. Then, bend the joints. Again pull on/pinch each muscle and note how the bones move. On your drawing, color each muscle that flexes (bends) a joint in yellow. Then color each muscle that extends (straightens) a joint in green. The muscles in the chicken’s body are very similar to the muscles we learned in the humans. On your diagram, label each muscle on the section of the wing that was directly attached to the chicken’s body (just use the names for those muscles in humans). 4. Blood vessels – blood vessels include arteries, veins, and capillaries. They carry blood to and from the body from the heart. What kind of muscle is the heart? ____________________________ What kind of muscle is in the arteries to help blood circulate? ____________________________ Blood vessels are the thin brownish-red tubes that you see on the surface of the muscle. Arteries are thicker than veins; locate an artery and a vein. Blood vessels and nerves enter and leave the bone through the outer membrane of the bone. 5. Nerves – nerves carry information from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body and vice versa. They are white and about the diameter of a pencil lead. A likely place to find a nerve is between the muscles near a bone. Raise your hand to show Mr. Beckerman an artery, a vein, and a nerve that you found before moving on. 6. Tendons – Tendons connect _____________ to _____________. They are skinny, tough, silvery-white tissue at the end of muscles. Why do you think tendons need to be so tough? ___________________________________________________ Find as many tendons as possible in your chicken wing. Determine where each tendon connects to a bone. Color the tendons in your drawing blue. Cut all of the tendons using the scissors and remove all muscle from the wing. Also remove all blood vessels and nerves. 7. Bone – Bones have 5 major functions. List them below: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Chicken bones are also very similar to human bones. On your diagram, draw in the bones in black and label the chicken bones using the bone names we learned in the human arm. Which chicken bones are most similar to human bones? Do they have a similar function? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Which chicken bones are least similar to human bones? Do they have a very different function from humans? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Ligaments – Ligaments connect _____________ to _____________. How do the ligaments at the shoulder differ from the ligaments at the elbow? How does this affect the type of movement those joints can do? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Carefully cut the ligaments with scissors to separate the bones. 9. Cartilage- hard tissue (but not as hard as bone) that is found at the end of long bones. It is usually pearly white in color. Feel the texture of the end of the bones at the joint (this is where cartilage is located). Why do you think the cartilage has the texture it does? __________________________________________________________________________________________ CLEAN UP Throw away all chicken parts in the trash. Wash everything that touched the chicken thoroughly with soap and water. Lay out everything you have washed on top of paper towels on the counter to dry. Mr. Beckerman must approve of your lab station before you can hand in your lab packet.