PowerPoint Presentation - American Realism & Naturalism
advertisement

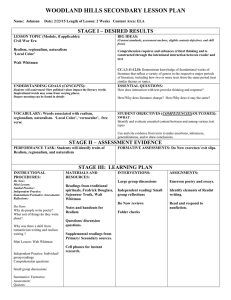
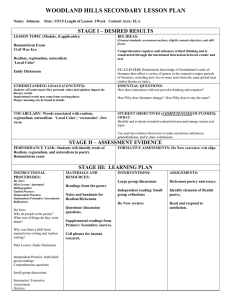
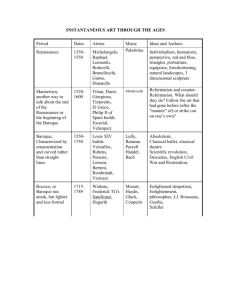
American Realism & Naturalism No More Romantic Sunshine & Rainbows… Origins/Influences Began during the Civil War & continued into the early 20th century Reaction to Romanticism & Transcendentalism: CONTRAST Fertile literary environment – Rising middle class & literacy rates Social/Political Context Reaction to Civil War suffering Invention of photograph – Increased literacy & democracy = public hungry for truth & awareness Abolitionism & post-slavery stories – Captured true life Dark side of America Origins of Muckraking journalism – – Expose corruption, particularly political & corporate (continues today…) Literature affected: tried to do the same Realism: Values/Beliefs Contrasts w/Romanticism & Transcendentalism Describes life w/out Romantic subjectivity & idealism Romantics transcend the immediate to find the ideal; Realists focus on the immediate, the here & now and its consequences Present life as it is, not as it might be Like Romantics, focus on common person & daily human experience & progressive, but stimulated change through telling a story that reveals truth & portrays ugliness & cruelty, not preaching (left readers to draw their own conclusions) Multiple views of life: all classes, races, genders – – – Particularly lower/middle classes Highlight class stratification/inequity Reveal the ugliness & cruelty of life, but leave conclusions to the reader Literary Conventions Characters product of social & environmental factors – Often poorly educated or lower class Renders reality closely & often in minute detail, even at the expense of plot Settings usually familiar to the writer Character more important than plot Plausible events avoid sensational, overly dramatic elements Usually uses the omniscient point of view Conventions Cont. Natural vernacular/speech, not heightened or poetic (like the Romantics) – Tone is comic, satiric, or matter-of-fact Considers seemingly ordinary & uninteresting characters/events in order to extract full value & true meaning – Written just as spoken Simple stories far more complex than they appear Realistically conveyed sexuality, both its dark and light sides…. Regionalism & Psychological Realism Regionalism: focuses on small geographical area in attempt to reproduce speech & mannerisms Psychological Fiction: character perspective—as “real” as any reality… Naturalism Branch of Realism Philosophical position: scientific laws control life Heavily influenced by Darwinism – – Darker & more fatalistic (fatalistic = determined by fate, not choice) Lives governed by heredity, instinct, & passion – Natural Selection Survival of the Fittest Nature NOT nurture…. Forces beyond a character’s control restrict attempts to exercise free will or choice More negative than Realism Famous Authors Naturalist: •Jack London Realist: Mark Twain –Call of the Wild, “To Build a Fire” •Stephen Crane –Maggie: Girl of the Street Stephen Crane •Henry James – Red Badge of Courage –Portrait of a Lady, Daisy Upton Sinclair Miller – The Jungle •John Steinbeck William Dean Howells •Of Mice & Men (debatable) Kate Chopin – Adventures of Huckleberry Finn – “Story of an Hour,” Desiree’s Baby, The Awakening